| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Cellular respiration must be regulated in order to provide balanced amounts of energy in the form of ATP. The cell also must generate a number of intermediate compounds that are used in the anabolism and catabolism of macromolecules. Without controls, metabolic reactions would quickly come to a stand still as the forward and backward reactions reached a state of equilibrium. Resources would be used inappropriately. A cell does not need the maximum amount of ATP that it can make all the time: At times, the cell needs to shunt some of the intermediates to pathways for amino acid, protein, glycogen, lipid, and nucleic acid production. In short, the cell needs to control its metabolism.
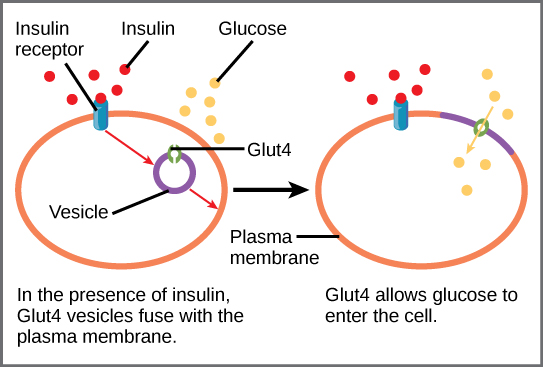
A variety of mechanisms is used to control cellular respiration. Some type of control exists at each stage of glucose metabolism. Access of glucose to the cell can be regulated using the GLUT proteins that transport glucose ( [link] ). Different forms of the GLUT protein control passage of glucose into the cells of specific tissues.
Some reactions are controlled by having two different enzymes—one each for the two directions of a reversible reaction. Reactions that are catalyzed by only one enzyme can go to equilibrium, stalling the reaction. In contrast, if two different enzymes (each specific for a given direction) are necessary for a reversible reaction, the opportunity to control the rate of the reaction increases, and equilibrium is not reached.
A number of enzymes involved in each of the pathways—in particular, the enzyme catalyzing the first committed reaction of the pathway—are controlled by attachment of a molecule to an allosteric site on the protein. The molecules most commonly used in this capacity are the nucleotides ATP, ADP, AMP, NAD + , and NADH. These regulators, allosteric effectors, may increase or decrease enzyme activity, depending on the prevailing conditions. The allosteric effector alters the steric structure of the enzyme, usually affecting the configuration of the active site. This alteration of the protein’s (the enzyme’s) structure either increases or decreases its affinity for its substrate, with the effect of increasing or decreasing the rate of the reaction. The attachment signals to the enzyme. This binding can increase or decrease the enzyme’s activity, providing feedback. This feedback type of control is effective as long as the chemical affecting it is attached to the enzyme. Once the overall concentration of the chemical decreases, it will diffuse away from the protein, and the control is relaxed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?