| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are two kinds of communication in the world of living cells. Communication between cells is called intercellular signaling , and communication within a cell is called intracellular signaling . An easy way to remember the distinction is by understanding the Latin origin of the prefixes: inter- means "between" (for example, intersecting lines are those that cross each other) and intra- means "inside" (like intravenous).
Chemical signals are released by signaling cells in the form of small, usually volatile or soluble molecules called ligands. A ligand is a molecule that binds another specific molecule, in some cases, delivering a signal in the process. Ligands can thus be thought of as signaling molecules. Ligands interact with proteins in target cells , which are cells that are affected by chemical signals; these proteins are also called receptors . Ligands and receptors exist in several varieties; however, a specific ligand will have a specific receptor that typically binds only that ligand.
There are four categories of chemical signaling found in multicellular organisms: paracrine signaling, endocrine signaling, autocrine signaling, and direct signaling across gap junctions ( [link] ). The main difference between the different categories of signaling is the distance that the signal travels through the organism to reach the target cell. Not all cells are affected by the same signals.
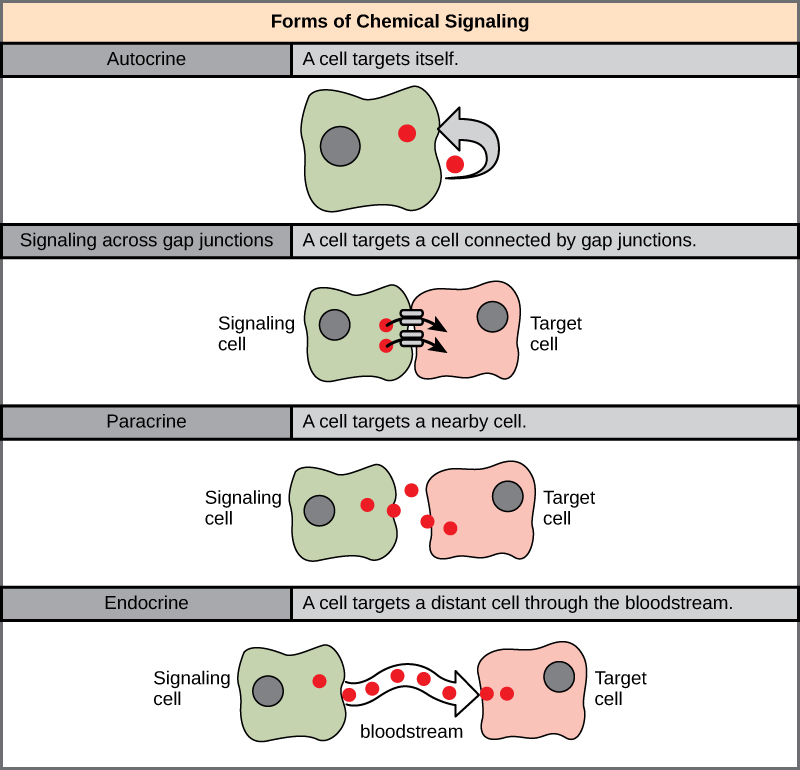
Signals that act locally between cells that are close together are called paracrine signals . Paracrine signals move by diffusion through the extracellular matrix. These types of signals usually elicit quick responses that last only a short amount of time. In order to keep the response localized, paracrine ligand molecules are normally quickly degraded by enzymes or removed by neighboring cells. Removing the signals will reestablish the concentration gradient for the signal, allowing them to quickly diffuse through the intracellular space if released again.
One example of paracrine signaling is the transfer of signals across synapses between nerve cells. A nerve cell consists of a cell body, several short, branched extensions called dendrites that receive stimuli, and a long extension called an axon, which transmits signals to other nerve cells or muscle cells. The junction between nerve cells where signal transmission occurs is called a synapse. A synaptic signal is a chemical signal that travels between nerve cells. Signals within the nerve cells are propagated by fast-moving electrical impulses. When these impulses reach the end of the axon, the signal continues on to a dendrite of the next cell by the release of chemical ligands called neurotransmitters by the presynaptic cell (the cell emitting the signal). The neurotransmitters are transported across the very small distances between nerve cells, which are called chemical synapses ( [link] ). The small distance between nerve cells allows the signal to travel quickly; this enables an immediate response, such as, Take your hand off the stove!

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?