| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sulfur is an essential element for the macromolecules of living things. As a part of the amino acid cysteine, it is involved in the formation of disulfide bonds within proteins, which help to determine their 3-D folding patterns, and hence their functions. As shown in [link] , sulfur cycles between the oceans, land, and atmosphere. Atmospheric sulfur is found in the form of sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ) and enters the atmosphere in three ways: from the decomposition of organic molecules, from volcanic activity and geothermal vents, and from the burning of fossil fuels by humans.
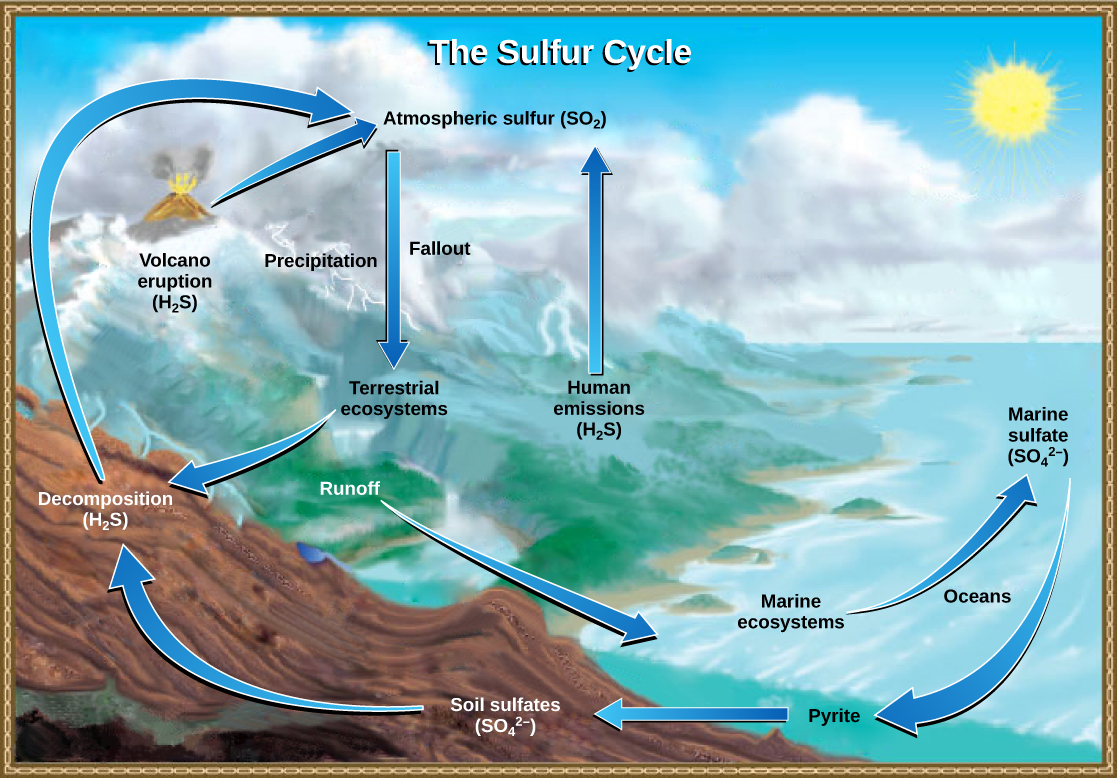
On land, sulfur is deposited in four major ways: precipitation, direct fallout from the atmosphere, rock weathering, and geothermal vents ( [link] ). Atmospheric sulfur is found in the form of sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ), and as rain falls through the atmosphere, sulfur is dissolved in the form of weak sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ). Sulfur can also fall directly from the atmosphere in a process called fallout . Also, the weathering of sulfur-containing rocks releases sulfur into the soil. These rocks originate from ocean sediments that are moved to land by the geologic uplifting of ocean sediments. Terrestrial ecosystems can then make use of these soil sulfates ( ), and upon the death and decomposition of these organisms, release the sulfur back into the atmosphere as hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S) gas.

Sulfur enters the ocean via runoff from land, from atmospheric fallout, and from underwater geothermal vents. Some ecosystems ( [link] ) rely on chemoautotrophs using sulfur as a biological energy source. This sulfur then supports marine ecosystems in the form of sulfates.
Human activities have played a major role in altering the balance of the global sulfur cycle. The burning of large quantities of fossil fuels, especially from coal, releases larger amounts of hydrogen sulfide gas into the atmosphere. As rain falls through this gas, it creates the phenomenon known as acid rain. Acid rain is corrosive rain caused by rainwater falling to the ground through sulfur dioxide gas, turning it into weak sulfuric acid, which causes damage to aquatic ecosystems. Acid rain damages the natural environment by lowering the pH of lakes, which kills many of the resident fauna; it also affects the man-made environment through the chemical degradation of buildings. For example, many marble monuments, such as the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, DC, have suffered significant damage from acid rain over the years. These examples show the wide-ranging effects of human activities on our environment and the challenges that remain for our future.
Click this link to learn more about global climate change.
Mineral nutrients are cycled through ecosystems and their environment. Of particular importance are water, carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. All of these cycles have major impacts on ecosystem structure and function. As human activities have caused major disturbances to these cycles, their study and modeling is especially important. A variety of human activities, such as pollution, oil spills, and events) have damaged ecosystems, potentially causing global climate change. The health of Earth depends on understanding these cycles and how to protect the environment from irreversible damage.
[link] Which of the following statements about the nitrogen cycle is false?
[link] C: Nitrification by bacteria converts nitrates (NO 3 − ) to nitrites (NO 2 − ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?