| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
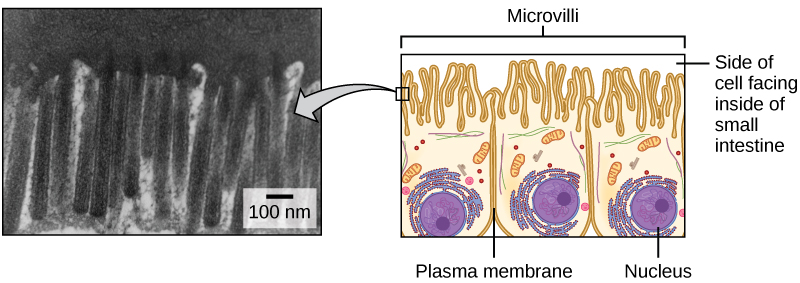
The cytoplasm is the entire region of a cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope (a structure to be discussed shortly). It is made up of organelles suspended in the gel-like cytosol , the cytoskeleton, and various chemicals ( [link] ). Even though the cytoplasm consists of 70 to 80 percent water, it has a semi-solid consistency, which comes from the proteins within it. However, proteins are not the only organic molecules found in the cytoplasm. Glucose and other simple sugars, polysaccharides, amino acids, nucleic acids, fatty acids, and derivatives of glycerol are found there, too. Ions of sodium, potassium, calcium, and many other elements are also dissolved in the cytoplasm. Many metabolic reactions, including protein synthesis, take place in the cytoplasm.
Typically, the nucleus is the most prominent organelle in a cell ( [link] ). The nucleus (plural = nuclei) houses the cell’s DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins. Let’s look at it in more detail ( [link] ).
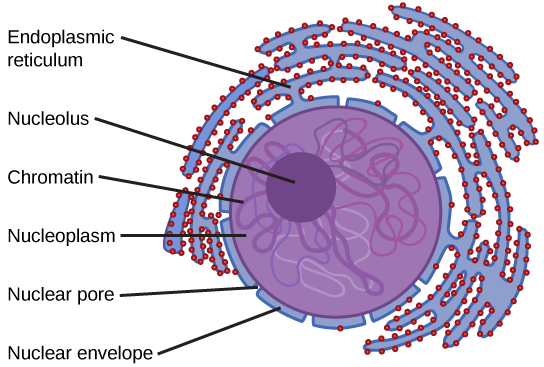
The nuclear envelope is a double-membrane structure that constitutes the outermost portion of the nucleus ( [link] ). Both the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope are phospholipid bilayers.
The nuclear envelope is punctuated with pores that control the passage of ions, molecules, and RNA between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm. The nucleoplasm is the semi-solid fluid inside the nucleus, where we find the chromatin and the nucleolus.
To understand chromatin, it is helpful to first consider chromosomes. Chromosomes are structures within the nucleus that are made up of DNA, the hereditary material. You may remember that in prokaryotes, DNA is organized into a single circular chromosome. In eukaryotes, chromosomes are linear structures. Every eukaryotic species has a specific number of chromosomes in the nuclei of its body’s cells. For example, in humans, the chromosome number is 46, while in fruit flies, it is eight. Chromosomes are only visible and distinguishable from one another when the cell is getting ready to divide. When the cell is in the growth and maintenance phases of its life cycle, proteins are attached to chromosomes, and they resemble an unwound, jumbled bunch of threads. These unwound protein-chromosome complexes are called chromatin ( [link] ); chromatin describes the material that makes up the chromosomes both when condensed and decondensed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?