| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Scientists Oswald Avery, Colin MacLeod, and Maclyn McCarty (1944) were interested in exploring this transforming principle further. They isolated the S strain from the dead mice and isolated the proteins and nucleic acids, namely RNA and DNA, as these were possible candidates for the molecule of heredity. They conducted a systematic elimination study. They used enzymes that specifically degraded each component and then used each mixture separately to transform the R strain. They found that when DNA was degraded, the resulting mixture was no longer able to transform the bacteria, whereas all of the other combinations were able to transform the bacteria. This led them to conclude that DNA was the transforming principle.
Forensic scientists analyze many items, including documents, handwriting, firearms, and biological samples. They analyze the DNA content of hair, semen, saliva, and blood, and compare it with a database of DNA profiles of known criminals. Analysis includes DNA isolation, sequencing, and sequence analysis; most forensic DNA analysis involves polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of short tandem repeat (STR) loci and electrophoresis to determine the length of the PCR-amplified fragment. Only mitochondrial DNA is sequenced for forensics. Forensic scientists are expected to appear at court hearings to present their findings. They are usually employed in crime labs of city and state government agencies. Geneticists experimenting with DNA techniques also work for scientific and research organizations, pharmaceutical industries, and college and university labs. Students wishing to pursue a career as a forensic scientist should have at least a bachelor's degree in chemistry, biology, or physics, and preferably some experience working in a laboratory.
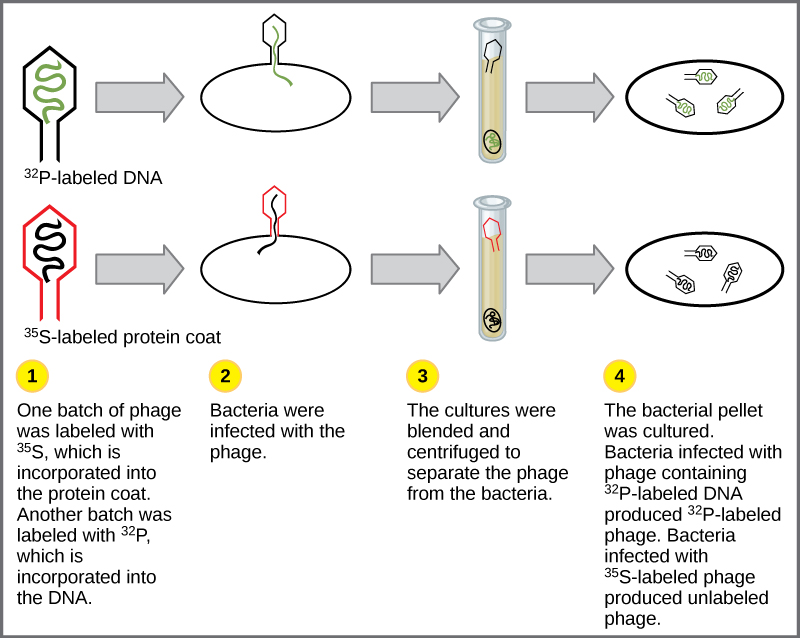
Experiments conducted by Martha Chase and Alfred Hershey in 1952 provided confirmatory evidence that DNA was the genetic material and not proteins. Chase and Hershey were studying a bacteriophage, which is a virus that infects bacteria. Viruses typically have a simple structure: a protein coat, called the capsid, and a nucleic acid core that contains the genetic material, either DNA or RNA. The bacteriophage infects the host bacterial cell by attaching to its surface, and then it injects its nucleic acids inside the cell. The phage DNA makes multiple copies of itself using the host machinery, and eventually the host cell bursts, releasing a large number of bacteriophages. Hershey and Chase labeled one batch of phage with radioactive sulfur, 35 S, to label the protein coat. Another batch of phage were labeled with radioactive phosphorus, 32 P. Because phosphorous is found in DNA, but not protein, the DNA and not the protein would be tagged with radioactive phosphorus.
Each batch of phage was allowed to infect the cells separately. After infection, the phage bacterial suspension was put in a blender, which caused the phage coat to be detached from the host cell. The phage and bacterial suspension was spun down in a centrifuge. The heavier bacterial cells settled down and formed a pellet, whereas the lighter phage particles stayed in the supernatant. In the tube that contained phage labeled with 35 S, the supernatant contained the radioactively labeled phage, whereas no radioactivity was detected in the pellet. In the tube that contained the phage labeled with 32 P, the radioactivity was detected in the pellet that contained the heavier bacterial cells, and no radioactivity was detected in the supernatant. Hershey and Chase concluded that it was the phage DNA that was injected into the cell and carried information to produce more phage particles, thus providing evidence that DNA was the genetic material and not proteins ( [link] ).
Around this same time, Austrian biochemist Erwin Chargaff examined the content of DNA in different species and found that the amounts of adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine were not found in equal quantities, and that it varied from species to species, but not between individuals of the same species. He found that the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of cytosine equals the amount of guanine, or A = T and G = C. This is also known as Chargaff’s rules. This finding proved immensely useful when Watson and Crick were getting ready to propose their DNA double helix model.
DNA was first isolated from white blood cells by Friedrich Miescher, who called it nuclein because it was isolated from nuclei. Frederick Griffith's experiments with strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae provided the first hint that DNA may be the transforming principle. Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty proved that DNA is required for the transformation of bacteria. Later experiments by Hershey and Chase using bacteriophage T2 proved that DNA is the genetic material. Chargaff found that the ratio of A = T and C = G, and that the percentage content of A, T, G, and C is different for different species.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?