| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Plasmids with foreign DNA inserted into them are called recombinant DNA molecules because they are created artificially and do not occur in nature. They are also called chimeric molecules because the origin of different parts of the molecules can be traced back to different species of biological organisms or even to chemical synthesis. Proteins that are expressed from recombinant DNA molecules are called recombinant proteins . Not all recombinant plasmids are capable of expressing genes. The recombinant DNA may need to be moved into a different vector (or host) that is better designed for gene expression. Plasmids may also be engineered to express proteins only when stimulated by certain environmental factors, so that scientists can control the expression of the recombinant proteins.
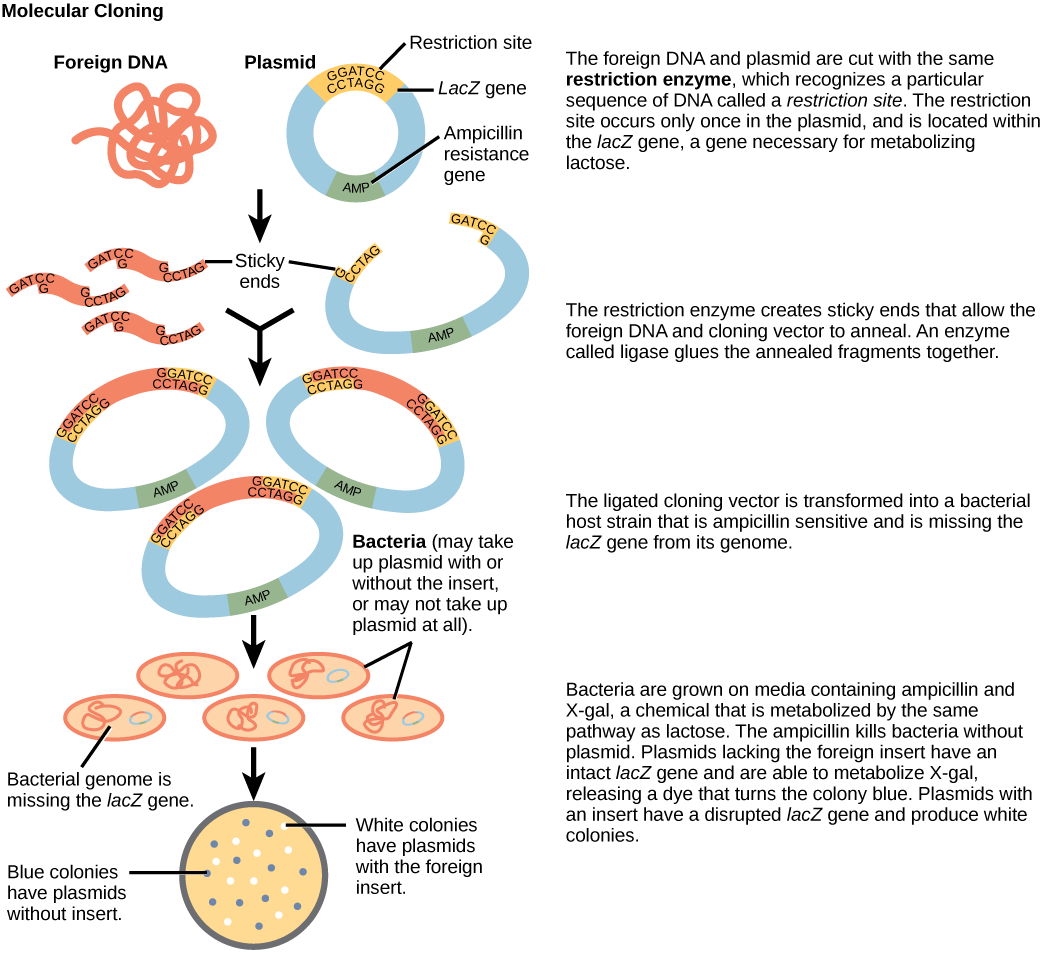
You are working in a molecular biology lab and, unbeknownst to you, your lab partner left the foreign genomic DNA that you are planning to clone on the lab bench overnight instead of storing it in the freezer. As a result, it was degraded by nucleases, but still used in the experiment. The plasmid, on the other hand, is fine. What results would you expect from your molecular cloning experiment?
View an animation of recombination in cloning from the DNA Learning Center.
Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria and yeast, naturally produce clones of themselves when they replicate asexually by binary fission; this is known as cellular cloning . The nuclear DNA duplicates by the process of mitosis, which creates an exact replica of the genetic material.
Reproductive cloning is a method used to make a clone or an identical copy of an entire multicellular organism. Most multicellular organisms undergo reproduction by sexual means, which involves genetic hybridization of two individuals (parents), making it impossible for generation of an identical copy or a clone of either parent. Recent advances in biotechnology have made it possible to artificially induce asexual reproduction of mammals in the laboratory.
Parthenogenesis, or “virgin birth,” occurs when an embryo grows and develops without the fertilization of the egg occurring; this is a form of asexual reproduction. An example of parthenogenesis occurs in species in which the female lays an egg and if the egg is fertilized, it is a diploid egg and the individual develops into a female; if the egg is not fertilized, it remains a haploid egg and develops into a male. The unfertilized egg is called a parthenogenic, or virgin, egg. Some insects and reptiles lay parthenogenic eggs that can develop into adults.
Sexual reproduction requires two cells; when the haploid egg and sperm cells fuse, a diploid zygote results. The zygote nucleus contains the genetic information to produce a new individual. However, early embryonic development requires the cytoplasmic material contained in the egg cell. This idea forms the basis for reproductive cloning. Therefore, if the haploid nucleus of an egg cell is replaced with a diploid nucleus from the cell of any individual of the same species (called a donor), it will become a zygote that is genetically identical to the donor. Somatic cell nuclear transfer is the technique of transferring a diploid nucleus into an enucleated egg. It can be used for either therapeutic cloning or reproductive cloning.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?