| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
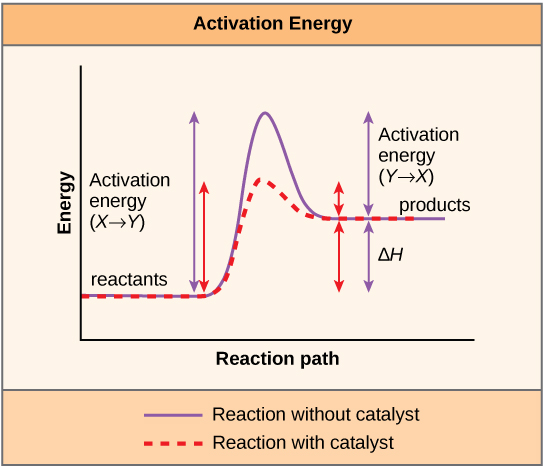
A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions are called enzymes. Almost all enzymes are proteins, made up of chains of amino acids, and they perform the critical task of lowering the activation energies of chemical reactions inside the cell. Enzymes do this by binding to the reactant molecules, and holding them in such a way as to make the chemical bond-breaking and bond-forming processes take place more readily. It is important to remember that enzymes don’t change the ∆G of a reaction. In other words, they don’t change whether a reaction is exergonic (spontaneous) or endergonic. This is because they don’t change the free energy of the reactants or products. They only reduce the activation energy required to reach the transition state ( [link] ).
The chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds are the enzyme’s substrates . There may be one or more substrates, depending on the particular chemical reaction. In some reactions, a single-reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. In others, two substrates may come together to create one larger molecule. Two reactants might also enter a reaction, both become modified, and leave the reaction as two products. The location within the enzyme where the substrate binds is called the enzyme’s active site . The active site is where the “action” happens, so to speak. Since enzymes are proteins, there is a unique combination of amino acid residues (also called side chains, or R groups) within the active site. Each residue is characterized by different properties. Residues can be large or small, weakly acidic or basic, hydrophilic or hydrophobic, positively or negatively charged, or neutral. The unique combination of amino acid residues, their positions, sequences, structures, and properties, creates a very specific chemical environment within the active site. This specific environment is suited to bind, albeit briefly, to a specific chemical substrate (or substrates). Due to this jigsaw puzzle-like match between an enzyme and its substrates (which adapts to find the best fit between the transition state and the active site), enzymes are known for their specificity. The “best fit” results from the shape and the amino acid functional group’s attraction to the substrate. There is a specifically matched enzyme for each substrate and, thus, for each chemical reaction; however, there is flexibility as well.
The fact that active sites are so perfectly suited to provide specific environmental conditions also means that they are subject to influences by the local environment. It is true that increasing the environmental temperature generally increases reaction rates, enzyme-catalyzed or otherwise. However, increasing or decreasing the temperature outside of an optimal range can affect chemical bonds within the active site in such a way that they are less well suited to bind substrates. High temperatures will eventually cause enzymes, like other biological molecules, to denature , a process that changes the natural properties of a substance. Likewise, the pH of the local environment can also affect enzyme function. Active site amino acid residues have their own acidic or basic properties that are optimal for catalysis. These residues are sensitive to changes in pH that can impair the way substrate molecules bind. Enzymes are suited to function best within a certain pH range, and, as with temperature, extreme pH values (acidic or basic) of the environment can cause enzymes to denature.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?