| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Other lipid-soluble hormones that are not steroid hormones, such as vitamin D and thyroxine, have receptors located in the nucleus. The hormones diffuse across both the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope, then bind to receptors in the nucleus. The hormone-receptor complex stimulates transcription of specific genes.
Amino acid derived hormones and polypeptide hormones are not lipid-derived (lipid-soluble) and therefore cannot diffuse through the plasma membrane of cells. Lipid insoluble hormones bind to receptors on the outer surface of the plasma membrane, via plasma membrane hormone receptors . Unlike steroid hormones, lipid insoluble hormones do not directly affect the target cell because they cannot enter the cell and act directly on DNA. Binding of these hormones to a cell surface receptor results in activation of a signaling pathway; this triggers intracellular activity and carries out the specific effects associated with the hormone. In this way, nothing passes through the cell membrane; the hormone that binds at the surface remains at the surface of the cell while the intracellular product remains inside the cell. The hormone that initiates the signaling pathway is called a first messenger , which activates a second messenger in the cytoplasm, as illustrated in [link] .
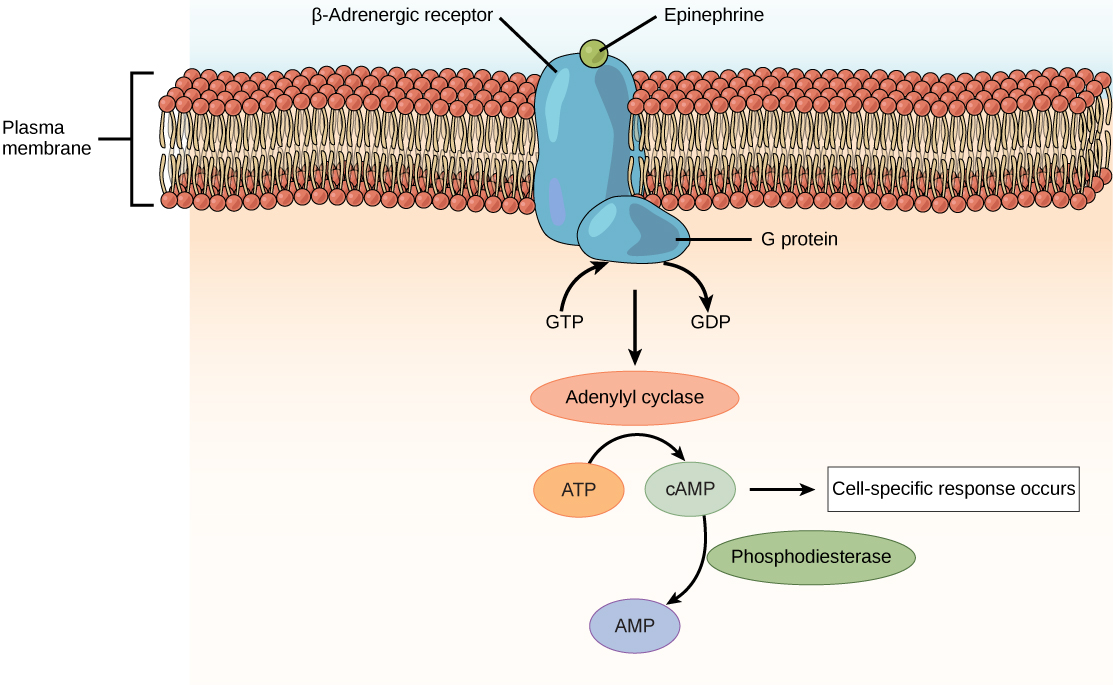
One very important second messenger is cyclic AMP (cAMP). When a hormone binds to its membrane receptor, a G-protein that is associated with the receptor is activated; G-proteins are proteins separate from receptors that are found in the cell membrane. When a hormone is not bound to the receptor, the G-protein is inactive and is bound to guanosine diphosphate, or GDP. When a hormone binds to the receptor, the G-protein is activated by binding guanosine triphosphate, or GTP, in place of GDP. After binding, GTP is hydrolysed by the G-protein into GDP and becomes inactive.
The activated G-protein in turn activates a membrane-bound enzyme called adenylyl cyclase . Adenylyl cyclase catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP. cAMP, in turn, activates a group of proteins called protein kinases, which transfer a phosphate group from ATP to a substrate molecule in a process called phosphorylation. The phosphorylation of a substrate molecule changes its structural orientation, thereby activating it. These activated molecules can then mediate changes in cellular processes.
The effect of a hormone is amplified as the signaling pathway progresses. The binding of a hormone at a single receptor causes the activation of many G-proteins, which activates adenylyl cyclase. Each molecule of adenylyl cyclase then triggers the formation of many molecules of cAMP. Further amplification occurs as protein kinases, once activated by cAMP, can catalyze many reactions. In this way, a small amount of hormone can trigger the formation of a large amount of cellular product. To stop hormone activity, cAMP is deactivated by the cytoplasmic enzyme phosphodiesterase , or PDE. PDE is always present in the cell and breaks down cAMP to control hormone activity, preventing overproduction of cellular products.
The specific response of a cell to a lipid insoluble hormone depends on the type of receptors that are present on the cell membrane and the substrate molecules present in the cell cytoplasm. Cellular responses to hormone binding of a receptor include altering membrane permeability and metabolic pathways, stimulating synthesis of proteins and enzymes, and activating hormone release.
Hormones cause cellular changes by binding to receptors on target cells. The number of receptors on a target cell can increase or decrease in response to hormone activity. Hormones can affect cells directly through intracellular hormone receptors or indirectly through plasma membrane hormone receptors.
Lipid-derived (soluble) hormones can enter the cell by diffusing across the plasma membrane and binding to DNA to regulate gene transcription and to change the cell’s activities by inducing production of proteins that affect, in general, the long-term structure and function of the cell. Lipid insoluble hormones bind to receptors on the plasma membrane surface and trigger a signaling pathway to change the cell’s activities by inducing production of various cell products that affect the cell in the short-term. The hormone is called a first messenger and the cellular component is called a second messenger. G-proteins activate the second messenger (cyclic AMP), triggering the cellular response. Response to hormone binding is amplified as the signaling pathway progresses. Cellular responses to hormones include the production of proteins and enzymes and altered membrane permeability.
[link] Heat shock proteins (HSP) are so named because they help refold mis-folded proteins. In response to increased temperature (a “heat shock”), heat shock proteins are activated by release from the NR/HSP complex. At the same time, transcription of HSP genes is activated. Why do you think the cell responds to a heat shock by increasing the activity of proteins that help refold misfolded proteins?
[link] Proteins unfold, or denature, at higher temperatures.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?