| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
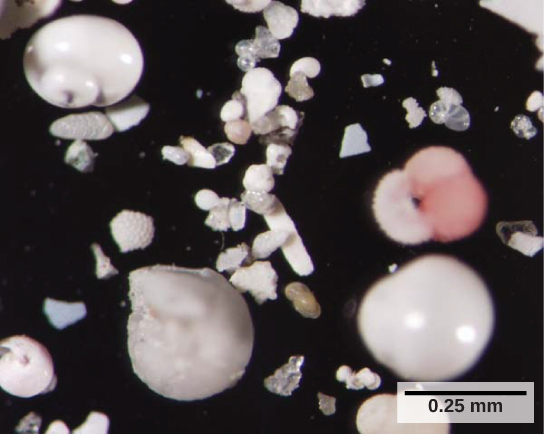

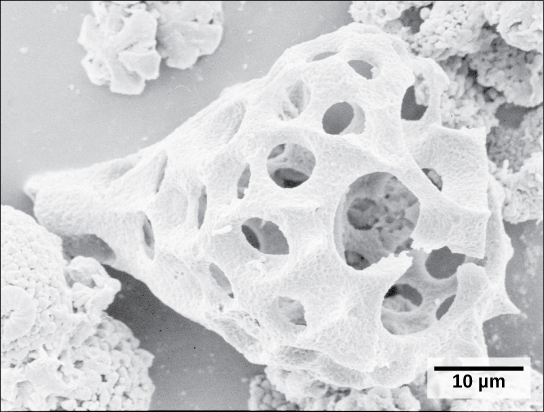
A second subtype of Rhizaria, the radiolarians, exhibit intricate exteriors of glassy silica with radial or bilateral symmetry ( [link] ). Needle-like pseudopods supported by microtubules radiate outward from the cell bodies of these protists and function to catch food particles. The shells of dead radiolarians sink to the ocean floor, where they may accumulate in 100 meter-thick depths. Preserved, sedimented radiolarians are very common in the fossil record.
Red algae and green algae are included in the supergroup Archaeplastida. It was from a common ancestor of these protists that the land plants evolved, since their closest relatives are found in this group. Molecular evidence supports that all Archaeplastida are descendents of an endosymbiotic relationship between a heterotrophic protist and a cyanobacterium. The red and green algae include unicellular, multicellular, and colonial forms.
Red algae, or rhodophytes, are primarily multicellular, lack flagella, and range in size from microscopic, unicellular protists to large, multicellular forms grouped into the informal seaweed category. The red algae life cycle is an alternation of generations. Some species of red algae contain phycoerythrins, photosynthetic accessory pigments that are red in color and outcompete the green tint of chlorophyll, making these species appear as varying shades of red. Other protists classified as red algae lack phycoerythrins and are parasites. Red algae are common in tropical waters where they have been detected at depths of 260 meters. Other red algae exist in terrestrial or freshwater environments.
The most abundant group of algae is the green algae. The green algae exhibit similar features to the land plants, particularly in terms of chloroplast structure. That this group of protists shared a relatively recent common ancestor with land plants is well supported. The green algae are subdivided into the chlorophytes and the charophytes. The charophytes are the closest living relatives to land plants and resemble them in morphology and reproductive strategies. Charophytes are common in wet habitats, and their presence often signals a healthy ecosystem.
The chlorophytes exhibit great diversity of form and function. Chlorophytes primarily inhabit freshwater and damp soil, and are a common component of plankton. Chlamydomonas is a simple, unicellular chlorophyte with a pear-shaped morphology and two opposing, anterior flagella that guide this protist toward light sensed by its eyespot. More complex chlorophyte species exhibit haploid gametes and spores that resemble Chlamydomonas .
The chlorophyte Volvox is one of only a few examples of a colonial organism, which behaves in some ways like a collection of individual cells, but in other ways like the specialized cells of a multicellular organism ( [link] ). Volvox colonies contain 500 to 60,000 cells, each with two flagella, contained within a hollow, spherical matrix composed of a gelatinous glycoprotein secretion. Individual Volvox cells move in a coordinated fashion and are interconnected by cytoplasmic bridges. Only a few of the cells reproduce to create daughter colonies, an example of basic cell specialization in this organism.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?