| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |



Play this interactive PBS evolution-based mating game to learn more about reproductive strategies.
In a 1981 study, male fruit flies were placed in enclosures with either virgin or inseminated females. The males that mated with virgin females had shorter life spans than those in contact with the same number of inseminated females with which they were unable to mate. This effect occurred regardless of how large (indicative of their age) the males were. Thus, males that did not mate lived longer, allowing them more opportunities to find mates in the future.
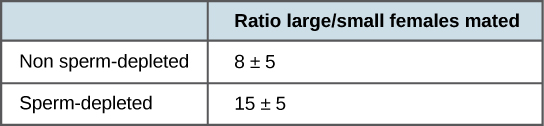
More recent studies, performed in 2006, show how males select the female with which they will mate and how this is affected by previous matings ( [link] ). Adapted from Phillip G. Byrne and William R. Rice, “Evidence for adaptive male mate choice in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, ” Proc Biol Sci. 273, no. 1589 (2006): 917-922, doi: 10.1098/rspb.2005.3372. Males were allowed to select between smaller and larger females. Findings showed that larger females had greater fecundity, producing twice as many offspring per mating as the smaller females did. Males that had previously mated, and thus had lower supplies of sperm, were termed “resource-depleted,” while males that had not mated were termed “non-resource-depleted.” The study showed that although non-resource-depleted males preferentially mated with larger females, this selection of partners was more pronounced in the resource-depleted males. Thus, males with depleted sperm supplies, which were limited in the number of times that they could mate before they replenished their sperm supply, selected larger, more fecund females, thus maximizing their chances for offspring. This study was one of the first to show that the physiological state of the male affected its mating behavior in a way that clearly maximizes its use of limited reproductive resources.
These studies demonstrate two ways in which the energy budget is a factor in reproduction. First, energy expended on mating may reduce an animal’s lifespan, but by this time they have already reproduced, so in the context of natural selection this early death is not of much evolutionary importance. Second, when resources such as sperm (and the energy needed to replenish it) are low, an organism’s behavior can change to give them the best chance of passing their genes on to the next generation. These changes in behavior, so important to evolution, are studied in a discipline known as behavioral biology, or ethology, at the interface between population biology and psychology.
All species have evolved a pattern of living, called a life history strategy, in which they partition energy for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. These patterns evolve through natural selection; they allow species to adapt to their environment to obtain the resources they need to successfully reproduce. There is an inverse relationship between fecundity and parental care. A species may reproduce early in life to ensure surviving to a reproductive age or reproduce later in life to become larger and healthier and better able to give parental care. A species may reproduce once (semelparity) or many times (iteroparity) in its life.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?