| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Since the rates of biochemical reactions are controlled by activation energy, and enzymes lower and determine activation energies for chemical reactions, the relative amounts and functioning of the variety of enzymes within a cell ultimately determine which reactions will proceed and at which rates. This determination is tightly controlled. In certain cellular environments, enzyme activity is partly controlled by environmental factors, like pH and temperature. There are other mechanisms through which cells control the activity of enzymes and determine the rates at which various biochemical reactions will occur.
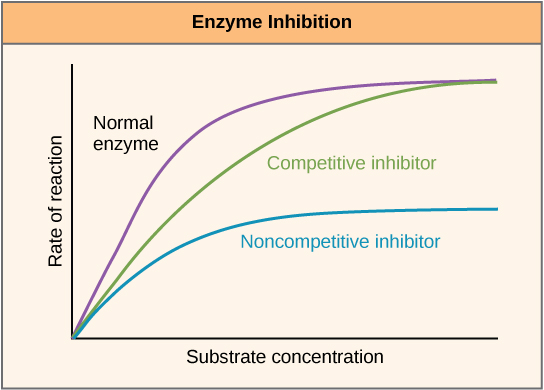
Enzymes can be regulated in ways that either promote or reduce their activity. There are many different kinds of molecules that inhibit or promote enzyme function, and various mechanisms exist for doing so. In some cases of enzyme inhibition, for example, an inhibitor molecule is similar enough to a substrate that it can bind to the active site and simply block the substrate from binding. When this happens, the enzyme is inhibited through competitive inhibition , because an inhibitor molecule competes with the substrate for active site binding ( [link] ). On the other hand, in noncompetitive inhibition, an inhibitor molecule binds to the enzyme in a location other than an allosteric site and still manages to block substrate binding to the active site.
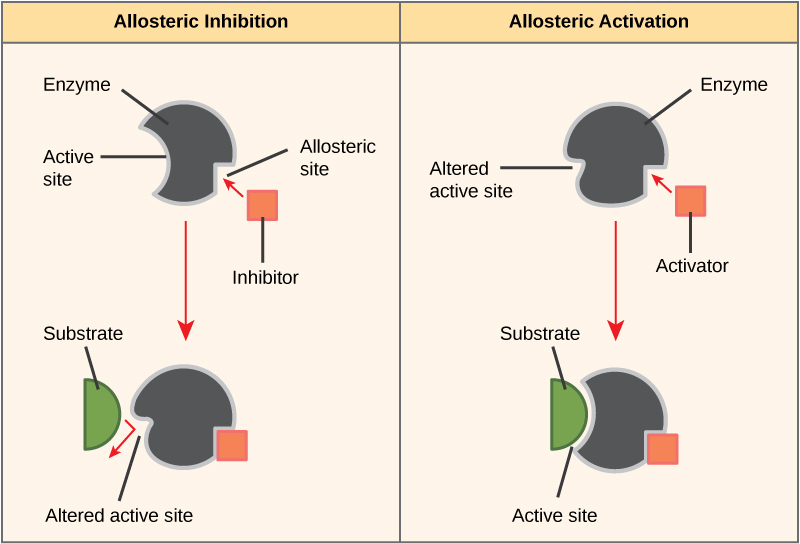
Some inhibitor molecules bind to enzymes in a location where their binding induces a conformational change that reduces the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate. This type of inhibition is called allosteric inhibition ( [link] ). Most allosterically regulated enzymes are made up of more than one polypeptide, meaning that they have more than one protein subunit. When an allosteric inhibitor binds to an enzyme, all active sites on the protein subunits are changed slightly such that they bind their substrates with less efficiency. There are allosteric activators as well as inhibitors. Allosteric activators bind to locations on an enzyme away from the active site, inducing a conformational change that increases the affinity of the enzyme’s active site(s) for its substrate(s).

Consider statins for example—which is the name given to the class of drugs that reduces cholesterol levels. These compounds are essentially inhibitors of the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. HMG-CoA reductase is the enzyme that synthesizes cholesterol from lipids in the body. By inhibiting this enzyme, the levels of cholesterol synthesized in the body can be reduced. Similarly, acetaminophen, popularly marketed under the brand name Tylenol, is an inhibitor of the enzyme cyclooxygenase. While it is effective in providing relief from fever and inflammation (pain), its mechanism of action is still not completely understood.
How are drugs developed? One of the first challenges in drug development is identifying the specific molecule that the drug is intended to target. In the case of statins, HMG-CoA reductase is the drug target. Drug targets are identified through painstaking research in the laboratory. Identifying the target alone is not sufficient; scientists also need to know how the target acts inside the cell and which reactions go awry in the case of disease. Once the target and the pathway are identified, then the actual process of drug design begins. During this stage, chemists and biologists work together to design and synthesize molecules that can either block or activate a particular reaction. However, this is only the beginning: both if and when a drug prototype is successful in performing its function, then it must undergo many tests from in vitro experiments to clinical trials before it can get FDA approval to be on the market.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?