| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
ACh is broken down by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) into acetyl and choline. AChE resides in the synaptic cleft, breaking down ACh so that it does not remain bound to ACh receptors, which would cause unwanted extended muscle contraction ( [link] ).
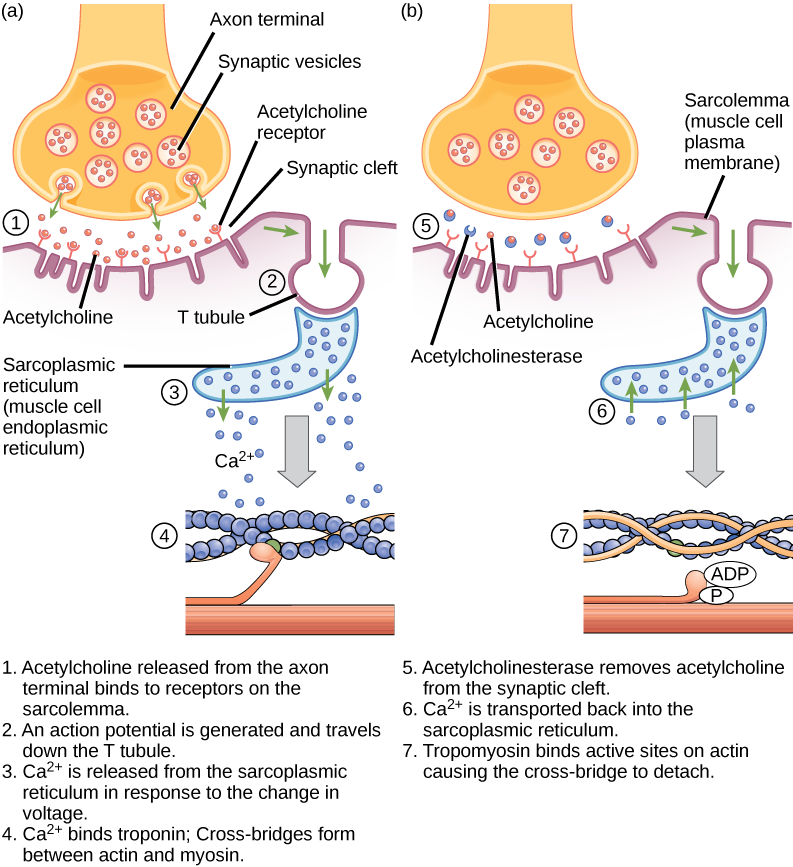
The deadly nerve gas Sarin irreversibly inhibits acetycholinesterase. What effect would Sarin have on muscle contraction?
After depolarization, the membrane returns to its resting state. This is called repolarization, during which voltage-gated sodium channels close. Potassium channels continue at 90% conductance. Because the plasma membrane sodium–potassium ATPase always transports ions, the resting state (negatively charged inside relative to the outside) is restored. The period immediately following the transmission of an impulse in a nerve or muscle, in which a neuron or muscle cell regains its ability to transmit another impulse, is called the refractory period. During the refractory period, the membrane cannot generate another action potential. . The refractory period allows the voltage-sensitive ion channels to return to their resting configurations. The sodium potassium ATPase continually moves Na + back out of the cell and K + back into the cell, and the K + leaks out leaving negative charge behind. Very quickly, the membrane repolarizes, so that it can again be depolarized.
Neural control initiates the formation of actin–myosin cross-bridges, leading to the sarcomere shortening involved in muscle contraction. These contractions extend from the muscle fiber through connective tissue to pull on bones, causing skeletal movement. The pull exerted by a muscle is called tension, and the amount of force created by this tension can vary. This enables the same muscles to move very light objects and very heavy objects. In individual muscle fibers, the amount of tension produced depends on the cross-sectional area of the muscle fiber and the frequency of neural stimulation.
The number of cross-bridges formed between actin and myosin determine the amount of tension that a muscle fiber can produce. Cross-bridges can only form where thick and thin filaments overlap, allowing myosin to bind to actin. If more cross-bridges are formed, more myosin will pull on actin, and more tension will be produced.
The ideal length of a sarcomere during production of maximal tension occurs when thick and thin filaments overlap to the greatest degree. If a sarcomere at rest is stretched past an ideal resting length, thick and thin filaments do not overlap to the greatest degree, and fewer cross-bridges can form. This results in fewer myosin heads pulling on actin, and less tension is produced. As a sarcomere is shortened, the zone of overlap is reduced as the thin filaments reach the H zone, which is composed of myosin tails. Because it is myosin heads that form cross-bridges, actin will not bind to myosin in this zone, reducing the tension produced by this myofiber. If the sarcomere is shortened even more, thin filaments begin to overlap with each other—reducing cross-bridge formation even further, and producing even less tension. Conversely, if the sarcomere is stretched to the point at which thick and thin filaments do not overlap at all, no cross-bridges are formed and no tension is produced. This amount of stretching does not usually occur because accessory proteins, internal sensory nerves, and connective tissue oppose extreme stretching.
The primary variable determining force production is the number of myofibers within the muscle that receive an action potential from the neuron that controls that fiber. When using the biceps to pick up a pencil, the motor cortex of the brain only signals a few neurons of the biceps, and only a few myofibers respond. In vertebrates, each myofiber responds fully if stimulated. When picking up a piano, the motor cortex signals all of the neurons in the biceps and every myofiber participates. This is close to the maximum force the muscle can produce. As mentioned above, increasing the frequency of action potentials (the number of signals per second) can increase the force a bit more, because the tropomyosin is flooded with calcium.
The body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Skeleton muscle tissue is composed of sarcomeres, the functional units of muscle tissue. Muscle contraction occurs when sarcomeres shorten, as thick and thin filaments slide past each other, which is called the sliding filament model of muscle contraction. ATP provides the energy for cross-bridge formation and filament sliding. Regulatory proteins, such as troponin and tropomyosin, control cross-bridge formation. Excitation–contraction coupling transduces the electrical signal of the neuron, via acetylcholine, to an electrical signal on the muscle membrane, which initiates force production. The number of muscle fibers contracting determines how much force the whole muscle produces.
[link] Which of the following statements about muscle contraction is true?
[link] B
[link] The deadly nerve gas Sarin irreversibly inhibits acetycholinesterase. What effect would Sarin have on muscle contraction?
[link] In the presence of Sarin, acetycholine is not removed from the synapse, resulting in continuous stimulation of the muscle plasma membrane. At first, muscle activity is intense and uncontrolled, but the ion gradients dissipate, so electrical signals in the T-tubules are no longer possible. The result is paralysis, leading to death by asphyxiation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?