| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The Earth’s biomes are categorized into two major groups: terrestrial and aquatic. Terrestrial biomes are based on land, while aquatic biomes include both ocean and freshwater biomes. The eight major terrestrial biomes on Earth are each distinguished by characteristic temperatures and amount of precipitation. Comparing the annual totals of precipitation and fluctuations in precipitation from one biome to another provides clues as to the importance of abiotic factors in the distribution of biomes. Temperature variation on a daily and seasonal basis is also important for predicting the geographic distribution of the biome and the vegetation type in the biome. The distribution of these biomes shows that the same biome can occur in geographically distinct areas with similar climates ( [link] ).
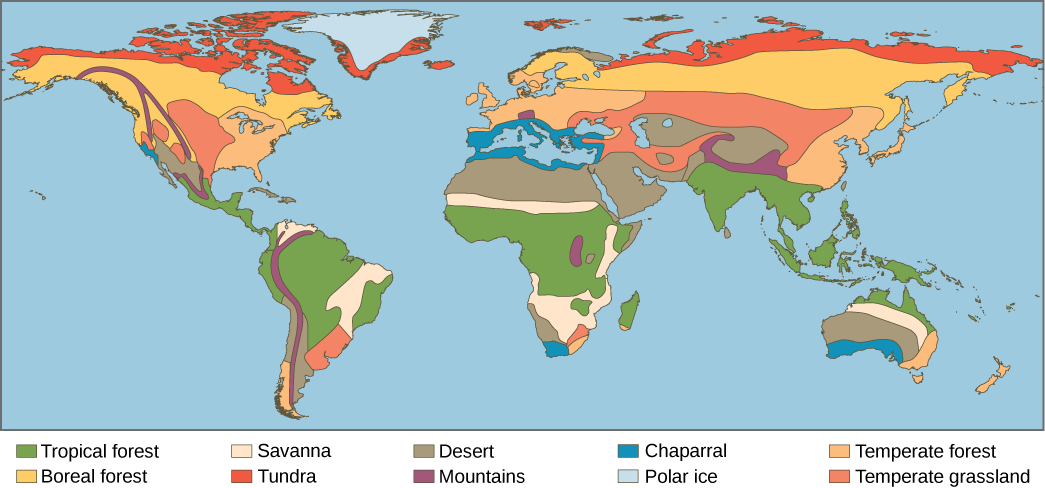
Which of the following statements about biomes is false?
Tropical wet forests are also referred to as tropical rainforests. This biome is found in equatorial regions ( [link] ). The vegetation is characterized by plants with broad leaves that fall off throughout the year. Unlike the trees of deciduous forests, the trees in this biome do not have a seasonal loss of leaves associated with variations in temperature and sunlight; these forests are “evergreen” year-round.
The temperature and sunlight profiles of tropical wet forests are very stable in comparison to that of other terrestrial biomes, with the temperatures ranging from 20 °C to 34 °C (68 °F to 93 °F). When one compares the annual temperature variation of tropical wet forests with that of other forest biomes, the lack of seasonal temperature variation in the tropical wet forest becomes apparent. This lack of seasonality leads to year-round plant growth, rather than the seasonal (spring, summer, and fall) growth seen in other biomes. In contrast to other ecosystems, tropical ecosystems do not have long days and short days during the yearly cycle. Instead, a constant daily amount of sunlight (11–12 hrs per day) provides more solar radiation, thereby, a longer period of time for plant growth.
The annual rainfall in tropical wet forests ranges from 125 to 660 cm (50–200 in) with some monthly variation. While sunlight and temperature remain fairly consistent, annual rainfall is highly variable. Tropical wet forests have wet months in which there can be more than 30 cm (11–12 in) of precipitation, as well as dry months in which there are fewer than 10 cm (3.5 in) of rainfall. However, the driest month of a tropical wet forest still exceeds the annual rainfall of some other biomes, such as deserts.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?