| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
| Ion Concentration Inside and Outside Neurons | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ion | Extracellular concentration (mM) | Intracellular concentration (mM) | Ratio outside/inside |
| Na + | 145 | 12 | 12 |
| K+ | 4 | 155 | 0.026 |
| Cl − | 120 | 4 | 30 |
| Organic anions (A−) | — | 100 |

A neuron can receive input from other neurons and, if this input is strong enough, send the signal to downstream neurons. Transmission of a signal between neurons is generally carried by a chemical called a neurotransmitter. Transmission of a signal within a neuron (from dendrite to axon terminal) is carried by a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential called an action potential . When neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors located on a neuron’s dendrites, ion channels open. At excitatory synapses, this opening allows positive ions to enter the neuron and results in depolarization of the membrane—a decrease in the difference in voltage between the inside and outside of the neuron. A stimulus from a sensory cell or another neuron depolarizes the target neuron to its threshold potential (-55 mV). Na + channels in the axon hillock open, allowing positive ions to enter the cell ( [link] and [link] ). Once the sodium channels open, the neuron completely depolarizes to a membrane potential of about +40 mV. Action potentials are considered an "all-or nothing" event, in that, once the threshold potential is reached, the neuron always completely depolarizes. Once depolarization is complete, the cell must now "reset" its membrane voltage back to the resting potential. To accomplish this, the Na + channels close and cannot be opened. This begins the neuron's refractory period , in which it cannot produce another action potential because its sodium channels will not open. At the same time, voltage-gated K + channels open, allowing K + to leave the cell. As K + ions leave the cell, the membrane potential once again becomes negative. The diffusion of K + out of the cell actually hyperpolarizes the cell, in that the membrane potential becomes more negative than the cell's normal resting potential. At this point, the sodium channels will return to their resting state, meaning they are ready to open again if the membrane potential again exceeds the threshold potential. Eventually the extra K + ions diffuse out of the cell through the potassium leakage channels, bringing the cell from its hyperpolarized state, back to its resting membrane potential.
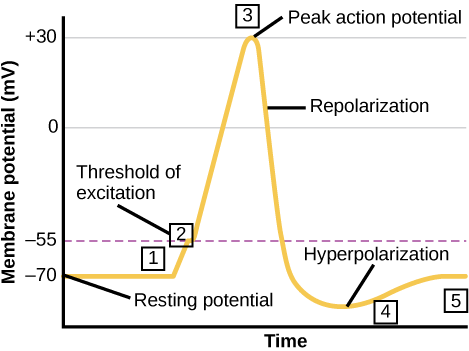
Potassium channel blockers, such as amiodarone and procainamide, which are used to treat abnormal electrical activity in the heart, called cardiac dysrhythmia, impede the movement of K + through voltage-gated K + channels. Which part of the action potential would you expect potassium channels to affect?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?