| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Glomerular filtration filters out most of the solutes due to high blood pressure and specialized membranes in the afferent arteriole. The blood pressure in the glomerulus is maintained independent of factors that affect systemic blood pressure. The “leaky” connections between the endothelial cells of the glomerular capillary network allow solutes to pass through easily. All solutes in the glomerular capillaries, except for macromolecules like proteins, pass through by passive diffusion. There is no energy requirement at this stage of the filtration process. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the volume of glomerular filtrate formed per minute by the kidneys. GFR is regulated by multiple mechanisms and is an important indicator of kidney function.
To learn more about the vascular system of kidneys, click through this review and the steps of blood flow.
Tubular reabsorption occurs in the PCT part of the renal tubule. Almost all nutrients are reabsorbed, and this occurs either by passive or active transport. Reabsorption of water and some key electrolytes are regulated and can be influenced by hormones. Sodium (Na + ) is the most abundant ion and most of it is reabsorbed by active transport and then transported to the peritubular capillaries. Because Na + is actively transported out of the tubule, water follows it to even out the osmotic pressure. Water is also independently reabsorbed into the peritubular capillaries due to the presence of aquaporins, or water channels, in the PCT. This occurs due to the low blood pressure and high osmotic pressure in the peritubular capillaries. However, every solute has a transport maximum and the excess is not reabsorbed.
In the loop of Henle, the permeability of the membrane changes. The descending limb is permeable to water, not solutes; the opposite is true for the ascending limb. Additionally, the loop of Henle invades the renal medulla, which is naturally high in salt concentration and tends to absorb water from the renal tubule and concentrate the filtrate. The osmotic gradient increases as it moves deeper into the medulla. Because two sides of the loop of Henle perform opposing functions, as illustrated in [link] , it acts as a countercurrent multiplier . The vasa recta around it acts as the countercurrent exchanger .
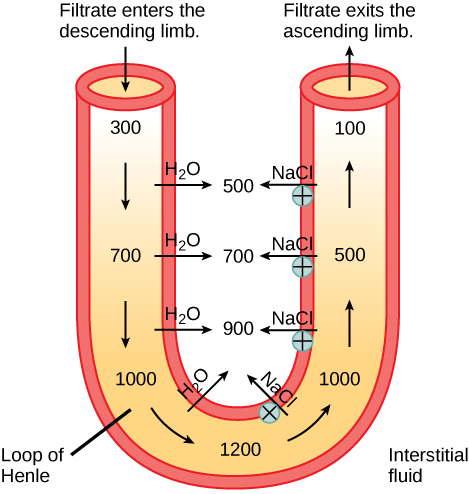
Loop diuretics are drugs sometimes used to treat hypertension. These drugs inhibit the reabsorption of Na + and Cl - ions by the ascending limb of the loop of Henle. A side effect is that they increase urination. Why do you think this is the case?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?