| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of the G 1 , S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The G 1 phase, which is also called the first gap phase, is the first phase of the interphase and is focused on cell growth. The S phase is the second phase of interphase, during which the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated. Finally, the G 2 phase, also called the second gap phase, is the third and final phase of interphase; in this phase, the cell undergoes the final preparations for meiosis.
During DNA duplication in the S phase, each chromosome is replicated to produce two identical copies, called sister chromatids, that are held together at the centromere by cohesin proteins. Cohesin holds the chromatids together until anaphase II. The centrosomes, which are the structures that organize the microtubules of the meiotic spindle, also replicate. This prepares the cell to enter prophase I, the first meiotic phase.
Early in prophase I, before the chromosomes can be seen clearly microscopically, the homologous chromosomes are attached at their tips to the nuclear envelope by proteins. As the nuclear envelope begins to break down, the proteins associated with homologous chromosomes bring the pair close to each other. Recall that, in mitosis, homologous chromosomes do not pair together. In mitosis, homologous chromosomes line up end-to-end so that when they divide, each daughter cell receives a sister chromatid from both members of the homologous pair. The synaptonemal complex , a lattice of proteins between the homologous chromosomes, first forms at specific locations and then spreads to cover the entire length of the chromosomes. The tight pairing of the homologous chromosomes is called synapsis . In synapsis, the genes on the chromatids of the homologous chromosomes are aligned precisely with each other. The synaptonemal complex supports the exchange of chromosomal segments between non-sister homologous chromatids, a process called crossing over. Crossing over can be observed visually after the exchange as chiasmata (singular = chiasma) ( [link] ).
In species such as humans, even though the X and Y sex chromosomes are not homologous (most of their genes differ), they have a small region of homology that allows the X and Y chromosomes to pair up during prophase I. A partial synaptonemal complex develops only between the regions of homology.
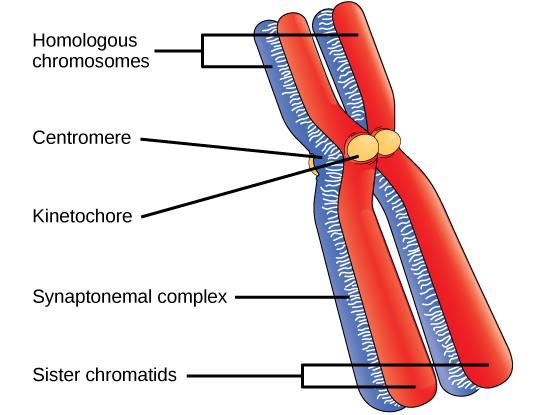
Located at intervals along the synaptonemal complex are large protein assemblies called recombination nodules . These assemblies mark the points of later chiasmata and mediate the multistep process of crossover —or genetic recombination—between the non-sister chromatids. Near the recombination nodule on each chromatid, the double-stranded DNA is cleaved, the cut ends are modified, and a new connection is made between the non-sister chromatids. As prophase I progresses, the synaptonemal complex begins to break down and the chromosomes begin to condense. When the synaptonemal complex is gone, the homologous chromosomes remain attached to each other at the centromere and at chiasmata. The chiasmata remain until anaphase I. The number of chiasmata varies according to the species and the length of the chromosome. There must be at least one chiasma per chromosome for proper separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I, but there may be as many as 25. Following crossover, the synaptonemal complex breaks down and the cohesin connection between homologous pairs is also removed. At the end of prophase I, the pairs are held together only at the chiasmata ( [link] ) and are called tetrads because the four sister chromatids of each pair of homologous chromosomes are now visible.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?