| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A scientist characterizing a new gene can determine which polymerase transcribes it by testing whether the gene is expressed in the presence of a particular mushroom poison, α-amanitin ( [link] ). Interestingly, α-amanitin produced by Amanita phalloides , the Death Cap mushroom, affects the three polymerases very differently. RNA polymerase I is completely insensitive to α-amanitin, meaning that the polymerase can transcribe DNA in vitro in the presence of this poison. In contrast, RNA polymerase II is extremely sensitive to α-amanitin, and RNA polymerase III is moderately sensitive. Knowing the transcribing polymerase can clue a researcher into the general function of the gene being studied. Because RNA polymerase II transcribes the vast majority of genes, we will focus on this polymerase in our subsequent discussions about eukaryotic transcription factors and promoters.
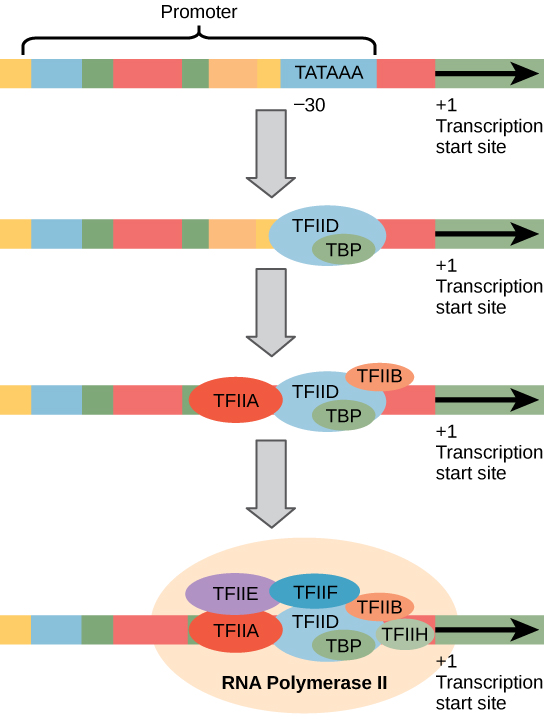
Eukaryotic promoters are much larger and more complex than prokaryotic promoters, but both have a TATA box. For example, in the mouse thymidine kinase gene, the TATA box is located at approximately -30 relative to the initiation (+1) site ( [link] ). For this gene, the exact TATA box sequence is TATAAAA, as read in the 5' to 3' direction on the nontemplate strand. This sequence is not identical to the E. coli TATA box, but it conserves the A–T rich element. The thermostability of A–T bonds is low and this helps the DNA template to locally unwind in preparation for transcription.

A scientist splices a eukaryotic promoter in front of a bacterial gene and inserts the gene in a bacterial chromosome. Would you expect the bacteria to transcribe the gene?
The mouse genome includes one gene and two pseudogenes for cytoplasmic thymidine kinase. Pseudogenes are genes that have lost their protein-coding ability or are no longer expressed by the cell. These pseudogenes are copied from mRNA and incorporated into the chromosome. For example, the mouse thymidine kinase promoter also has a conserved CAAT box (GGCCAATCT) at approximately -80. This sequence is essential and is involved in binding transcription factors. Further upstream of the TATA box, eukaryotic promoters may also contain one or more GC-rich boxes (GGCG) or octamer boxes (ATTTGCAT). These elements bind cellular factors that increase the efficiency of transcription initiation and are often identified in more “active” genes that are constantly being expressed by the cell.
The complexity of eukaryotic transcription does not end with the polymerases and promoters. An army of basal transcription factors, enhancers, and silencers also help to regulate the frequency with which pre-mRNA is synthesized from a gene. Enhancers and silencers affect the efficiency of transcription but are not necessary for transcription to proceed. Basal transcription factors are crucial in the formation of a preinitiation complex on the DNA template that subsequently recruits RNA polymerase II for transcription initiation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?