| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Sclerenchyma cells also provide support to the plant, but unlike collenchyma cells, many of them are dead at maturity. There are two types of sclerenchyma cells: fibers and sclereids. Both types have secondary cell walls that are thickened with deposits of lignin, an organic compound that is a key component of wood. Fibers are long, slender cells; sclereids are smaller-sized. Sclereids give pears their gritty texture. Humans use sclerenchyma fibers to make linen and rope ( [link] ).
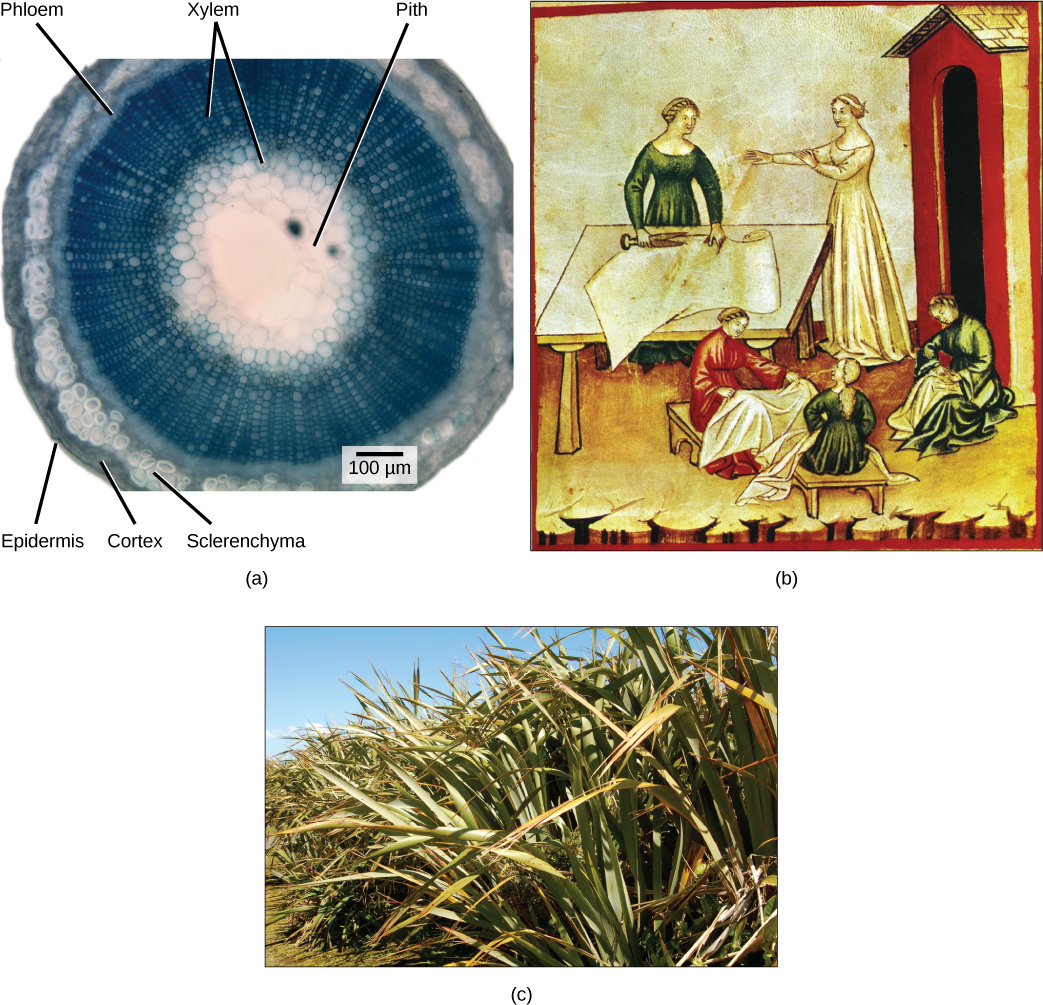

Which layers of the stem are made of parenchyma cells?
Like the rest of the plant, the stem has three tissue systems: dermal, vascular, and ground tissue. Each is distinguished by characteristic cell types that perform specific tasks necessary for the plant’s growth and survival.
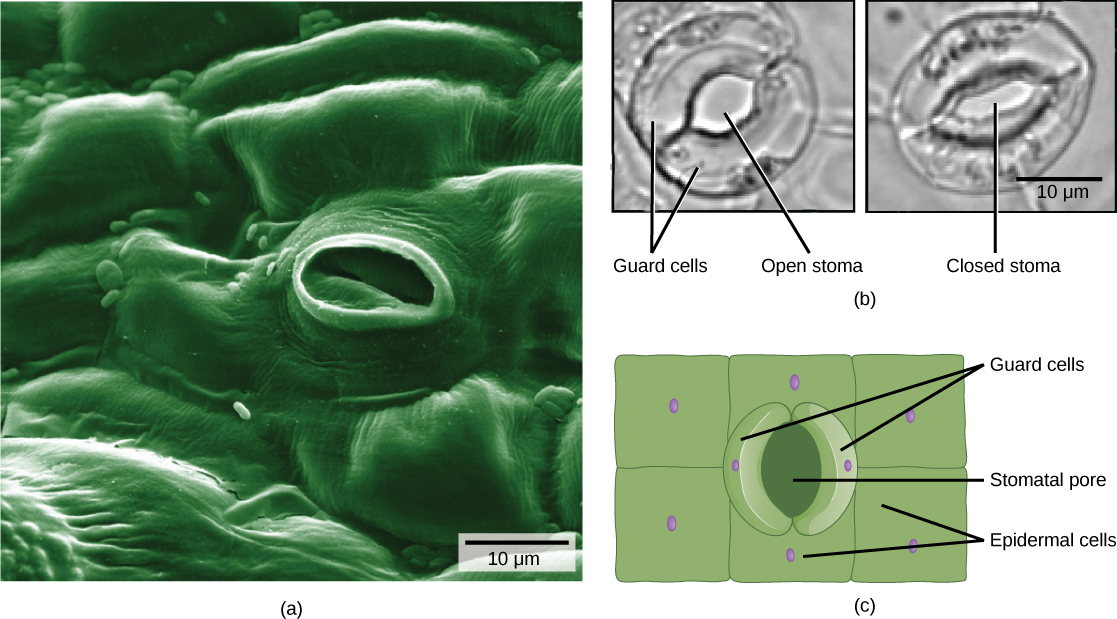
The dermal tissue of the stem consists primarily of epidermis , a single layer of cells covering and protecting the underlying tissue. Woody plants have a tough, waterproof outer layer of cork cells commonly known as bark , which further protects the plant from damage. Epidermal cells are the most numerous and least differentiated of the cells in the epidermis. The epidermis of a leaf also contains openings known as stomata, through which the exchange of gases takes place ( [link] ). Two cells, known as guard cells , surround each leaf stoma, controlling its opening and closing and thus regulating the uptake of carbon dioxide and the release of oxygen and water vapor. Trichomes are hair-like structures on the epidermal surface. They help to reduce transpiration (the loss of water by aboveground plant parts), increase solar reflectance, and store compounds that defend the leaves against predation by herbivores.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?