| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If oxygen is available, aerobic respiration will go forward. In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria, which are the sites of cellular respiration. There, pyruvate will be transformed into an acetyl group that will be picked up and activated by a carrier compound called coenzyme A (CoA). The resulting compound is called acetyl CoA . CoA is made from vitamin B5, pantothenic acid. Acetyl CoA can be used in a variety of ways by the cell, but its major function is to deliver the acetyl group derived from pyruvate to the next stage of the pathway in glucose catabolism.
In order for pyruvate, the product of glycolysis, to enter the next pathway, it must undergo several changes. The conversion is a three-step process ( [link] ).
Step 1. A carboxyl group is removed from pyruvate, releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide into the surrounding medium. The result of this step is a two-carbon hydroxyethyl group bound to the enzyme (pyruvate dehydrogenase). This is the first of the six carbons from the original glucose molecule to be removed. This step proceeds twice (remember: there are two pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolsis) for every molecule of glucose metabolized; thus, two of the six carbons will have been removed at the end of both steps.
Step 2. The hydroxyethyl group is oxidized to an acetyl group, and the electrons are picked up by NAD + , forming NADH. The high-energy electrons from NADH will be used later to generate ATP.
Step 3. The enzyme-bound acetyl group is transferred to CoA, producing a molecule of acetyl CoA.
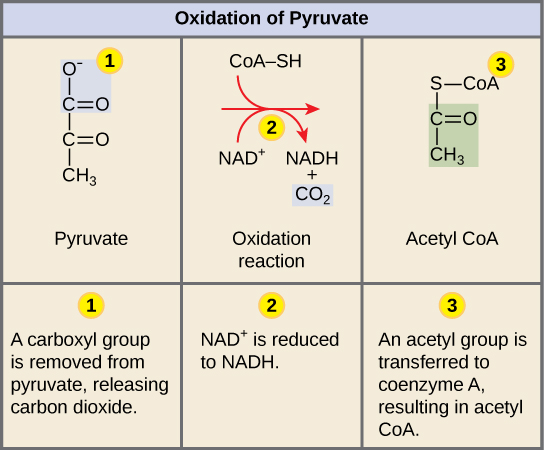
Note that during the second stage of glucose metabolism, whenever a carbon atom is removed, it is bound to two oxygen atoms, producing carbon dioxide, one of the major end products of cellular respiration.
In the presence of oxygen, acetyl CoA delivers its acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, to form citrate, a six-carbon molecule with three carboxyl groups; this pathway will harvest the remainder of the extractable energy from what began as a glucose molecule. This single pathway is called by different names: the citric acid cycle (for the first intermediate formed—citric acid, or citrate—when acetate joins to the oxaloacetate), the TCA cycle (since citric acid or citrate and isocitrate are tricarboxylic acids), and the Krebs cycle , after Hans Krebs, who first identified the steps in the pathway in the 1930s in pigeon flight muscles.
Like the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the citric acid cycle takes place in the matrix of mitochondria. Almost all of the enzymes of the citric acid cycle are soluble, with the single exception of the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase, which is embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. Unlike glycolysis, the citric acid cycle is a closed loop: The last part of the pathway regenerates the compound used in the first step. The eight steps of the cycle are a series of redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions that produce two carbon dioxide molecules, one GTP/ATP, and reduced forms of NADH and FADH 2 ( [link] ). This is considered an aerobic pathway because the NADH and FADH 2 produced must transfer their electrons to the next pathway in the system, which will use oxygen. If this transfer does not occur, the oxidation steps of the citric acid cycle also do not occur. Note that the citric acid cycle produces very little ATP directly and does not directly consume oxygen.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?