| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The capillary network that originates from the renal arteries supplies the nephron with blood that needs to be filtered. The branch that enters the glomerulus is called the afferent arteriole . The branch that exits the glomerulus is called the efferent arteriole . Within the glomerulus, the network of capillaries is called the glomerular capillary bed. Once the efferent arteriole exits the glomerulus, it forms the peritubular capillary network , which surrounds and interacts with parts of the renal tubule. In cortical nephrons, the peritubular capillary network surrounds the PCT and DCT. In juxtamedullary nephrons, the peritubular capillary network forms a network around the loop of Henle and is called the vasa recta .
Go to this website to see another coronal section of the kidney and to explore an animation of the workings of nephrons.
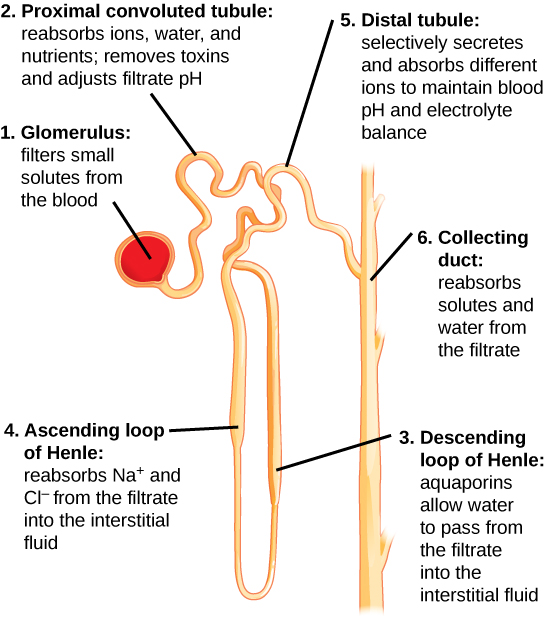
Kidneys filter blood in a three-step process. First, the nephrons filter blood that runs through the capillary network in the glomerulus. Almost all solutes, except for proteins, are filtered out into the glomerulus by a process called glomerular filtration . Second, the filtrate is collected in the renal tubules. Most of the solutes get reabsorbed in the PCT by a process called tubular reabsorption . In the loop of Henle, the filtrate continues to exchange solutes and water with the renal medulla and the peritubular capillary network. Water is also reabsorbed during this step. Then, additional solutes and wastes are secreted into the kidney tubules during tubular secretion , which is, in essence, the opposite process to tubular reabsorption. The collecting ducts collect filtrate coming from the nephrons and fuse in the medullary papillae. From here, the papillae deliver the filtrate, now called urine, into the minor calyces that eventually connect to the ureters through the renal pelvis. This entire process is illustrated in [link] .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?