| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The intermediate filaments are the most diverse group of cytoskeletal elements. Several types of fibrous proteins are found in the intermediate filaments. You are probably most familiar with keratin, the fibrous protein that strengthens your hair, nails, and the epidermis of the skin.
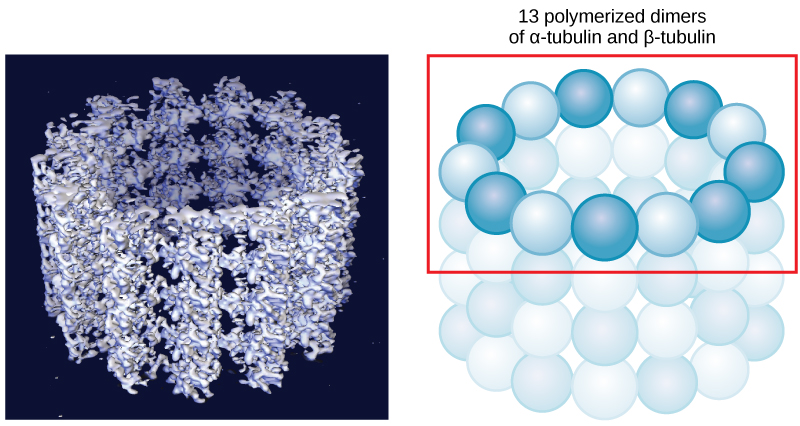
As their name implies, microtubules are small hollow tubes. The walls of the microtubule are made of polymerized dimers of α-tubulin and β-tubulin, two globular proteins ( [link] ). With a diameter of about 25 nm, microtubules are the widest components of the cytoskeleton. They help the cell resist compression, provide a track along which vesicles move through the cell, and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell. Like microfilaments, microtubules can dissolve and reform quickly.
Microtubules are also the structural elements of flagella, cilia, and centrioles (the latter are the two perpendicular bodies of the centrosome). In fact, in animal cells, the centrosome is the microtubule-organizing center. In eukaryotic cells, flagella and cilia are quite different structurally from their counterparts in prokaryotes, as discussed below.
To refresh your memory, flagella (singular = flagellum) are long, hair-like structures that extend from the plasma membrane and are used to move an entire cell (for example, sperm, Euglena ). When present, the cell has just one flagellum or a few flagella. When cilia (singular = cilium) are present, however, many of them extend along the entire surface of the plasma membrane. They are short, hair-like structures that are used to move entire cells (such as paramecia) or substances along the outer surface of the cell (for example, the cilia of cells lining the Fallopian tubes that move the ovum toward the uterus, or cilia lining the cells of the respiratory tract that trap particulate matter and move it toward your nostrils.)
Despite their differences in length and number, flagella and cilia share a common structural arrangement of microtubules called a “9 + 2 array.” This is an appropriate name because a single flagellum or cilium is made of a ring of nine microtubule doublets, surrounding a single microtubule doublet in the center ( [link] ).

You have now completed a broad survey of the components of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. For a summary of cellular components in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, see [link] .
| Components of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Component | Function | Present in Prokaryotes? | Present in Animal Cells? | Present in Plant Cells? |
| Plasma membrane | Separates cell from external environment; controls passage of organic molecules, ions, water, oxygen, and wastes into and out of cell | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cytoplasm | Provides turgor pressure to plant cells as fluid inside the central vacuole; site of many metabolic reactions; medium in which organelles are found | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Nucleolus | Darkened area within the nucleus where ribosomal subunits are synthesized. | No | Yes | Yes |
| Nucleus | Cell organelle that houses DNA and directs synthesis of ribosomes and proteins | No | Yes | Yes |
| Ribosomes | Protein synthesis | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Mitochondria | ATP production/cellular respiration | No | Yes | Yes |
| Peroxisomes | Oxidizes and thus breaks down fatty acids and amino acids, and detoxifies poisons | No | Yes | Yes |
| Vesicles and vacuoles | Storage and transport; digestive function in plant cells | No | Yes | Yes |
| Centrosome | Unspecified role in cell division in animal cells; source of microtubules in animal cells | No | Yes | No |
| Lysosomes | Digestion of macromolecules; recycling of worn-out organelles | No | Yes | No |
| Cell wall | Protection, structural support and maintenance of cell shape | Yes, primarily peptidoglycan | No | Yes, primarily cellulose |
| Chloroplasts | Photosynthesis | No | No | Yes |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids | No | Yes | Yes |
| Golgi apparatus | Modifies, sorts, tags, packages, and distributes lipids and proteins | No | Yes | Yes |
| Cytoskeleton | Maintains cell’s shape, secures organelles in specific positions, allows cytoplasm and vesicles to move within cell, and enables unicellular organisms to move independently | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Flagella | Cellular locomotion | Some | Some | No, except for some plant sperm cells. |
| Cilia | Cellular locomotion, movement of particles along extracellular surface of plasma membrane, and filtration | Some | Some | No |
The cytoskeleton has three different types of protein elements. From narrowest to widest, they are the microfilaments (actin filaments), intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Microfilaments are often associated with myosin. They provide rigidity and shape to the cell and facilitate cellular movements. Intermediate filaments bear tension and anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place. Microtubules help the cell resist compression, serve as tracks for motor proteins that move vesicles through the cell, and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell. They are also the structural element of centrioles, flagella, and cilia.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?