| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
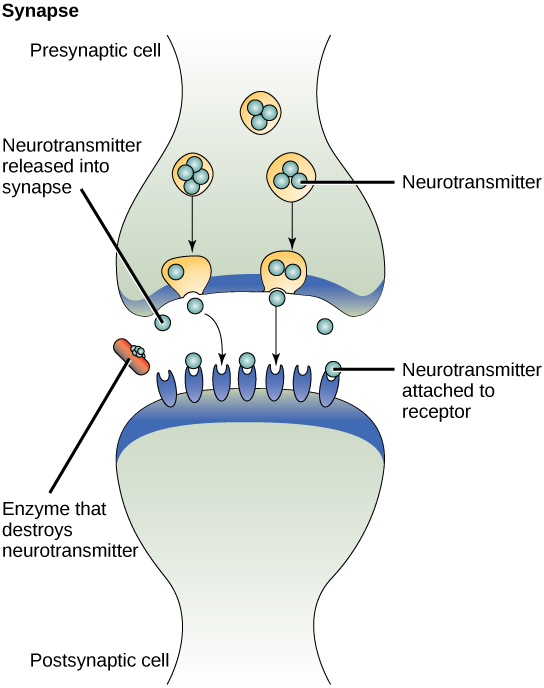
When the neurotransmitter binds the receptor on the surface of the postsynaptic cell, the electrochemical potential of the target cell changes, and the next electrical impulse is launched. The neurotransmitters that are released into the chemical synapse are degraded quickly or get reabsorbed by the presynaptic cell so that the recipient nerve cell can recover quickly and be prepared to respond rapidly to the next synaptic signal.
Signals from distant cells are called endocrine signals , and they originate from endocrine cells . (In the body, many endocrine cells are located in endocrine glands, such as the thyroid gland, the hypothalamus, and the pituitary gland.) These types of signals usually produce a slower response but have a longer-lasting effect. The ligands released in endocrine signaling are called hormones, signaling molecules that are produced in one part of the body but affect other body regions some distance away.
Hormones travel the large distances between endocrine cells and their target cells via the bloodstream, which is a relatively slow way to move throughout the body. Because of their form of transport, hormones get diluted and are present in low concentrations when they act on their target cells. This is different from paracrine signaling, in which local concentrations of ligands can be very high.
Autocrine signals are produced by signaling cells that can also bind to the ligand that is released. This means the signaling cell and the target cell can be the same or a similar cell (the prefix auto- means self, a reminder that the signaling cell sends a signal to itself). This type of signaling often occurs during the early development of an organism to ensure that cells develop into the correct tissues and take on the proper function. Autocrine signaling also regulates pain sensation and inflammatory responses. Further, if a cell is infected with a virus, the cell can signal itself to undergo programmed cell death, killing the virus in the process. In some cases, neighboring cells of the same type are also influenced by the released ligand. In embryological development, this process of stimulating a group of neighboring cells may help to direct the differentiation of identical cells into the same cell type, thus ensuring the proper developmental outcome.
Gap junctions in animals and plasmodesmata in plants are connections between the plasma membranes of neighboring cells. These water-filled channels allow small signaling molecules, called intracellular mediators , to diffuse between the two cells. Small molecules, such as calcium ions (Ca 2+ ), are able to move between cells, but large molecules like proteins and DNA cannot fit through the channels. The specificity of the channels ensures that the cells remain independent but can quickly and easily transmit signals. The transfer of signaling molecules communicates the current state of the cell that is directly next to the target cell; this allows a group of cells to coordinate their response to a signal that only one of them may have received. In plants, plasmodesmata are ubiquitous, making the entire plant into a giant, communication network.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?