| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When tryptophan is not present in the cell, the repressor by itself does not bind to the operator; therefore, the operon is active and tryptophan is synthesized. Because the repressor protein actively binds to the operator to keep the genes turned off, the trp operon is negatively regulated and the proteins that bind to the operator to silence trp expression are negative regulators .
Watch this video to learn more about the trp operon.
Just as the trp operon is negatively regulated by tryptophan molecules, there are proteins that bind to the operator sequences that act as a positive regulator to turn genes on and activate them. For example, when glucose is scarce, E. coli bacteria can turn to other sugar sources for fuel. To do this, new genes to process these alternate genes must be transcribed. When glucose levels drop, cyclic AMP (cAMP) begins to accumulate in the cell. The cAMP molecule is a signaling molecule that is involved in glucose and energy metabolism in E. coli . When glucose levels decline in the cell, accumulating cAMP binds to the positive regulator catabolite activator protein (CAP) , a protein that binds to the promoters of operons that control the processing of alternative sugars. When cAMP binds to CAP, the complex binds to the promoter region of the genes that are needed to use the alternate sugar sources ( [link] ). In these operons, a CAP binding site is located upstream of the RNA polymerase binding site in the promoter. This increases the binding ability of RNA polymerase to the promoter region and the transcription of the genes.
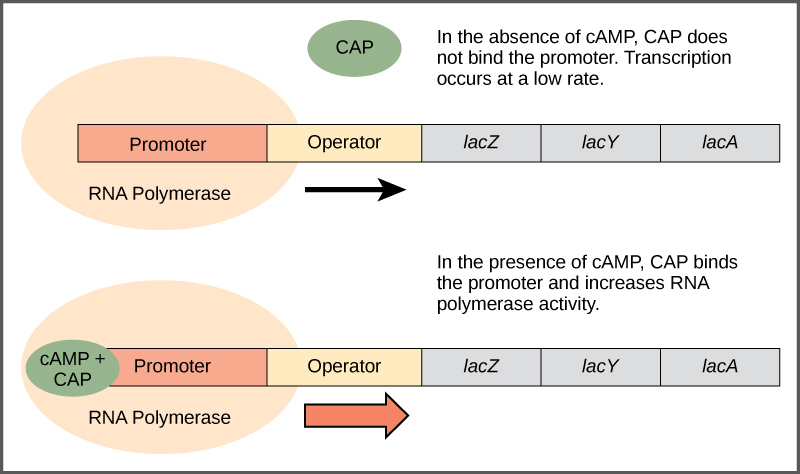
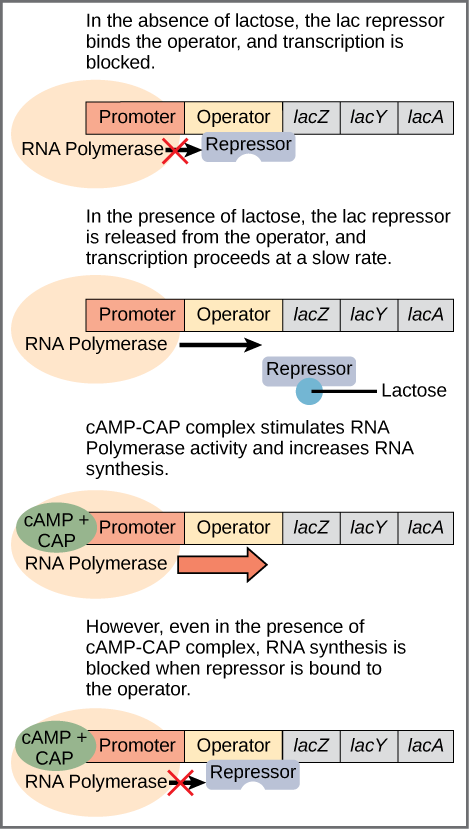
The third type of gene regulation in prokaryotic cells occurs through inducible operons , which have proteins that bind to activate or repress transcription depending on the local environment and the needs of the cell. The lac operon is a typical inducible operon. As mentioned previously, E. coli is able to use other sugars as energy sources when glucose concentrations are low. To do so, the cAMP–CAP protein complex serves as a positive regulator to induce transcription. One such sugar source is lactose. The lac operon encodes the genes necessary to acquire and process the lactose from the local environment. CAP binds to the operator sequence upstream of the promoter that initiates transcription of the lac operon. However, for the lac operon to be activated, two conditions must be met. First, the level of glucose must be very low or non-existent. Second, lactose must be present. Only when glucose is absent and lactose is present will the lac operon be transcribed ( [link] ). This makes sense for the cell, because it would be energetically wasteful to create the proteins to process lactose if glucose was plentiful or lactose was not available.
In E. coli , the trp operon is on by default, while the lac operon is off. Why do you think this is the case?
If glucose is absent, then CAP can bind to the operator sequence to activate transcription. If lactose is absent, then the repressor binds to the operator to prevent transcription. If either of these requirements is met, then transcription remains off. Only when both conditions are satisfied is the lac operon transcribed ( [link] ).
| Signals that Induce or Repress Transcription of the lac Operon | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | CAP binds | Lactose | Repressor binds | Transcription |
| + | - | - | + | No |
| + | - | + | - | Some |
| - | + | - | + | No |
| - | + | + | - | Yes |
Watch an animated tutorial about the workings of lac operon here.
The regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cells occurs at the transcriptional level. There are three ways to control the transcription of an operon: repressive control, activator control, and inducible control. Repressive control, typified by the trp operon, uses proteins bound to the operator sequence to physically prevent the binding of RNA polymerase and the activation of transcription. Therefore, if tryptophan is not needed, the repressor is bound to the operator and transcription remains off. Activator control, typified by the action of CAP, increases the binding ability of RNA polymerase to the promoter when CAP is bound. In this case, low levels of glucose result in the binding of cAMP to CAP. CAP then binds the promoter, which allows RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter better. In the last example—the lac operon—two conditions must be met to initiate transcription. Glucose must not be present, and lactose must be available for the lac operon to be transcribed. If glucose is absent, CAP binds to the operator. If lactose is present, the repressor protein does not bind to its operator. Only when both conditions are met will RNA polymerase bind to the promoter to induce transcription.
[link] In E. coli , the trp operon is on by default, while the lac operon is off. Why do you think that this is the case?
[link] Tryptophan is an amino acid essential for making proteins, so the cell always needs to have some on hand. However, if plenty of tryptophan is present, it is wasteful to make more, and the expression of the trp receptor is repressed. Lactose, a sugar found in milk, is not always available. It makes no sense to make the enzymes necessary to digest an energy source that is not available, so the lac operon is only turned on when lactose is present.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?