| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A living cell cannot store significant amounts of free energy. Excess free energy would result in an increase of heat in the cell, which would result in excessive thermal motion that could damage and then destroy the cell. Rather, a cell must be able to handle that energy in a way that enables the cell to store energy safely and release it for use only as needed. Living cells accomplish this by using the compound adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is often called the “energy currency” of the cell, and, like currency, this versatile compound can be used to fill any energy need of the cell. How? It functions similarly to a rechargeable battery.
When ATP is broken down, usually by the removal of its terminal phosphate group, energy is released. The energy is used to do work by the cell, usually by the released phosphate binding to another molecule, activating it. For example, in the mechanical work of muscle contraction, ATP supplies the energy to move the contractile muscle proteins. Recall the active transport work of the sodium-potassium pump in cell membranes. ATP alters the structure of the integral protein that functions as the pump, changing its affinity for sodium and potassium. In this way, the cell performs work, pumping ions against their electrochemical gradients.
At the heart of ATP is a molecule of adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which is composed of an adenine molecule bonded to a ribose molecule and to a single phosphate group ( [link] ). Ribose is a five-carbon sugar found in RNA, and AMP is one of the nucleotides in RNA. The addition of a second phosphate group to this core molecule results in the formation of adenosine di phosphate (ADP); the addition of a third phosphate group forms adenosine tri phosphate (ATP).
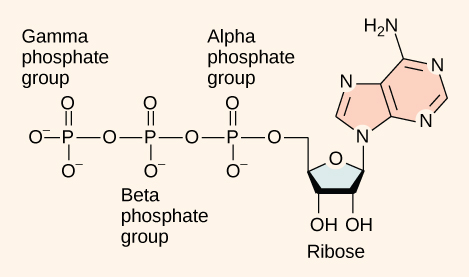
The addition of a phosphate group to a molecule requires energy. Phosphate groups are negatively charged and thus repel one another when they are arranged in series, as they are in ADP and ATP. This repulsion makes the ADP and ATP molecules inherently unstable. The release of one or two phosphate groups from ATP, a process called dephosphorylation , releases energy.
Hydrolysis is the process of breaking complex macromolecules apart. During hydrolysis, water is split, or lysed, and the resulting hydrogen atom (H + ) and a hydroxyl group (OH - ) are added to the larger molecule. The hydrolysis of ATP produces ADP, together with an inorganic phosphate ion (P i ), and the release of free energy. To carry out life processes, ATP is continuously broken down into ADP, and like a rechargeable battery, ADP is continuously regenerated into ATP by the reattachment of a third phosphate group. Water, which was broken down into its hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group during ATP hydrolysis, is regenerated when a third phosphate is added to the ADP molecule, reforming ATP.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?