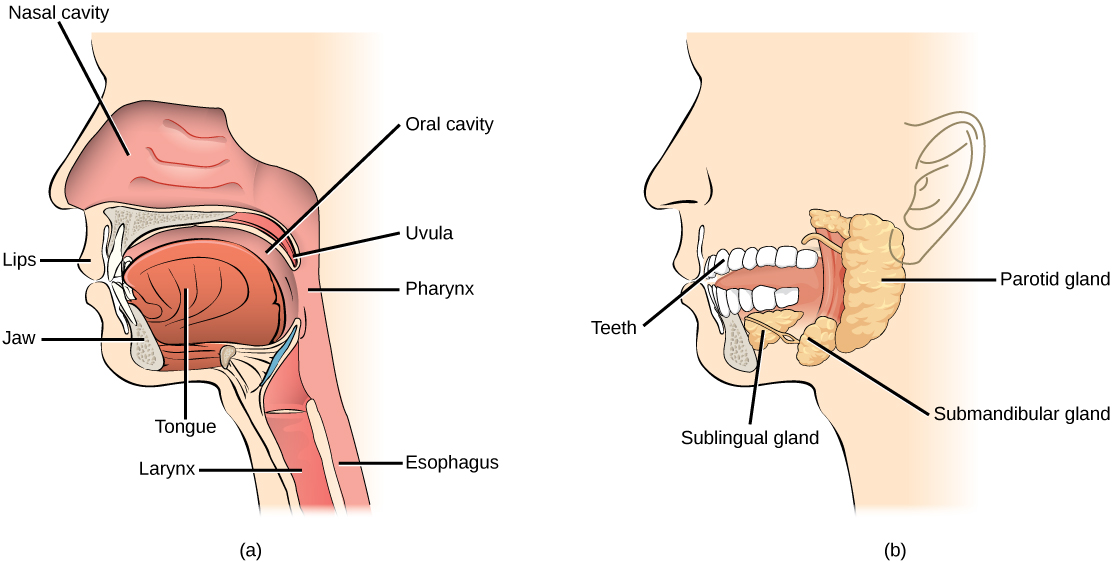
| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The esophagus is a tubular organ that connects the mouth to the stomach. The chewed and softened food passes through the esophagus after being swallowed. The smooth muscles of the esophagus undergo a series of wave like movements called peristalsis that push the food toward the stomach, as illustrated in [link] . The peristalsis wave is unidirectional—it moves food from the mouth to the stomach, and reverse movement is not possible. The peristaltic movement of the esophagus is an involuntary reflex; it takes place in response to the act of swallowing.
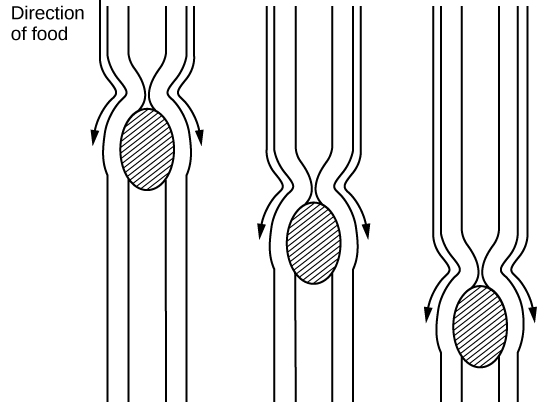
A ring-like muscle called a sphincter forms valves in the digestive system. The gastro-esophageal sphincter is located at the stomach end of the esophagus. In response to swallowing and the pressure exerted by the bolus of food, this sphincter opens, and the bolus enters the stomach. When there is no swallowing action, this sphincter is shut and prevents the contents of the stomach from traveling up the esophagus. Many animals have a true sphincter; however, in humans, there is no true sphincter, but the esophagus remains closed when there is no swallowing action. Acid reflux or “heartburn” occurs when the acidic digestive juices escape into the esophagus.
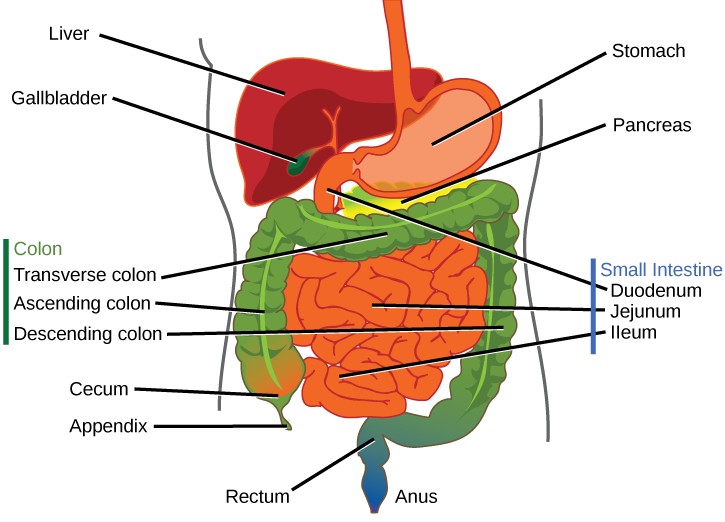
A large part of digestion occurs in the stomach, shown in [link] . The stomach is a saclike organ that secretes gastric digestive juices. The pH in the stomach is between 1.5 and 2.5. This highly acidic environment is required for the chemical breakdown of food and the extraction of nutrients. When empty, the stomach is a rather small organ; however, it can expand to up to 20 times its resting size when filled with food. This characteristic is particularly useful for animals that need to eat when food is available.
Which of the following statements about the digestive system is false?
The stomach is also the major site for protein digestion in animals other than ruminants. Protein digestion is mediated by an enzyme called pepsin in the stomach chamber. Pepsin is secreted by the chief cells in the stomach in an inactive form called pepsinogen . Pepsin breaks peptide bonds and cleaves proteins into smaller polypeptides; it also helps activate more pepsinogen, starting a positive feedback mechanism that generates more pepsin. Another cell type—parietal cells—secrete hydrogen and chloride ions, which combine in the lumen to form hydrochloric acid, the primary acidic component of the stomach juices. Hydrochloric acid helps to convert the inactive pepsinogen to pepsin. The highly acidic environment also kills many microorganisms in the food and, combined with the action of the enzyme pepsin, results in the hydrolysis of protein in the food. Chemical digestion is facilitated by the churning action of the stomach. Contraction and relaxation of smooth muscles mixes the stomach contents about every 20 minutes. The partially digested food and gastric juice mixture is called chyme . Chyme passes from the stomach to the small intestine. Further protein digestion takes place in the small intestine. Gastric emptying occurs within two to six hours after a meal. Only a small amount of chyme is released into the small intestine at a time. The movement of chyme from the stomach into the small intestine is regulated by the pyloric sphincter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?