| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
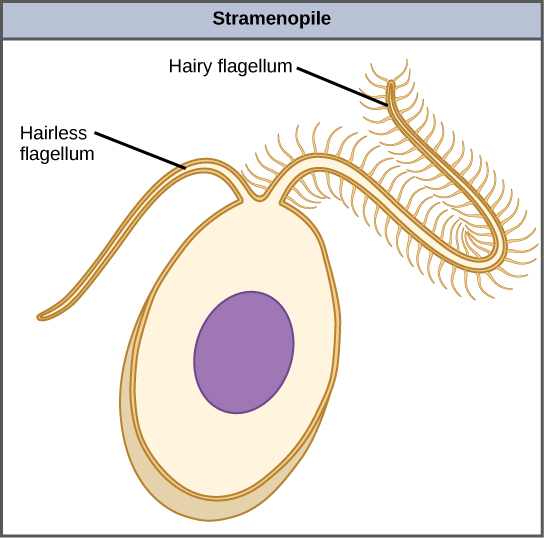
The other subgroup of chromalveolates, the stramenopiles, includes photosynthetic marine algae and heterotrophic protists. The unifying feature of this group is the presence of a textured, or “hairy,” flagellum. Many stramenopiles also have an additional flagellum that lacks hair-like projections ( [link] ). Members of this subgroup range in size from single-celled diatoms to the massive and multicellular kelp.
The diatoms are unicellular photosynthetic protists that encase themselves in intricately patterned, glassy cell walls composed of silicon dioxide in a matrix of organic particles ( [link] ). These protists are a component of freshwater and marine plankton. Most species of diatoms reproduce asexually, although some instances of sexual reproduction and sporulation also exist. Some diatoms exhibit a slit in their silica shell, called a raphe . By expelling a stream of mucopolysaccharides from the raphe, the diatom can attach to surfaces or propel itself in one direction.
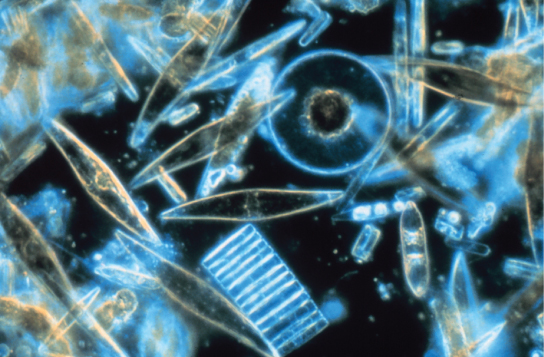
During periods of nutrient availability, diatom populations bloom to numbers greater than can be consumed by aquatic organisms. The excess diatoms die and sink to the sea floor where they are not easily reached by saprobes that feed on dead organisms. As a result, the carbon dioxide that the diatoms had consumed and incorporated into their cells during photosynthesis is not returned to the atmosphere. In general, this process by which carbon is transported deep into the ocean is described as the biological carbon pump , because carbon is “pumped” to the ocean depths where it is inaccessible to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. The biological carbon pump is a crucial component of the carbon cycle that maintains lower atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
Like diatoms, golden algae are largely unicellular, although some species can form large colonies. Their characteristic gold color results from their extensive use of carotenoids, a group of photosynthetic pigments that are generally yellow or orange in color. Golden algae are found in both freshwater and marine environments, where they form a major part of the plankton community.
The brown algae are primarily marine, multicellular organisms that are known colloquially as seaweeds. Giant kelps are a type of brown algae. Some brown algae have evolved specialized tissues that resemble terrestrial plants, with root-like holdfasts, stem-like stipes, and leaf-like blades that are capable of photosynthesis. The stipes of giant kelps are enormous, extending in some cases for 60 meters. A variety of algal life cycles exists, but the most complex is alternation of generations, in which both haploid and diploid stages involve multicellularity. Compare this life cycle to that of humans, for instance. Haploid gametes produced by meiosis (sperm and egg) combine in fertilization to generate a diploid zygote that undergoes many rounds of mitosis to produce a multicellular embryo and then a fetus. However, the individual sperm and egg themselves never become multicellular beings. Terrestrial plants also have evolved alternation of generations. In the brown algae genus Laminaria , haploid spores develop into multicellular gametophytes, which produce haploid gametes that combine to produce diploid organisms that then become multicellular organisms with a different structure from the haploid form ( [link] ). Certain other organisms perform alternation of generations in which both the haploid and diploid forms look the same.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?