| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Another type of protein embedded in the plasma membrane is a carrier protein . This aptly named protein binds a substance and, in doing so, triggers a change of its own shape, moving the bound molecule from the outside of the cell to its interior ( [link] ); depending on the gradient, the material may move in the opposite direction. Carrier proteins are typically specific for a single substance. This selectivity adds to the overall selectivity of the plasma membrane. The exact mechanism for the change of shape is poorly understood. Proteins can change shape when their hydrogen bonds are affected, but this may not fully explain this mechanism. Each carrier protein is specific to one substance, and there are a finite number of these proteins in any membrane. This can cause problems in transporting enough of the material for the cell to function properly. When all of the proteins are bound to their ligands, they are saturated and the rate of transport is at its maximum. Increasing the concentration gradient at this point will not result in an increased rate of transport.
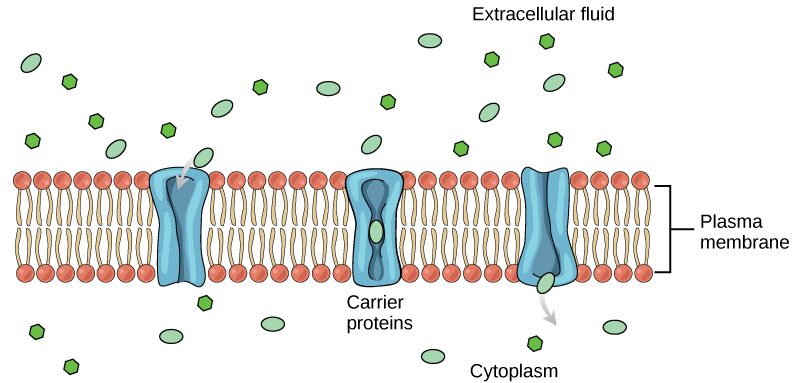
An example of this process occurs in the kidney. Glucose, water, salts, ions, and amino acids needed by the body are filtered in one part of the kidney. This filtrate, which includes glucose, is then reabsorbed in another part of the kidney. Because there are only a finite number of carrier proteins for glucose, if more glucose is present than the proteins can handle, the excess is not transported and it is excreted from the body in the urine. In a diabetic individual, this is described as “spilling glucose into the urine.” A different group of carrier proteins called glucose transport proteins, or GLUTs, are involved in transporting glucose and other hexose sugars through plasma membranes within the body.
Channel and carrier proteins transport material at different rates. Channel proteins transport much more quickly than do carrier proteins. Channel proteins facilitate diffusion at a rate of tens of millions of molecules per second, whereas carrier proteins work at a rate of a thousand to a million molecules per second.
Osmosis is the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane according to the concentration gradient of water across the membrane, which is inversely proportional to the concentration of solutes. While diffusion transports material across membranes and within cells, osmosis transports only water across a membrane and the membrane limits the diffusion of solutes in the water. Not surprisingly, the aquaporins that facilitate water movement play a large role in osmosis, most prominently in red blood cells and the membranes of kidney tubules.
Osmosis is a special case of diffusion. Water, like other substances, moves from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration. An obvious question is what makes water move at all? Imagine a beaker with a semipermeable membrane separating the two sides or halves ( [link] ). On both sides of the membrane the water level is the same, but there are different concentrations of a dissolved substance, or solute , that cannot cross the membrane (otherwise the concentrations on each side would be balanced by the solute crossing the membrane). If the volume of the solution on both sides of the membrane is the same, but the concentrations of solute are different, then there are different amounts of water, the solvent, on either side of the membrane.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?