| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

The processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two types of metabolic pathways. A metabolic pathway is a series of interconnected biochemical reactions that convert a substrate molecule or molecules, step-by-step, through a series of metabolic intermediates, eventually yielding a final product or products. In the case of sugar metabolism, the first metabolic pathway synthesized sugar from smaller molecules, and the other pathway broke sugar down into smaller molecules. These two opposite processes—the first requiring energy and the second producing energy—are referred to as anabolic (building) and catabolic (breaking down) pathways, respectively. Consequently, metabolism is composed of building (anabolism) and degradation (catabolism).
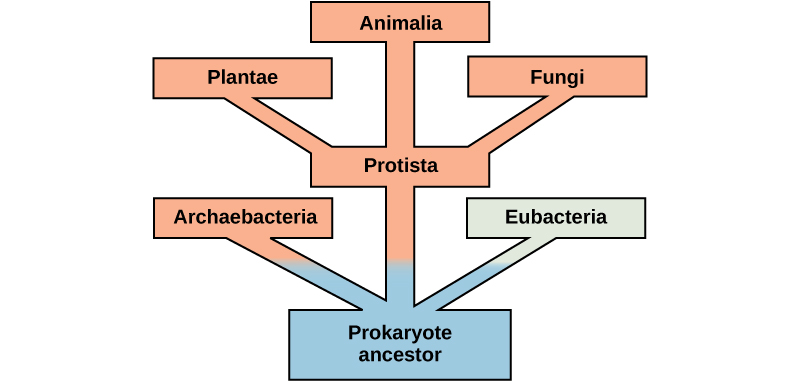
Organisms probably evolved anaerobic metabolism to survive (living organisms came into existence about 3.8 billion years ago, when the atmosphere lacked oxygen). Despite the differences between organisms and the complexity of metabolism, researchers have found that all branches of life share some of the same metabolic pathways, suggesting that all organisms evolved from the same ancient common ancestor ( [link] ). Evidence indicates that over time, the pathways diverged, adding specialized enzymes to allow organisms to better adapt to their environment, thus increasing their chance to survive. However, the underlying principle remains that all organisms must harvest energy from their environment and convert it to ATP to carry out cellular functions.
Anabolic pathways require an input of energy to synthesize complex molecules from simpler ones. Synthesizing sugar from CO 2 is one example. Other examples are the synthesis of large proteins from amino acid building blocks, and the synthesis of new DNA strands from nucleic acid building blocks. These biosynthetic processes are critical to the life of the cell, take place constantly, and demand energy provided by ATP and other high-energy molecules like NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and NADPH ( [link] ).
ATP is an important molecule for cells to have in sufficient supply at all times. The breakdown of sugars illustrates how a single molecule of glucose can store enough energy to make a great deal of ATP, 36 to 38 molecules. This is a catabolic pathway. Catabolic pathways involve the degradation (or breakdown) of complex molecules into simpler ones. Molecular energy stored in the bonds of complex molecules is released in catabolic pathways and harvested in such a way that it can be used to produce ATP. Other energy-storing molecules, such as fats, are also broken down through similar catabolic reactions to release energy and make ATP ( [link] ).
It is important to know that the chemical reactions of metabolic pathways don’t take place spontaneously. Each reaction step is facilitated, or catalyzed, by a protein called an enzyme. Enzymes are important for catalyzing all types of biological reactions—those that require energy as well as those that release energy.
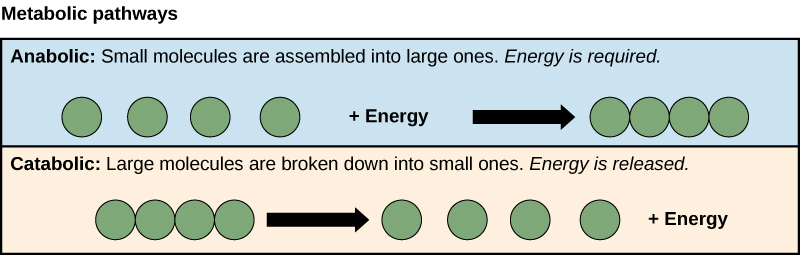
Cells perform the functions of life through various chemical reactions. A cell’s metabolism refers to the chemical reactions that take place within it. There are metabolic reactions that involve the breaking down of complex chemicals into simpler ones, such as the breakdown of large macromolecules. This process is referred to as catabolism, and such reactions are associated with a release of energy. On the other end of the spectrum, anabolism refers to metabolic processes that build complex molecules out of simpler ones, such as the synthesis of macromolecules. Anabolic processes require energy. Glucose synthesis and glucose breakdown are examples of anabolic and catabolic pathways, respectively.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?