| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
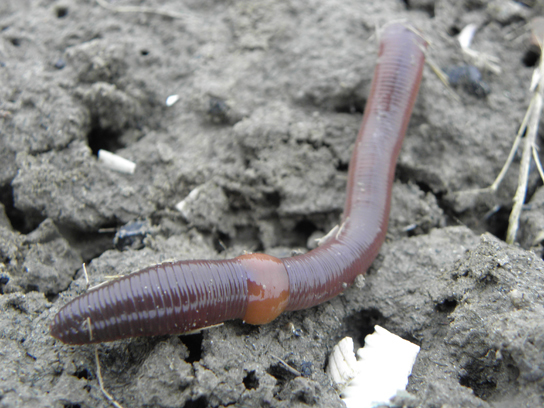

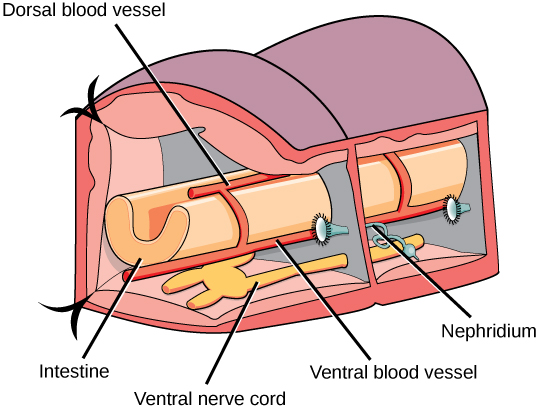
The epidermis is protected by an acellular, external cuticle, but this is much thinner than the cuticle found in the ecdysozoans and does not require periodic shedding for growth. Circular as well as longitudinal muscles are located interior to the epidermis. Chitinous hairlike extensions, anchored in the epidermis and projecting from the cuticle, called setae/chaetae are present in every segment. Annelids show the presence of a true coelom, derived from embryonic mesoderm and protostomy. Hence, they are the most advanced worms. A well-developed and complete digestive system is present in earthworms (oligochaetes) with a mouth, muscular pharynx, esophagus, crop, and gizzard being present. The gizzard leads to the intestine and ends in an anal opening. A cross-sectional view of a body segment of an earthworm (a terrestrial type of annelid) is shown in [link] ; each segment is limited by a membranous septum that divides the coelomic cavity into a series of compartments.
Annelids possess a closed circulatory system of dorsal and ventral blood vessels that run parallel to the alimentary canal as well as capillaries that service individual tissues. In addition, these vessels are connected by transverse loops in every segment. These animals lack a well-developed respiratory system, and gas exchange occurs across the moist body surface. Excretion is facilitated by a pair of metanephridia (a type of primitive “kidney” that consists of a convoluted tubule and an open, ciliated funnel) that is present in every segment towards the ventral side. Annelids show well-developed nervous systems with a nerve ring of fused ganglia present around the pharynx. The nerve cord is ventral in position and bears enlarged nodes or ganglia in each segment.
Annelids may be either monoecious with permanent gonads (as in earthworms and leeches) or dioecious with temporary or seasonal gonads that develop (as in polychaetes). However, cross-fertilization is preferred in hermaphroditic animals. These animals may also show simultaneous hermaphroditism and participate in simultaneous sperm exchange when they are aligned for copulation.
This combination video and animation provides a close-up look at annelid anatomy.
Phylum Annelida contains the class Polychaeta (the polychaetes) and the class Oligochaeta (the earthworms, leeches and their relatives).
Earthworms are the most abundant members of the class Oligochaeta, distinguished by the presence of the clitellum as well as few, reduced chaetae (“oligo- = “few”; -chaetae = “hairs”). The number and size of chaetae are greatly diminished in Oligochaeta compared to the polychaetes ( poly =many, chaetae = hairs). The many chetae of polychaetes are also arranged within fleshy, flat, paired appendages that protrude from each segment called parapodia , which may be specialized for different functions in the polychates. The subclass Hirudinea includes leeches such as Hirudo medicinalis and Hemiclepsis marginata . The class Oligochaeta includes the subclass Hirudinia and the subclass Brachiobdella. A significant difference between leeches and other annelids is the development of suckers at the anterior and posterior ends and a lack of chaetae. Additionally, the segmentation of the body wall may not correspond to the internal segmentation of the coelomic cavity. This adaptation possibly helps the leeches to elongate when they ingest copious quantities of blood from host vertebrates. The subclass Brachiobdella includes species like Branchiobdella balcanica sketi and Branchiobdella astaci , worms that show similarity with leeches as well as oligochaetes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?