| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Preserving biodiversity is an extraordinary challenge that must be met by greater understanding of biodiversity itself, changes in human behavior and beliefs, and various preservation strategies.
The technology of molecular genetics and data processing and storage are maturing to the point where cataloguing the planet’s species in an accessible way is close to feasible. DNA barcoding is one molecular genetic method, which takes advantage of rapid evolution in a mitochondrial gene present in eukaryotes, excepting the plants, to identify species using the sequence of portions of the gene. Plants may be barcoded using a combination of chloroplast genes. Rapid mass sequencing machines make the molecular genetics portion of the work relatively inexpensive and quick. Computer resources store and make available the large volumes of data. Projects are currently underway to use DNA barcoding to catalog museum specimens, which have already been named and studied, as well as testing the method on less studied groups. As of mid 2012, close to 150,000 named species had been barcoded. Early studies suggest there are significant numbers of undescribed species that looked too much like sibling species to previously be recognized as different. These now can be identified with DNA barcoding.
Numerous computer databases now provide information about named species and a framework for adding new species. However, as already noted, at the present rate of description of new species, it will take close to 500 years before the complete catalog of life is known. Many, perhaps most, species on the planet do not have that much time.
There is also the problem of understanding which species known to science are threatened and to what degree they are threatened. This task is carried out by the non-profit IUCN which, as previously mentioned, maintains the Red List—an online listing of endangered species categorized by taxonomy, type of threat, and other criteria ( [link] ). The Red List is supported by scientific research. In 2011, the list contained 61,000 species, all with supporting documentation.
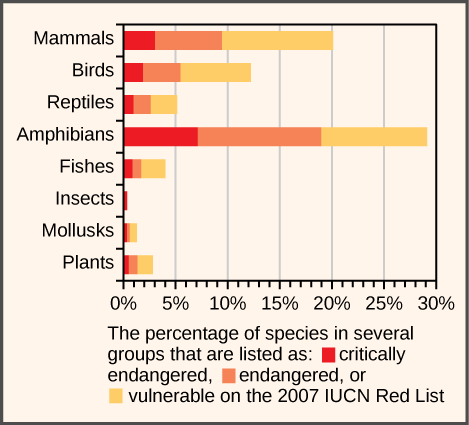
Which of the following statements is not supported by this graph?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?