| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Look at each of the processes shown, and decide if it is endergonic or exergonic. In each case, does enthalpy increase or decrease, and does entropy increase or decrease?
An important concept in the study of metabolism and energy is that of chemical equilibrium. Most chemical reactions are reversible. They can proceed in both directions, releasing energy into their environment in one direction, and absorbing it from the environment in the other direction ( [link] ). The same is true for the chemical reactions involved in cell metabolism, such as the breaking down and building up of proteins into and from individual amino acids, respectively. Reactants within a closed system will undergo chemical reactions in both directions until a state of equilibrium is reached. This state of equilibrium is one of the lowest possible free energy and a state of maximal entropy. Energy must be put into the system to push the reactants and products away from a state of equilibrium. Either reactants or products must be added, removed, or changed. If a cell were a closed system, its chemical reactions would reach equilibrium, and it would die because there would be insufficient free energy left to perform the work needed to maintain life. In a living cell, chemical reactions are constantly moving towards equilibrium, but never reach it. This is because a living cell is an open system. Materials pass in and out, the cell recycles the products of certain chemical reactions into other reactions, and chemical equilibrium is never reached. In this way, living organisms are in a constant energy-requiring, uphill battle against equilibrium and entropy. This constant supply of energy ultimately comes from sunlight, which is used to produce nutrients in the process of photosynthesis.
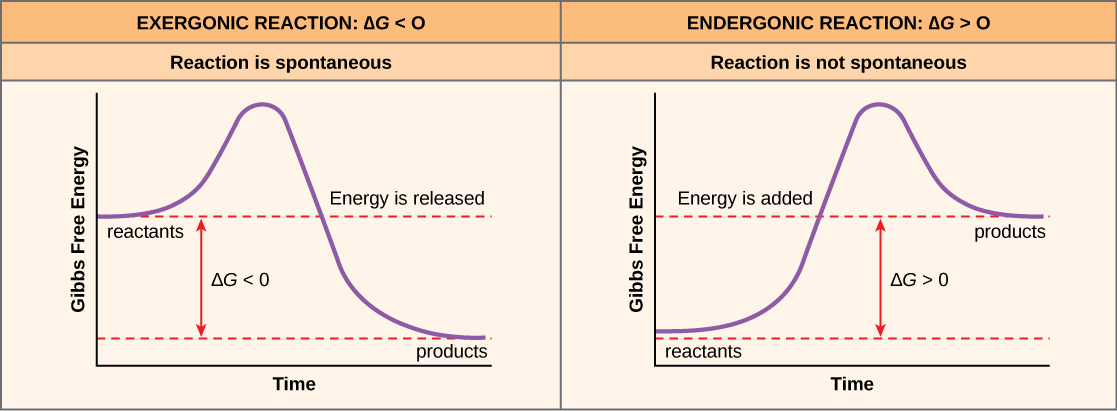
There is another important concept that must be considered regarding endergonic and exergonic reactions. Even exergonic reactions require a small amount of energy input to get going before they can proceed with their energy-releasing steps. These reactions have a net release of energy, but still require some energy in the beginning. This small amount of energy input necessary for all chemical reactions to occur is called the activation energy (or free energy of activation) and is abbreviated E A ( [link] ).
Why would an energy-releasing, negative ∆G reaction actually require some energy to proceed? The reason lies in the steps that take place during a chemical reaction. During chemical reactions, certain chemical bonds are broken and new ones are formed. For example, when a glucose molecule is broken down, bonds between the carbon atoms of the molecule are broken. Since these are energy-storing bonds, they release energy when broken. However, to get them into a state that allows the bonds to break, the molecule must be somewhat contorted. A small energy input is required to achieve this contorted state. This contorted state is called the transition state , and it is a high-energy, unstable state. For this reason, reactant molecules don’t last long in their transition state, but very quickly proceed to the next steps of the chemical reaction. Free energy diagrams illustrate the energy profiles for a given reaction. Whether the reaction is exergonic or endergonic determines whether the products in the diagram will exist at a lower or higher energy state than both the reactants and the products. However, regardless of this measure, the transition state of the reaction exists at a higher energy state than the reactants, and thus, E A is always positive.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?