| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Many fungal infections are superficial; that is, they occur on the animal’s skin. Termed cutaneous (“skin”) mycoses, they can have devastating effects. For example, the decline of the world’s frog population in recent years may be caused by the chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, which infects the skin of frogs and presumably interferes with gaseous exchange. Similarly, more than a million bats in the United States have been killed by white-nose syndrome, which appears as a white ring around the mouth of the bat. It is caused by the cold-loving fungus Pseudogymnoascus destructans , which disseminates its deadly spores in caves where bats hibernate. Mycologists are researching the transmission, mechanism, and control of P. destructans to stop its spread.
Fungi that cause the superficial mycoses of the epidermis, hair, and nails rarely spread to the underlying tissue ( [link] ). These fungi are often misnamed “dermatophytes”, from the Greek words dermis meaning skin and phyte meaning plant, although they are not plants. Dermatophytes are also called “ringworms” because of the red ring they cause on skin. They secrete extracellular enzymes that break down keratin (a protein found in hair, skin, and nails), causing conditions such as athlete’s foot and jock itch. These conditions are usually treated with over-the-counter topical creams and powders, and are easily cleared. More persistent superficial mycoses may require prescription oral medications.
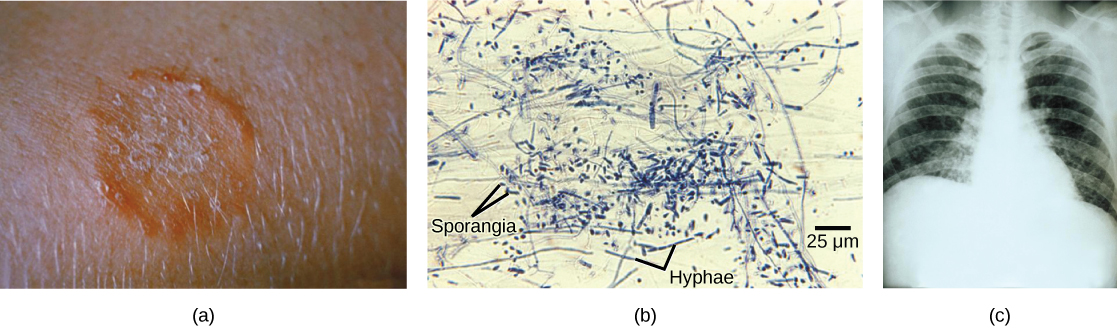
Systemic mycoses spread to internal organs, most commonly entering the body through the respiratory system. For example, coccidioidomycosis (valley fever) is commonly found in the southwestern United States, where the fungus resides in the dust. Once inhaled, the spores develop in the lungs and cause symptoms similar to those of tuberculosis. Histoplasmosis is caused by the dimorphic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. It also causes pulmonary infections, and in rarer cases, swelling of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord. Treatment of these and many other fungal diseases requires the use of antifungal medications that have serious side effects.
Opportunistic mycoses are fungal infections that are either common in all environments, or part of the normal biota. They mainly affect individuals who have a compromised immune system. Patients in the late stages of AIDS suffer from opportunistic mycoses that can be life threatening. The yeast Candida sp., a common member of the natural biota, can grow unchecked and infect the vagina or mouth (oral thrush) if the pH of the surrounding environment, the person’s immune defenses, or the normal population of bacteria are altered.
Mycetismus can occur when poisonous mushrooms are eaten. It causes a number of human fatalities during mushroom-picking season. Many edible fruiting bodies of fungi resemble highly poisonous relatives, and amateur mushroom hunters are cautioned to carefully inspect their harvest and avoid eating mushrooms of doubtful origin. The adage “there are bold mushroom pickers and old mushroom pickers, but are there no old, bold mushroom pickers” is unfortunately true.
Question : Do trees resistant to Dutch elm disease secrete antifungal compounds?
Hypothesis : Construct a hypothesis that addresses this question.
Background : Dutch elm disease is a fungal infestation that affects many species of elm ( Ulmus ) in North America. The fungus infects the vascular system of the tree, which blocks water flow within the plant and mimics drought stress. Accidently introduced to the United States in the early 1930s, it decimated shade trees across the continent. It is caused by the fungus Ophiostoma ulmi . The elm bark beetle acts as a vector and transmits the disease from tree to tree. Many European and Asiatic elms are less susceptible to the disease than are American elms.
Test the hypothesis : A researcher testing this hypothesis might do the following. Inoculate several Petri plates containing a medium that supports the growth of fungi with fragments of Ophiostoma mycelium. Cut (with a metal punch) several disks from the vascular tissue of susceptible varieties of American elms and resistant European and Asiatic elms. Include control Petri plates inoculated with mycelia without plant tissue to verify that the medium and incubation conditions do not interfere with fungal growth. As a positive control, add paper disks impregnated with a known fungicide to Petri plates inoculated with the mycelium.
Incubate the plates for a set number of days to allow fungal growth and spreading of the mycelium over the surface of the plate. Record the diameter of the zone of clearing, if any, around the tissue samples and the fungicide control disk.
Record your observations in the following table.
| Results of Antifungal Testing of Vascular Tissue from Different Species of Elm | |
|---|---|
| Disk | Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
| Distilled Water | |
| Fungicide | |
| Tissue from Susceptible Elm #1 | |
| Tissue from Susceptible Elm #2 | |
| Tissue from Resistant Elm #1 | |
| Tissue from Resistant Elm #2 |
Analyze the data and report the results. Compare the effect of distilled water to the fungicide. These are negative and positive controls that validate the experimental set up. The fungicide should be surrounded by a clear zone where the fungus growth was inhibited. Is there a difference among different species of elm?
Draw a conclusion : Was there antifungal activity as expected from the fungicide? Did the results support the hypothesis? If not, how can this be explained? There are several possible explanations for resistance to a pathogen. Active deterrence of infection is only one of them.
Fungi establish parasitic relationships with plants and animals. Fungal diseases can decimate crops and spoil food during storage. Compounds produced by fungi can be toxic to humans and other animals. Mycoses are infections caused by fungi. Superficial mycoses affect the skin, whereas systemic mycoses spread through the body. Fungal infections are difficult to cure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?