| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Fertilization and meiosis alternate in sexual life cycles . What happens between these two events depends on the organism. The process of meiosis reduces the chromosome number by half. Fertilization, the joining of two haploid gametes, restores the diploid condition. There are three main categories of life cycles in multicellular organisms: diploid-dominant , in which the multicellular diploid stage is the most obvious life stage, such as with most animals including humans; haploid-dominant , in which the multicellular haploid stage is the most obvious life stage, such as with all fungi and some algae; and alternation of generations , in which the two stages are apparent to different degrees depending on the group, as with plants and some algae.
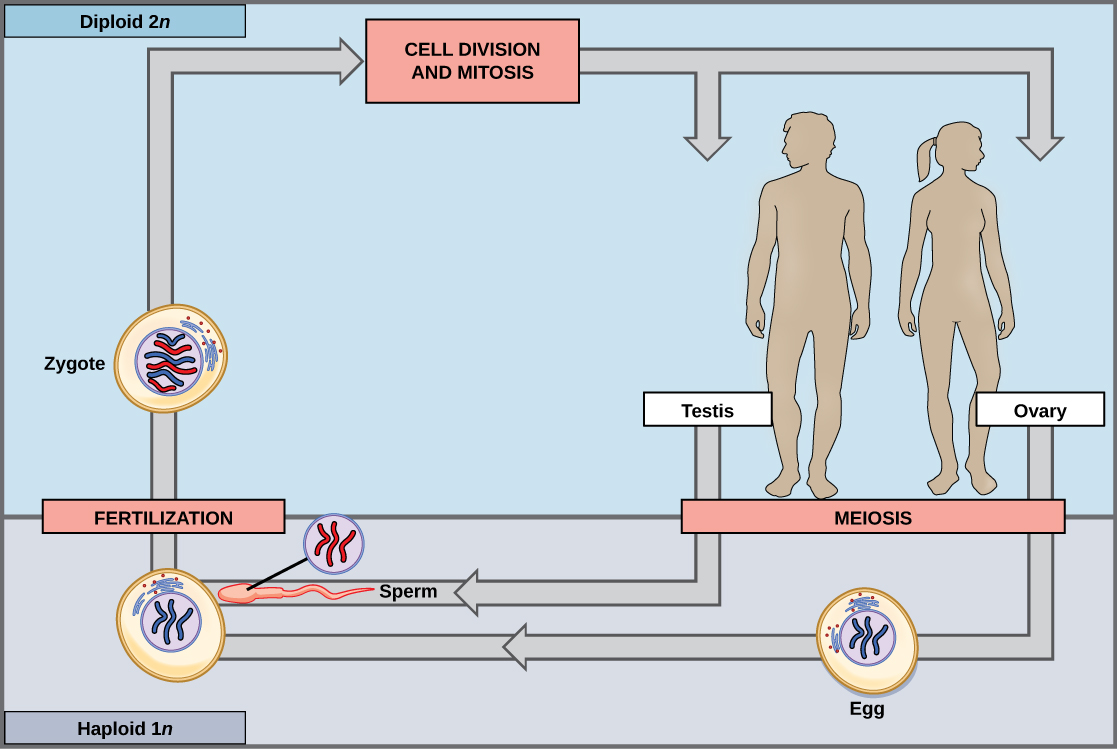
Nearly all animals employ a diploid-dominant life-cycle strategy in which the only haploid cells produced by the organism are the gametes. Early in the development of the embryo, specialized diploid cells, called germ cells , are produced within the gonads, such as the testes and ovaries. Germ cells are capable of mitosis to perpetuate the cell line and meiosis to produce gametes. Once the haploid gametes are formed, they lose the ability to divide again. There is no multicellular haploid life stage. Fertilization occurs with the fusion of two gametes, usually from different individuals, restoring the diploid state ( [link] ).
Most fungi and algae employ a life-cycle type in which the “body” of the organism—the ecologically important part of the life cycle—is haploid. The haploid cells that make up the tissues of the dominant multicellular stage are formed by mitosis. During sexual reproduction, specialized haploid cells from two individuals, designated the (+) and (−) mating types, join to form a diploid zygote. The zygote immediately undergoes meiosis to form four haploid cells called spores. Although haploid like the “parents,” these spores contain a new genetic combination from two parents. The spores can remain dormant for various time periods. Eventually, when conditions are conducive, the spores form multicellular haploid structures by many rounds of mitosis ( [link] ).
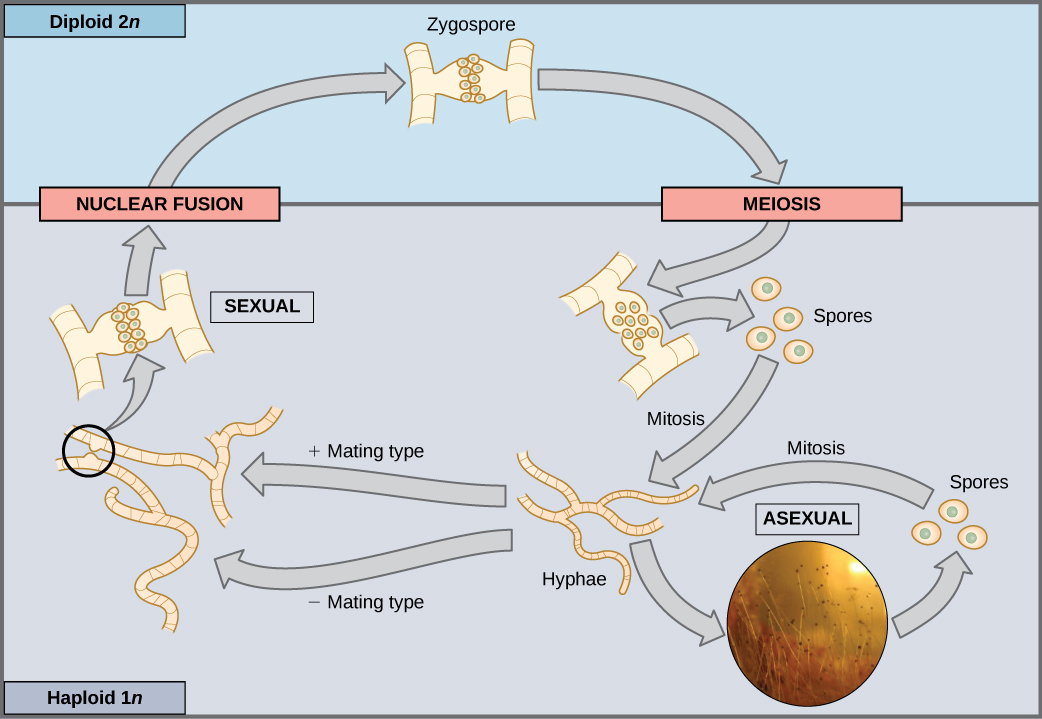
If a mutation occurs so that a fungus is no longer able to produce a minus mating type, will it still be able to reproduce?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?