| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In science, sometimes things are believed to be true, and then new information comes to light that changes our understanding. The story of the peppered moth is an example: the facts behind the selection toward darker moths have recently been called into question. Read this article to learn more.
Sometimes two or more distinct phenotypes can each have their advantages and be selected for by natural selection, while the intermediate phenotypes are, on average, less fit. Known as diversifying selection ( [link] ), this is seen in many populations of animals that have multiple male forms. Large, dominant alpha males obtain mates by brute force, while small males can sneak in for furtive copulations with the females in an alpha male’s territory. In this case, both the alpha males and the “sneaking” males will be selected for, but medium-sized males, which can’t overtake the alpha males and are too big to sneak copulations, are selected against. Diversifying selection can also occur when environmental changes favor individuals on either end of the phenotypic spectrum. Imagine a population of mice living at the beach where there is light-colored sand interspersed with patches of tall grass. In this scenario, light-colored mice that blend in with the sand would be favored, as well as dark-colored mice that can hide in the grass. Medium-colored mice, on the other hand, would not blend in with either the grass or the sand, and would thus be more likely to be eaten by predators. The result of this type of selection is increased genetic variance as the population becomes more diverse.
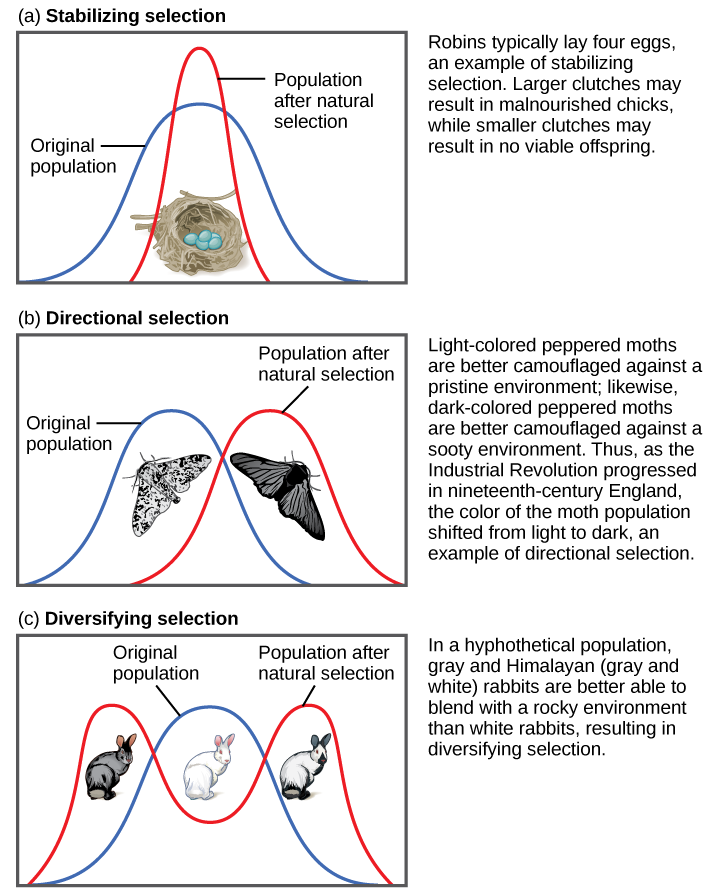
In recent years, factories have become cleaner, and less soot is released into the environment. What impact do you think this has had on the distribution of moth color in the population?
Another type of selection, called frequency-dependent selection , favors phenotypes that are either common (positive frequency-dependent selection) or rare (negative frequency-dependent selection). An interesting example of this type of selection is seen in a unique group of lizards of the Pacific Northwest. Male common side-blotched lizards come in three throat-color patterns: orange, blue, and yellow. Each of these forms has a different reproductive strategy: orange males are the strongest and can fight other males for access to their females; blue males are medium-sized and form strong pair bonds with their mates; and yellow males ( [link] ) are the smallest, and look a bit like females, which allows them to sneak copulations. Like a game of rock-paper-scissors, orange beats blue, blue beats yellow, and yellow beats orange in the competition for females. That is, the big, strong orange males can fight off the blue males to mate with the blue’s pair-bonded females, the blue males are successful at guarding their mates against yellow sneaker males, and the yellow males can sneak copulations from the potential mates of the large, polygynous orange males.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?