| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Populations rarely, if ever, live in isolation from populations of other species. In most cases, numerous species share a habitat. The interactions between these populations play a major role in regulating population growth and abundance. All populations occupying the same habitat form a community: populations inhabiting a specific area at the same time. The number of species occupying the same habitat and their relative abundance is known as species diversity. Areas with low diversity, such as the glaciers of Antarctica, still contain a wide variety of living things, whereas the diversity of tropical rainforests is so great that it cannot be counted. Ecology is studied at the community level to understand how species interact with each other and compete for the same resources.
Perhaps the classical example of species interaction is predation: the hunting of prey by its predator. Nature shows on television highlight the drama of one living organism killing another. Populations of predators and prey in a community are not constant over time: in most cases, they vary in cycles that appear to be related. The most often cited example of predator-prey dynamics is seen in the cycling of the lynx (predator) and the snowshoe hare (prey), using nearly 200 year-old trapping data from North American forests ( [link] ). This cycle of predator and prey lasts approximately 10 years, with the predator population lagging 1–2 years behind that of the prey population. As the hare numbers increase, there is more food available for the lynx, allowing the lynx population to increase as well. When the lynx population grows to a threshold level, however, they kill so many hares that hare population begins to decline, followed by a decline in the lynx population because of scarcity of food. When the lynx population is low, the hare population size begins to increase due, at least in part, to low predation pressure, starting the cycle anew.
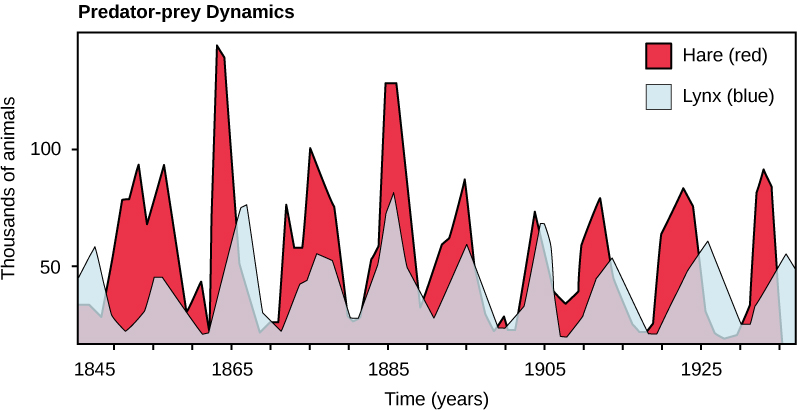
The idea that the population cycling of the two species is entirely controlled by predation models has come under question. More recent studies have pointed to undefined density-dependent factors as being important in the cycling, in addition to predation. One possibility is that the cycling is inherent in the hare population due to density-dependent effects such as lower fecundity (maternal stress) caused by crowding when the hare population gets too dense. The hare cycling would then induce the cycling of the lynx because it is the lynxes’ major food source. The more we study communities, the more complexities we find, allowing ecologists to derive more accurate and sophisticated models of population dynamics.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?