| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
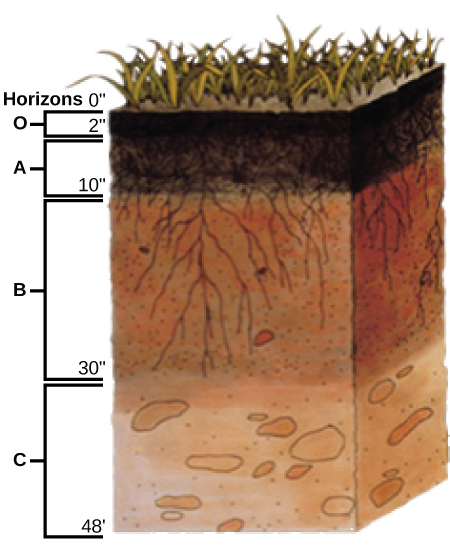

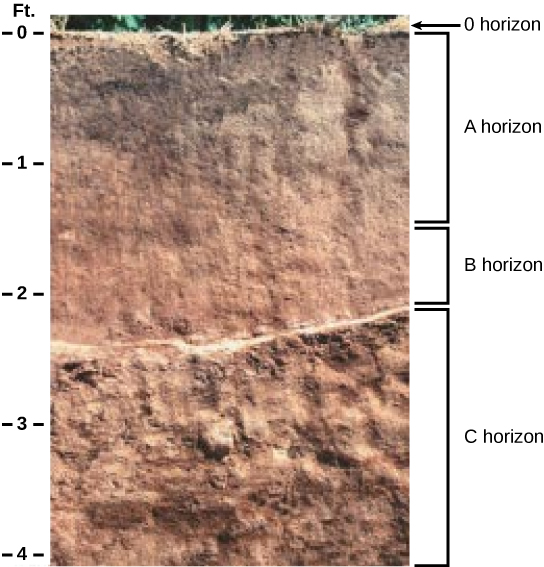
Which horizon is considered the topsoil, and which is considered the subsoil?
Some soils may have additional layers, or lack one of these layers. The thickness of the layers is also variable, and depends on the factors that influence soil formation. In general, immature soils may have O, A, and C horizons, whereas mature soils may display all of these, plus additional layers ( [link] ).

Many soil scientists work both in an office and in the field. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): “a soil scientist needs good observation skills to analyze and determine the characteristics of different types of soils. Soil types are complex and the geographical areas a soil scientist may survey are varied. Aerial photos or various satellite images are often used to research the areas. Computer skills and geographic information systems (GIS) help the scientist to analyze the multiple facets of geomorphology, topography, vegetation, and climate to discover the patterns left on the landscape.” National Resources Conservation Service / United States Department of Agriculture. “Careers in Soil Science.” http://soils.usda.gov/education/facts/careers.html Soil scientists play a key role in understanding the soil’s past, analyzing present conditions, and making recommendations for future soil-related practices.
Plants obtain mineral nutrients from the soil. Soil is the outer loose layer that covers the surface of Earth. Soil quality depends on the chemical composition of the soil, the topography, the presence of living organisms, the climate, and time. Agricultural practice and history may also modify the characteristics and fertility of soil. Soil consists of four major components: 1) inorganic mineral matter, 2) organic matter, 3) water and air, and 4) living matter. The organic material of soil is made of humus, which improves soil structure and provides water and minerals. Soil inorganic material consists of rock slowly broken down into smaller particles that vary in size, such as sand, silt, and loam.
Soil formation results from a combination of biological, physical, and chemical processes. Soil is not homogenous because its formation results in the production of layers called a soil profile. Factors that affect soil formation include: parent material, climate, topography, biological factors, and time. Soils are classified based on their horizons, soil particle size, and proportions. Most soils have four distinct horizons: O, A, B, and C.
[link] Soil compaction can result when soil is compressed by heavy machinery or even foot traffic. How might this compaction change the soil composition?
[link] The air content of the soil decreases.
[link] Which horizon is considered the topsoil, and which is considered the subsoil?
[link] The A horizon is the topsoil, and the B horizon is subsoil.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?