| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Detecting a taste (gustation) is fairly similar to detecting an odor (olfaction), given that both taste and smell rely on chemical receptors being stimulated by certain molecules. The primary organ of taste is the taste bud. A taste bud is a cluster of gustatory receptors (taste cells) that are located within the bumps on the tongue called papillae (singular: papilla) (illustrated in [link] ). There are several structurally distinct papillae. Filiform papillae, which are located across the tongue, are tactile, providing friction that helps the tongue move substances, and contain no taste cells. In contrast, fungiform papillae, which are located mainly on the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, each contain one to eight taste buds and also have receptors for pressure and temperature. The large circumvallate papillae contain up to 100 taste buds and form a V near the posterior margin of the tongue.
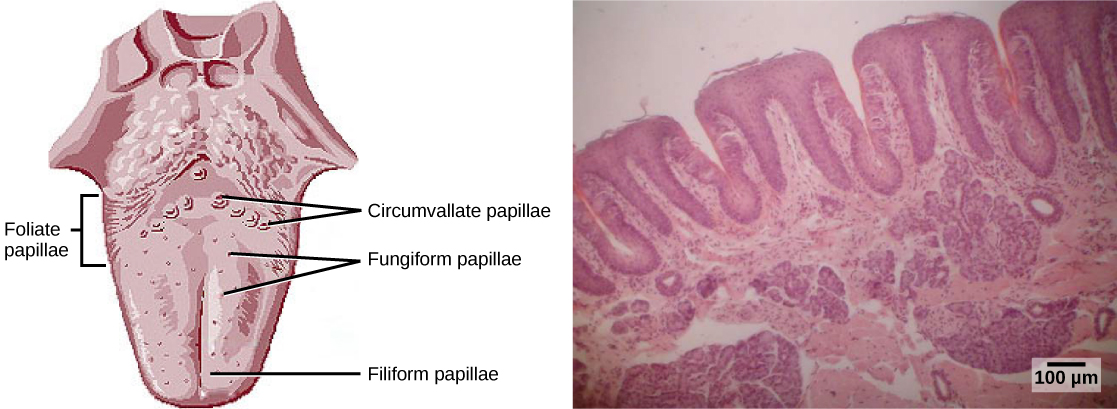
In addition to those two types of chemically and mechanically sensitive papillae are foliate papillae—leaf-like papillae located in parallel folds along the edges and toward the back of the tongue, as seen in the [link] micrograph. Foliate papillae contain about 1,300 taste buds within their folds. Finally, there are circumvallate papillae, which are wall-like papillae in the shape of an inverted “V” at the back of the tongue. Each of these papillae is surrounded by a groove and contains about 250 taste buds.
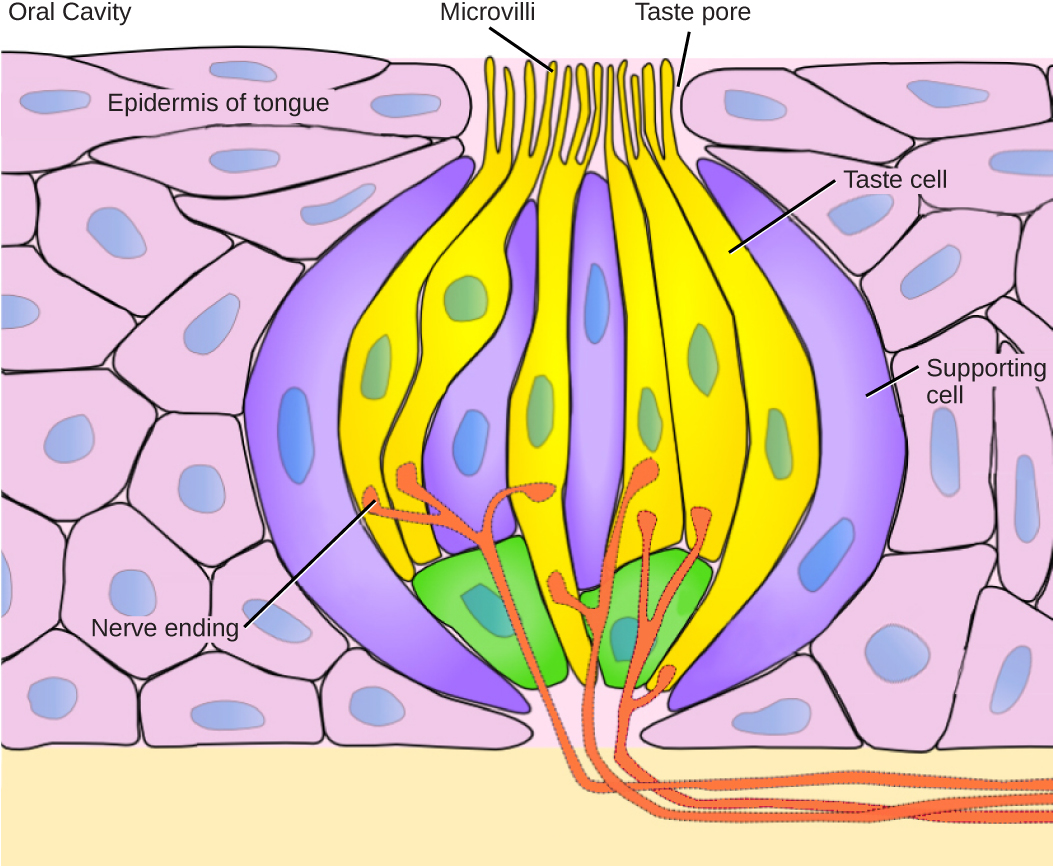
Each taste bud’s taste cells are replaced every 10 to 14 days. These are elongated cells with hair-like processes called microvilli at the tips that extend into the taste bud pore (illustrate in [link] ). Food molecules ( tastants ) are dissolved in saliva, and they bind with and stimulate the receptors on the microvilli. The receptors for tastants are located across the outer portion and front of the tongue, outside of the middle area where the filiform papillae are most prominent.
In humans, there are five primary tastes, and each taste has only one corresponding type of receptor. Thus, like olfaction, each receptor is specific to its stimulus (tastant). Transduction of the five tastes happens through different mechanisms that reflect the molecular composition of the tastant. A salty tastant (containing NaCl) provides the sodium ions (Na + ) that enter the taste neurons and excite them directly. Sour tastants are acids and belong to the thermoreceptor protein family. Binding of an acid or other sour-tasting molecule triggers a change in the ion channel and these increase hydrogen ion (H + ) concentrations in the taste neurons, thus depolarizing them. Sweet, bitter, and umami tastants require a G-protein coupled receptor. These tastants bind to their respective receptors, thereby exciting the specialized neurons associated with them.
Both tasting abilities and sense of smell change with age. In humans, the senses decline dramatically by age 50 and continue to decline. A child may find a food to be too spicy, whereas an elderly person may find the same food to be bland and unappetizing.
View this animation that shows how the sense of taste works.
Olfactory neurons project from the olfactory epithelium to the olfactory bulb as thin, unmyelinated axons. The olfactory bulb is composed of neural clusters called glomeruli , and each glomerulus receives signals from one type of olfactory receptor, so each glomerulus is specific to one odorant. From glomeruli, olfactory signals travel directly to the olfactory cortex and then to the frontal cortex and the thalamus. Recall that this is a different path from most other sensory information, which is sent directly to the thalamus before ending up in the cortex. Olfactory signals also travel directly to the amygdala, thereafter reaching the hypothalamus, thalamus, and frontal cortex. The last structure that olfactory signals directly travel to is a cortical center in the temporal lobe structure important in spatial, autobiographical, declarative, and episodic memories. Olfaction is finally processed by areas of the brain that deal with memory, emotions, reproduction, and thought.
Taste neurons project from taste cells in the tongue, esophagus, and palate to the medulla, in the brainstem. From the medulla, taste signals travel to the thalamus and then to the primary gustatory cortex. Information from different regions of the tongue is segregated in the medulla, thalamus, and cortex.
There are five primary tastes in humans: sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami. Each taste has its own receptor type that responds only to that taste. Tastants enter the body and are dissolved in saliva. Taste cells are located within taste buds, which are found on three of the four types of papillae in the mouth.
Regarding olfaction, there are many thousands of odorants, but humans detect only about 10,000. Like taste receptors, olfactory receptors are each responsive to only one odorant. Odorants dissolve in nasal mucosa, where they excite their corresponding olfactory sensory cells. When these cells detect an odorant, they send their signals to the main olfactory bulb and then to other locations in the brain, including the olfactory cortex.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?