| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
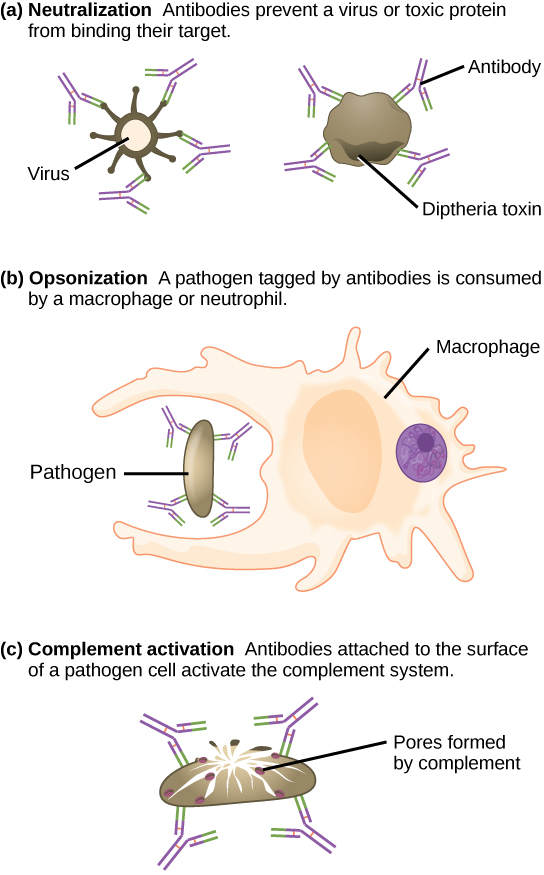
Antibodies also mark pathogens for destruction by phagocytic cells, such as macrophages or neutrophils, because phagocytic cells are highly attracted to macromolecules complexed with antibodies. Phagocytic enhancement by antibodies is called opsonization. In a process called complement fixation, IgM and IgG in serum bind to antigens and provide docking sites onto which sequential complement proteins can bind. The combination of antibodies and complement enhances opsonization even further and promotes rapid clearing of pathogens.
Not all antibodies bind with the same strength, specificity, and stability. In fact, antibodies exhibit different affinities (attraction) depending on the molecular complementarity between antigen and antibody molecules, as illustrated in [link] . An antibody with a higher affinity for a particular antigen would bind more strongly and stably, and thus would be expected to present a more challenging defense against the pathogen corresponding to the specific antigen.
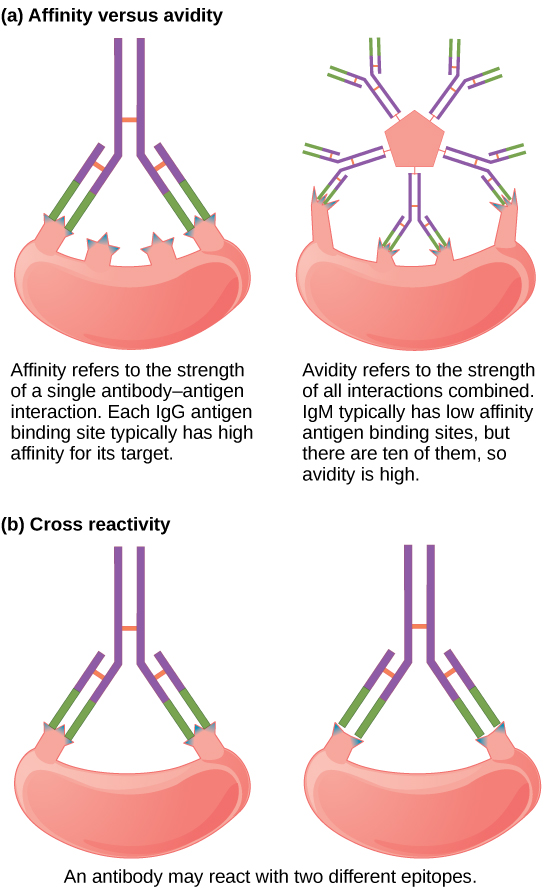
The term avidity describes binding by antibody classes that are secreted as joined, multivalent structures (such as IgM and IgA). Although avidity measures the strength of binding, just as affinity does, the avidity is not simply the sum of the affinities of the antibodies in a multimeric structure. The avidity depends on the number of identical binding sites on the antigen being detected, as well as other physical and chemical factors. Typically, multimeric antibodies, such as pentameric IgM, are classified as having lower affinity than monomeric antibodies, but high avidity. Essentially, the fact that multimeric antibodies can bind many antigens simultaneously balances their slightly lower binding strength for each antibody/antigen interaction.
Antibodies secreted after binding to one epitope on an antigen may exhibit cross reactivity for the same or similar epitopes on different antigens. Because an epitope corresponds to such a small region (the surface area of about four to six amino acids), it is possible for different macromolecules to exhibit the same molecular identities and orientations over short regions. Cross reactivity describes when an antibody binds not to the antigen that elicited its synthesis and secretion, but to a different antigen.
Cross reactivity can be beneficial if an individual develops immunity to several related pathogens despite having only been exposed to or vaccinated against one of them. For instance, antibody cross reactivity may occur against the similar surface structures of various Gram-negative bacteria. Conversely, antibodies raised against pathogenic molecular components that resemble self molecules may incorrectly mark host cells for destruction and cause autoimmune damage. Patients who develop systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) commonly exhibit antibodies that react with their own DNA. These antibodies may have been initially raised against the nucleic acid of microorganisms but later cross-reacted with self-antigens. This phenomenon is also called molecular mimicry.
Antibodies synthesized by the mucosal immune system include IgA and IgM. Activated B cells differentiate into mucosal plasma cells that synthesize and secrete dimeric IgA, and to a lesser extent, pentameric IgM. Secreted IgA is abundant in tears, saliva, breast milk, and in secretions of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. Antibody secretion results in a local humoral response at epithelial surfaces and prevents infection of the mucosa by binding and neutralizing pathogens.
Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are the molecules secreted from plasma cells that mediate the humoral immune response. There are five antibody classes; an antibody's class determines its mechanism of action and production site but does not control its binding specificity. Antibodies bind antigens via variable domains and can either neutralize pathogens or mark them for phagocytosis or activate the complement cascade.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?