| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Review the anatomical structure of the eye, clicking on each part to practice identification.
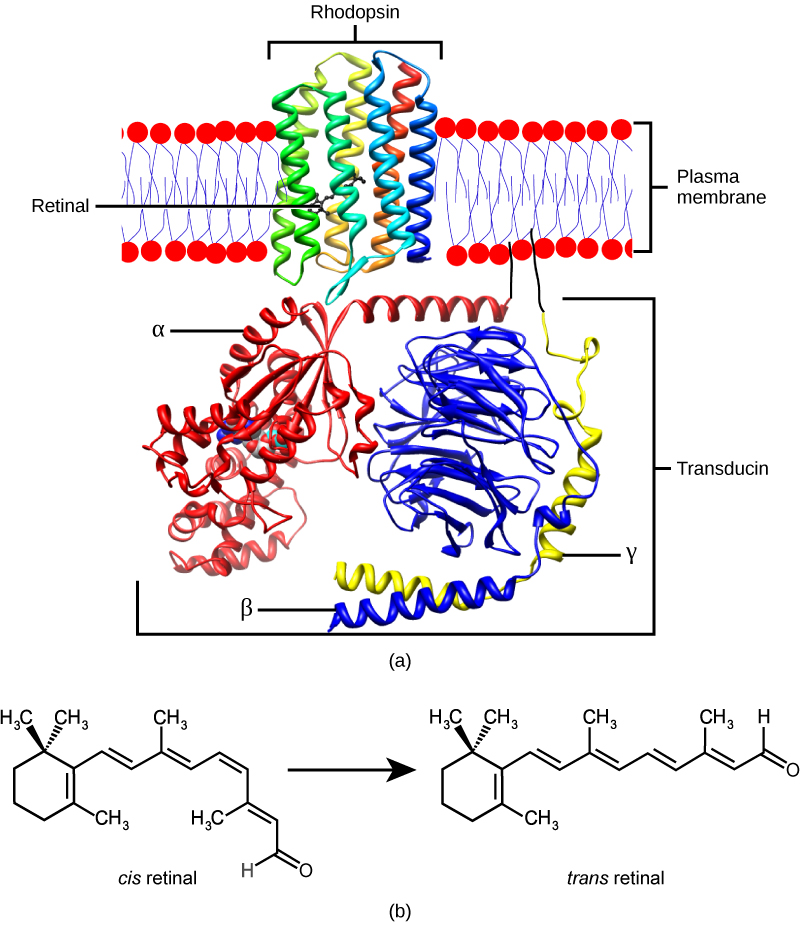
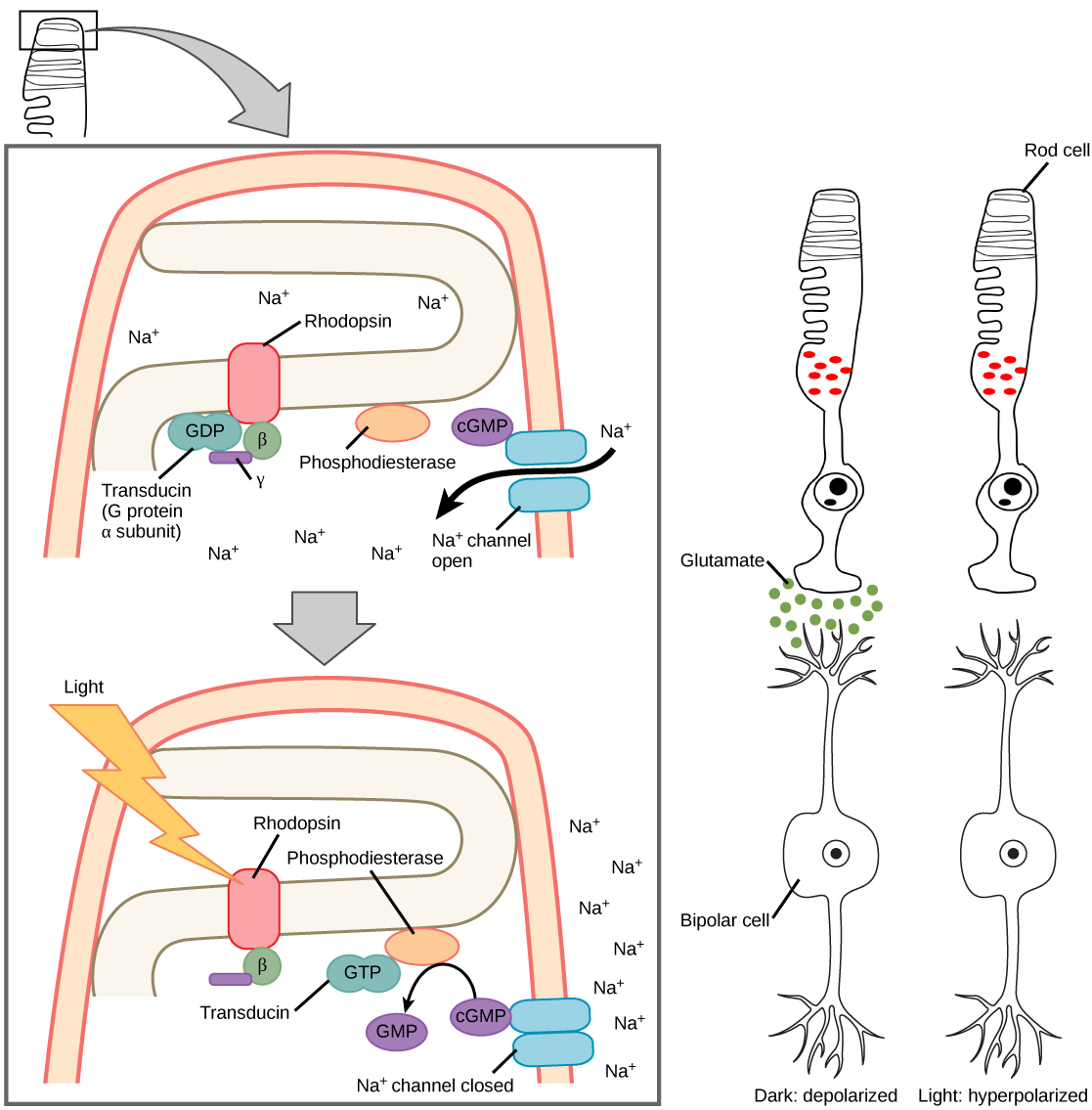
The rods and cones are the site of transduction of light to a neural signal. Both rods and cones contain photopigments. In vertebrates, the main photopigment, rhodopsin , has two main parts [link] ): an opsin, which is a membrane protein (in the form of a cluster of α-helices that span the membrane), and retinal—a molecule that absorbs light. When light hits a photoreceptor, it causes a shape change in the retinal, altering its structure from a bent ( cis ) form of the molecule to its linear ( trans ) isomer. This isomerization of retinal activates the rhodopsin, starting a cascade of events that ends with the closing of Na + channels in the membrane of the photoreceptor. Thus, unlike most other sensory neurons (which become depolarized by exposure to a stimulus) visual receptors become hyperpolarized and thus driven away from threshold ( [link] ).
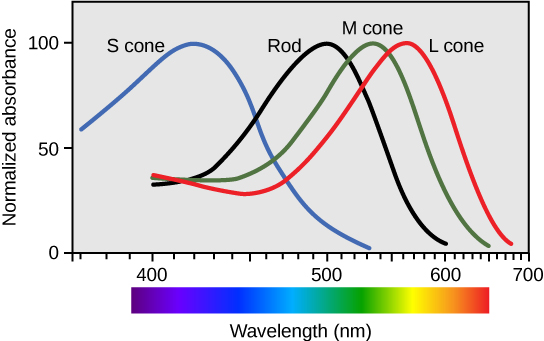
There are three types of cones (with different photopsins), and they differ in the wavelength to which they are most responsive, as shown in [link] . Some cones are maximally responsive to short light waves of 420 nm, so they are called S cones (“S” for “short”); others respond maximally to waves of 530 nm (M cones, for “medium”); a third group responds maximally to light of longer wavelengths, at 560 nm (L, or “long” cones). With only one type of cone, color vision would not be possible, and a two-cone (dichromatic) system has limitations. Primates use a three-cone (trichromatic) system, resulting in full color vision.
The color we perceive is a result of the ratio of activity of our three types of cones. The colors of the visual spectrum, running from long-wavelength light to short, are red (700 nm), orange (600 nm), yellow (565 nm), green (497 nm), blue (470 nm), indigo (450 nm), and violet (425 nm). Humans have very sensitive perception of color and can distinguish about 500 levels of brightness, 200 different hues, and 20 steps of saturation, or about 2 million distinct colors.
Visual signals leave the cones and rods, travel to the bipolar cells, and then to ganglion cells. A large degree of processing of visual information occurs in the retina itself, before visual information is sent to the brain.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?