| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
On a hot, dry day, plants close their stomata to conserve water. What impact will this have on photosynthesis?
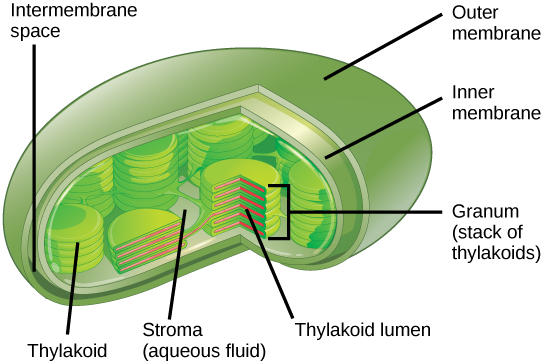
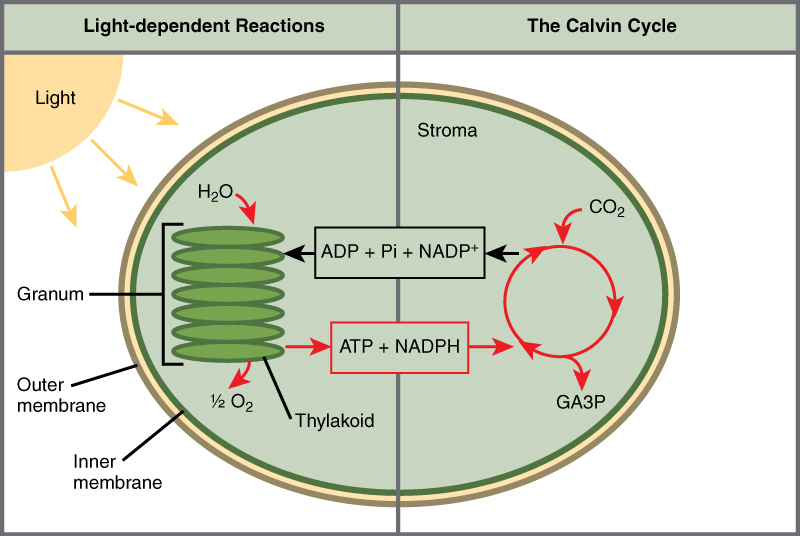
Photosynthesis takes place in two sequential stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light independent-reactions. In the light-dependent reactions , energy from sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll and that energy is converted into stored chemical energy. In the light-independent reactions , the chemical energy harvested during the light-dependent reactions drive the assembly of sugar molecules from carbon dioxide. Therefore, although the light-independent reactions do not use light as a reactant, they require the products of the light-dependent reactions to function. In addition, several enzymes of the light-independent reactions are activated by light. The light-dependent reactions utilize certain molecules to temporarily store the energy: These are referred to as energy carriers. The energy carriers that move energy from light-dependent reactions to light-independent reactions can be thought of as “full” because they are rich in energy. After the energy is released, the “empty” energy carriers return to the light-dependent reaction to obtain more energy. [link] illustrates the components inside the chloroplast where the light-dependent and light-independent reactions take place.
Click the link to learn more about photosynthesis.

Major grocery stores in the United States are organized into departments, such as dairy, meats, produce, bread, cereals, and so forth. Each aisle ( [link] ) contains hundreds, if not thousands, of different products for customers to buy and consume.
Although there is a large variety, each item links back to photosynthesis. Meats and dairy link, because the animals were fed plant-based foods. The breads, cereals, and pastas come largely from starchy grains, which are the seeds of photosynthesis-dependent plants. What about desserts and drinks? All of these products contain sugar—sucrose is a plant product, a disaccharide, a carbohydrate molecule, which is built directly from photosynthesis. Moreover, many items are less obviously derived from plants: For instance, paper goods are generally plant products, and many plastics (abundant as products and packaging) are derived from algae. Virtually every spice and flavoring in the spice aisle was produced by a plant as a leaf, root, bark, flower, fruit, or stem. Ultimately, photosynthesis connects to every meal and every food a person consumes.
The process of photosynthesis transformed life on Earth. By harnessing energy from the sun, photosynthesis evolved to allow living things access to enormous amounts of energy. Because of photosynthesis, living things gained access to sufficient energy that allowed them to build new structures and achieve the biodiversity evident today.
Only certain organisms, called photoautotrophs, can perform photosynthesis; they require the presence of chlorophyll, a specialized pigment that absorbs certain portions of the visible spectrum and can capture energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water to assemble carbohydrate molecules and release oxygen as a waste product into the atmosphere. Eukaryotic autotrophs, such as plants and algae, have organelles called chloroplasts in which photosynthesis takes place, and starch accumulates. In prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, the process is less localized and occurs within folded membranes, extensions of the plasma membrane, and in the cytoplasm.
[link] On a hot, dry day, plants close their stomata to conserve water. What impact will this have on photosynthesis?
[link] Levels of carbon dioxide (a necessary photosynthetic substrate) will immediately fall. As a result, the rate of photosynthesis will be inhibited.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?