| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
During phase three, or orgasm, rhythmic, involuntary contractions of muscles occur in both sexes. In the male, the reproductive accessory glands and tubules constrict placing semen in the urethra, then the urethra contracts expelling the semen through the penis. In women, the uterus and vaginal muscles contract in waves that may last slightly less than a second each. During phase four, or resolution, the processes described in the first three phases reverse themselves and return to their normal state. Men experience a refractory period in which they cannot maintain an erection or ejaculate for a period of time ranging from minutes to hours.
Gametogenesis, the production of sperm and eggs, takes place through the process of meiosis. During meiosis, two cell divisions separate the paired chromosomes in the nucleus and then separate the chromatids that were made during an earlier stage of the cell’s life cycle. Meiosis produces haploid cells with half of each pair of chromosomes normally found in diploid cells. The production of sperm is called spermatogenesis and the production of eggs is called oogenesis .
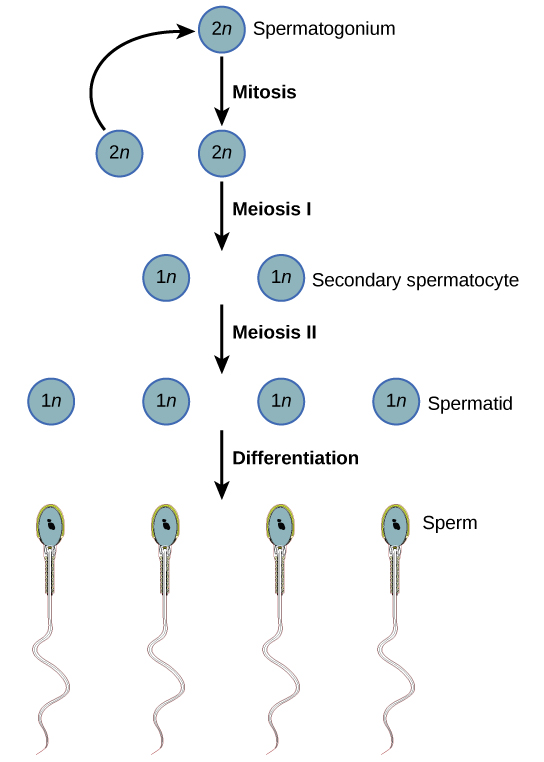
Spermatogenesis, illustrated in [link] , occurs in the wall of the seminiferous tubules ( [link] ), with stem cells at the periphery of the tube and the spermatozoa at the lumen of the tube. Immediately under the capsule of the tubule are diploid, undifferentiated cells. These stem cells, called spermatogonia (singular: spermatagonium), go through mitosis with one offspring going on to differentiate into a sperm cell and the other giving rise to the next generation of sperm.
Meiosis starts with a cell called a primary spermatocyte. At the end of the first meiotic division, a haploid cell is produced called a secondary spermatocyte. This cell is haploid and must go through another meiotic cell division. The cell produced at the end of meiosis is called a spermatid and when it reaches the lumen of the tubule and grows a flagellum, it is called a sperm cell. Four sperm result from each primary spermatocyte that goes through meiosis.
Stem cells are deposited during gestation and are present at birth through the beginning of adolescence, but in an inactive state. During adolescence, gonadotropic hormones from the anterior pituitary cause the activation of these cells and the production of viable sperm. This continues into old age.
Visit this site to see the process of spermatogenesis.
Oogenesis, illustrated in [link] , occurs in the outermost layers of the ovaries. As with sperm production, oogenesis starts with a germ cell, called an oogonium (plural: oogonia), but this cell undergoes mitosis to increase in number, eventually resulting in up to about one to two million cells in the embryo.
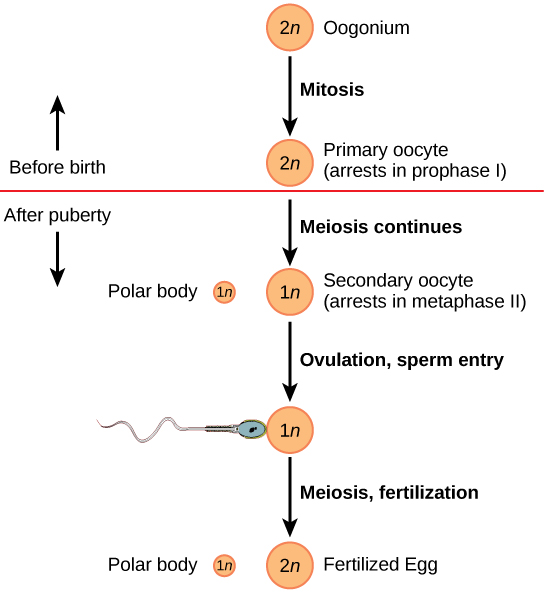
The cell starting meiosis is called a primary oocyte, as shown in [link] . This cell will start the first meiotic division and be arrested in its progress in the first prophase stage. At the time of birth, all future eggs are in the prophase stage. At adolescence, anterior pituitary hormones cause the development of a number of follicles in an ovary. This results in the primary oocyte finishing the first meiotic division. The cell divides unequally, with most of the cellular material and organelles going to one cell, called a secondary oocyte, and only one set of chromosomes and a small amount of cytoplasm going to the other cell. This second cell is called a polar body and usually dies. A secondary meiotic arrest occurs, this time at the metaphase II stage. At ovulation, this secondary oocyte will be released and travel toward the uterus through the oviduct. If the secondary oocyte is fertilized, the cell continues through the meiosis II, producing a second polar body and a fertilized egg containing all 46 chromosomes of a human being, half of them coming from the sperm.
Egg production begins before birth, is arrested during meiosis until puberty, and then individual cells continue through at each menstrual cycle. One egg is produced from each meiotic process, with the extra chromosomes and chromatids going into polar bodies that degenerate and are reabsorbed by the body.
As animals became more complex, specific organs and organ systems developed to support specific functions for the organism. The reproductive structures that evolved in land animals allow males and females to mate, fertilize internally, and support the growth and development of offspring. Processes developed to produce reproductive cells that had exactly half the number of chromosomes of each parent so that new combinations would have the appropriate amount of genetic material. Gametogenesis, the production of sperm (spermatogenesis) and eggs (oogenesis), takes place through the process of meiosis.
[link] Which of the following statements about the male reproductive system is false?
[link] D

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?