| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Until the 1990s, the sequencing of DNA (reading the sequence of DNA) was a relatively expensive and long process. Using radiolabeled nucleotides also compounded the problem through safety concerns. With currently available technology and automated machines, the process is cheap, safer, and can be completed in a matter of hours. Fred Sanger developed the sequencing method used for the human genome sequencing project, which is widely used today ( [link] ).
Visit this site to watch a video explaining the DNA sequence reading technique that resulted from Sanger’s work.
The method is known as the dideoxy chain termination method. The sequencing method is based on the use of chain terminators, the dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs). The dideoxynucleotides, or ddNTPSs, differ from the deoxynucleotides by the lack of a free 3' OH group on the five-carbon sugar. If a ddNTP is added to a growing a DNA strand, the chain is not extended any further because the free 3' OH group needed to add another nucleotide is not available. By using a predetermined ratio of deoxyribonucleotides to dideoxynucleotides, it is possible to generate DNA fragments of different sizes.
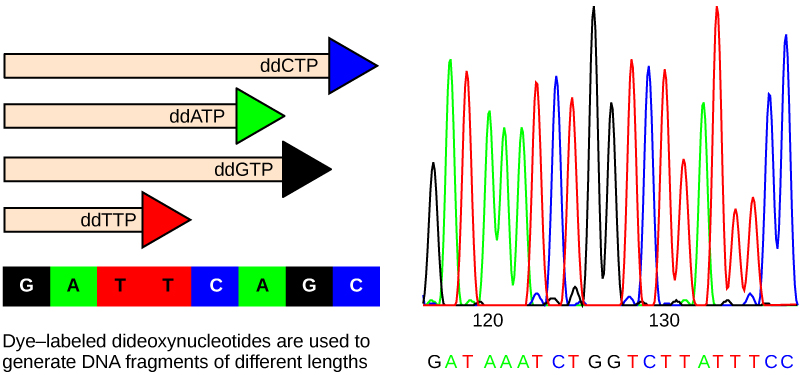
The DNA sample to be sequenced is denatured or separated into two strands by heating it to high temperatures. The DNA is divided into four tubes in which a primer, DNA polymerase, and all four nucleotides (A, T, G, and C) are added. In addition to each of the four tubes, limited quantities of one of the four dideoxynucleotides are added to each tube respectively. The tubes are labeled as A, T, G, and C according to the ddNTP added. For detection purposes, each of the four dideoxynucleotides carries a different fluorescent label. Chain elongation continues until a fluorescent dideoxy nucleotide is incorporated, after which no further elongation takes place. After the reaction is over, electrophoresis is performed. Even a difference in length of a single base can be detected. The sequence is read from a laser scanner. For his work on DNA sequencing, Sanger received a Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1980.
Sanger’s genome sequencing has led to a race to sequence human genomes at a rapid speed and low cost, often referred to as the $1000 in one day sequence. Learn more by selecting the Sequencing at Speed animation here .
Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments of different sizes. Usually the gel is made of a chemical called agarose. Agarose powder is added to a buffer and heated. After cooling, the gel solution is poured into a casting tray. Once the gel has solidified, the DNA is loaded on the gel and electric current is applied. The DNA has a net negative charge and moves from the negative electrode toward the positive electrode. The electric current is applied for sufficient time to let the DNA separate according to size; the smallest fragments will be farthest from the well (where the DNA was loaded), and the heavier molecular weight fragments will be closest to the well. Once the DNA is separated, the gel is stained with a DNA-specific dye for viewing it ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?