| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Impaired insulin function can lead to a condition called diabetes mellitus , the main symptoms of which are illustrated in [link] . This can be caused by low levels of insulin production by the beta cells of the pancreas, or by reduced sensitivity of tissue cells to insulin. This prevents glucose from being absorbed by cells, causing high levels of blood glucose, or hyperglycemia (high sugar). High blood glucose levels make it difficult for the kidneys to recover all the glucose from nascent urine, resulting in glucose being lost in urine. High glucose levels also result in less water being reabsorbed by the kidneys, causing high amounts of urine to be produced; this may result in dehydration. Over time, high blood glucose levels can cause nerve damage to the eyes and peripheral body tissues, as well as damage to the kidneys and cardiovascular system. Oversecretion of insulin can cause hypoglycemia , low blood glucose levels. This causes insufficient glucose availability to cells, often leading to muscle weakness, and can sometimes cause unconsciousness or death if left untreated.

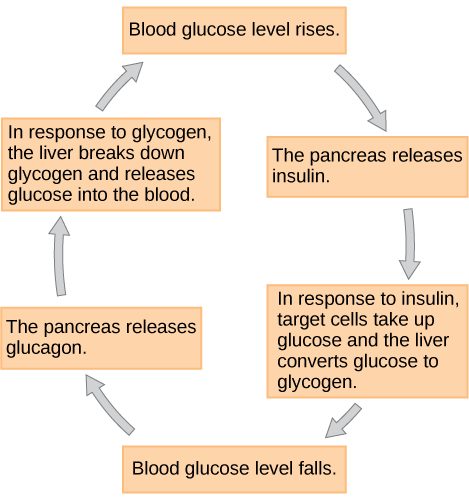
When blood glucose levels decline below normal levels, for example between meals or when glucose is utilized rapidly during exercise, the hormone glucagon is released from the alpha cells of the pancreas. Glucagon raises blood glucose levels, eliciting what is called a hyperglycemic effect, by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen to glucose in skeletal muscle cells and liver cells in a process called glycogenolysis . Glucose can then be utilized as energy by muscle cells and released into circulation by the liver cells. Glucagon also stimulates absorption of amino acids from the blood by the liver, which then converts them to glucose. This process of glucose synthesis is called gluconeogenesis . Glucagon also stimulates adipose cells to release fatty acids into the blood. These actions mediated by glucagon result in an increase in blood glucose levels to normal homeostatic levels. Rising blood glucose levels inhibit further glucagon release by the pancreas via a negative feedback mechanism. In this way, insulin and glucagon work together to maintain homeostatic glucose levels, as shown in [link] .
Pancreatic tumors may cause excess secretion of glucagon. Type I diabetes results from the failure of the pancreas to produce insulin. Which of the following statement about these two conditions is true?
The basal metabolic rate, which is the amount of calories required by the body at rest, is determined by two hormones produced by the thyroid gland: thyroxine , also known as tetraiodothyronine or T 4 , and triiodothyronine , also known as T 3 . These hormones affect nearly every cell in the body except for the adult brain, uterus, testes, blood cells, and spleen. They are transported across the plasma membrane of target cells and bind to receptors on the mitochondria resulting in increased ATP production. In the nucleus, T 3 and T 4 activate genes involved in energy production and glucose oxidation. This results in increased rates of metabolism and body heat production, which is known as the hormone’s calorigenic effect.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?