| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
DNA fragments can also be amplified from an RNA template in a process called reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) . The first step is to recreate the original DNA template strand (called cDNA) by applying DNA nucleotides to the mRNA. This process is called reverse transcription. This requires the presence of an enzyme called reverse transcriptase. After the cDNA is made, regular PCR can be used to amplify it.
Deepen your understanding of the polymerase chain reaction by clicking through this interactive exercise .
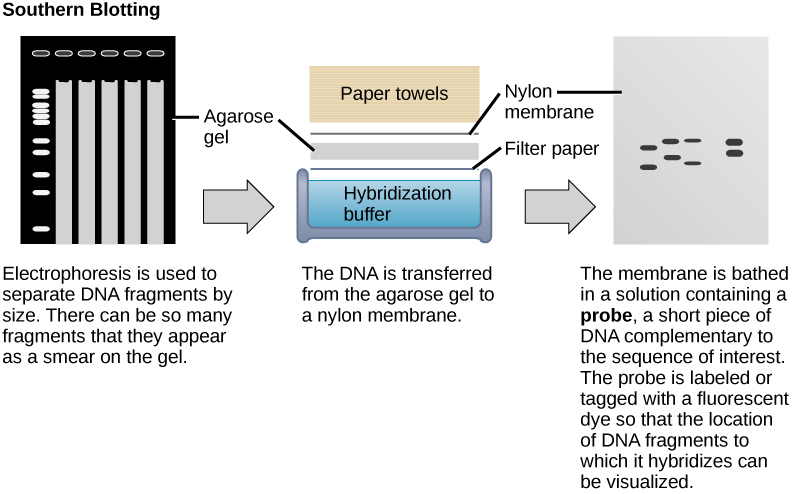
Nucleic acid samples, such as fragmented genomic DNA and RNA extracts, can be probed for the presence of certain sequences. Short DNA fragments called probes are designed and labeled with radioactive or fluorescent dyes to aid detection. Gel electrophoresis separates the nucleic acid fragments according to their size. The fragments in the gel are then transferred onto a nylon membrane in a procedure called blotting ( [link] ). The nucleic acid fragments that are bound to the surface of the membrane can then be probed with specific radioactively or fluorescently labeled probe sequences. When DNA is transferred to a nylon membrane, the technique is called Southern blotting , and when RNA is transferred to a nylon membrane, it is called northern blotting . Southern blots are used to detect the presence of certain DNA sequences in a given genome, and northern blots are used to detect gene expression.
In general, the word “cloning” means the creation of a perfect replica; however, in biology, the re-creation of a whole organism is referred to as “reproductive cloning.” Long before attempts were made to clone an entire organism, researchers learned how to reproduce desired regions or fragments of the genome, a process that is referred to as molecular cloning.
Cloning small fragments of the genome allows for the manipulation and study of specific genes (and their protein products), or noncoding regions in isolation. A plasmid (also called a vector) is a small circular DNA molecule that replicates independently of the chromosomal DNA. In cloning, the plasmid molecules can be used to provide a "folder" in which to insert a desired DNA fragment. Plasmids are usually introduced into a bacterial host for proliferation. In the bacterial context, the fragment of DNA from the human genome (or the genome of another organism that is being studied) is referred to as foreign DNA , or a transgene, to differentiate it from the DNA of the bacterium, which is called the host DNA .
Plasmids occur naturally in bacterial populations (such as Escherichia coli ) and have genes that can contribute favorable traits to the organism, such as antibiotic resistance (the ability to be unaffected by antibiotics). Plasmids have been repurposed and engineered as vectors for molecular cloning and the large-scale production of important reagents, such as insulin and human growth hormone. An important feature of plasmid vectors is the ease with which a foreign DNA fragment can be introduced via the multiple cloning site (MCS) . The MCS is a short DNA sequence containing multiple sites that can be cut with different commonly available restriction endonucleases. Restriction endonucleases recognize specific DNA sequences and cut them in a predictable manner; they are naturally produced by bacteria as a defense mechanism against foreign DNA. Many restriction endonucleases make staggered cuts in the two strands of DNA, such that the cut ends have a 2- or 4-base single-stranded overhang. Because these overhangs are capable of annealing with complementary overhangs, these are called “sticky ends.” Addition of an enzyme called DNA ligase permanently joins the DNA fragments via phosphodiester bonds. In this way, any DNA fragment generated by restriction endonuclease cleavage can be spliced between the two ends of a plasmid DNA that has been cut with the same restriction endonuclease ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?