| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Inside the root, the ground tissue forms two regions: the cortex and the pith ( [link] ). Compared to stems, roots have lots of cortex and little pith. Both regions include cells that store photosynthetic products. The cortex is between the epidermis and the vascular tissue, whereas the pith lies between the vascular tissue and the center of the root.
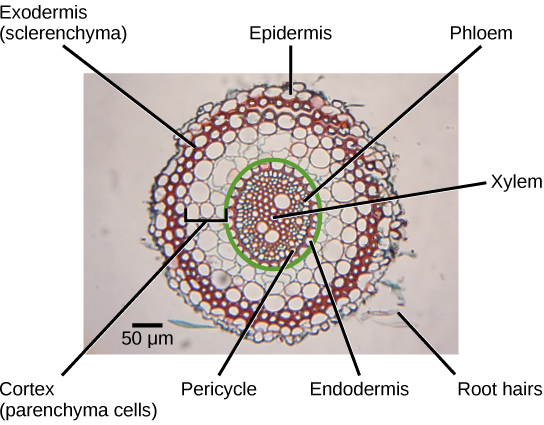
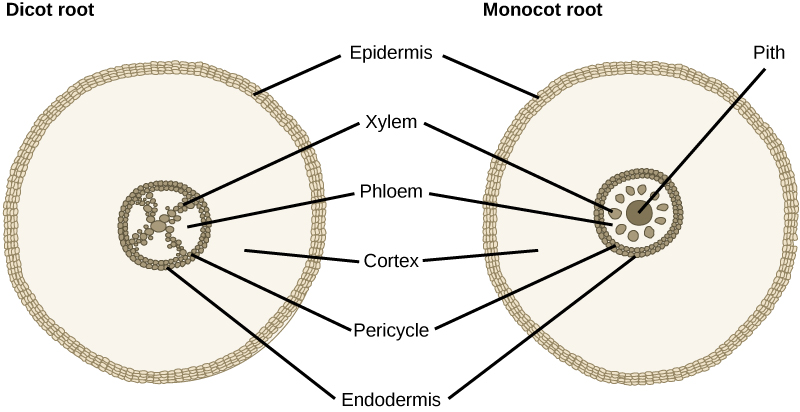
The vascular tissue in the root is arranged in the inner portion of the root, which is called the stele ( [link] ). A layer of cells known as the endodermis separates the stele from the ground tissue in the outer portion of the root. The endodermis is exclusive to roots, and serves as a checkpoint for materials entering the root’s vascular system. A waxy substance called suberin is present on the walls of the endodermal cells. This waxy region, known as the Casparian strip , forces water and solutes to cross the plasma membranes of endodermal cells instead of slipping between the cells. This ensures that only materials required by the root pass through the endodermis, while toxic substances and pathogens are generally excluded. The outermost cell layer of the root’s vascular tissue is the pericycle , an area that can give rise to lateral roots. In dicot roots, the xylem and phloem of the stele are arranged alternately in an X shape, whereas in monocot roots, the vascular tissue is arranged in a ring around the pith.
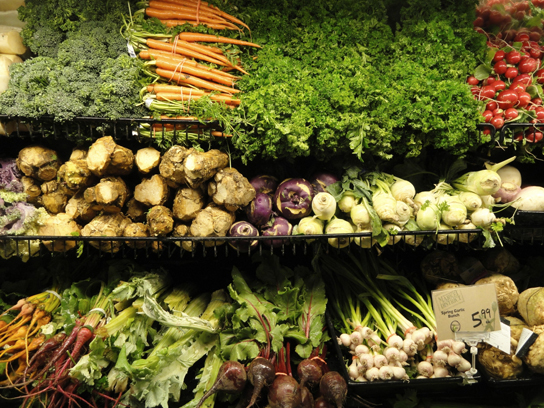
Root structures may be modified for specific purposes. For example, some roots are bulbous and store starch. Aerial roots and prop roots are two forms of aboveground roots that provide additional support to anchor the plant. Tap roots, such as carrots, turnips, and beets, are examples of roots that are modified for food storage ( [link] ).

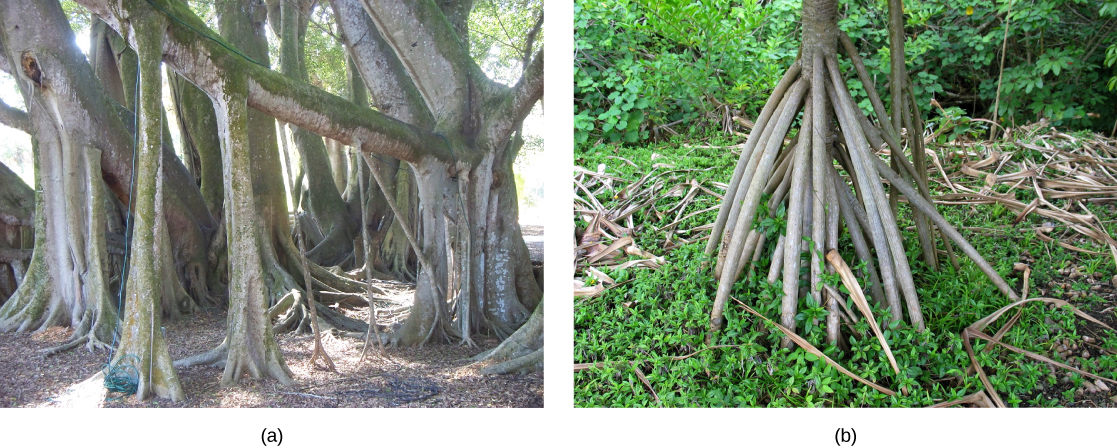
Epiphytic roots enable a plant to grow on another plant. For example, the epiphytic roots of orchids develop a spongy tissue to absorb moisture. The banyan tree ( Ficus sp.) begins as an epiphyte, germinating in the branches of a host tree; aerial roots develop from the branches and eventually reach the ground, providing additional support ( [link] ). In screwpine ( Pandanus sp.), a palm-like tree that grows in sandy tropical soils, aboveground prop roots develop from the nodes to provide additional support.

Roots help to anchor a plant, absorb water and minerals, and serve as storage sites for food. Taproots and fibrous roots are the two main types of root systems. In a taproot system, a main root grows vertically downward with a few lateral roots. Fibrous root systems arise at the base of the stem, where a cluster of roots forms a dense network that is shallower than a taproot. The growing root tip is protected by a root cap. The root tip has three main zones: a zone of cell division (cells are actively dividing), a zone of elongation (cells increase in length), and a zone of maturation (cells differentiate to form different kinds of cells). Root vascular tissue conducts water, minerals, and sugars. In some habitats, the roots of certain plants may be modified to form aerial roots or epiphytic roots.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?