| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
While the kidneys operate to maintain osmotic balance and blood pressure in the body, they also act in concert with hormones. Hormones are small molecules that act as messengers within the body. Hormones are typically secreted from one cell and travel in the bloodstream to affect a target cell in another portion of the body. Different regions of the nephron bear specialized cells that have receptors to respond to chemical messengers and hormones. [link] summarizes the hormones that control the osmoregulatory functions.
| Hormones That Affect Osmoregulation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Hormone | Where produced | Function |
| Epinephrine and Norepinephrine | Adrenal medulla | Can decrease kidney function temporarily by vasoconstriction |
| Renin | Kidney nephrons | Increases blood pressure by acting on angiotensinogen |
| Angiotensin | Liver | Angiotensin II affects multiple processes and increases blood pressure |
| Aldosterone | Adrenal cortex | Prevents loss of sodium and water |
| Anti-diuretic hormone (vasopressin) | Hypothalamus (stored in the posterior pituitary) | Prevents water loss |
| Atrial natriuretic peptide | Heart atrium | Decreases blood pressure by acting as a vasodilator and increasing glomerular filtration rate; decreases sodium reabsorption in kidneys |
Epinephrine and norepinephrine are released by the adrenal medulla and nervous system respectively. They are the flight/fight hormones that are released when the body is under extreme stress. During stress, much of the body’s energy is used to combat imminent danger. Kidney function is halted temporarily by epinephrine and norepinephrine. These hormones function by acting directly on the smooth muscles of blood vessels to constrict them. Once the afferent arterioles are constricted, blood flow into the nephrons stops. These hormones go one step further and trigger the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, illustrated in [link] proceeds through several steps to produce angiotensin II , which acts to stabilize blood pressure and volume. Renin (secreted by a part of the juxtaglomerular complex) is produced by the granular cells of the afferent and efferent arterioles. Thus, the kidneys control blood pressure and volume directly. Renin acts on angiotensinogen, which is made in the liver and converts it to angiotensin I . Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels. It also triggers the release of the mineralocorticoid aldosterone from the adrenal cortex, which in turn stimulates the renal tubules to reabsorb more sodium. Angiotensin II also triggers the release of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) from the hypothalamus, leading to water retention in the kidneys. It acts directly on the nephrons and decreases glomerular filtration rate. Medically, blood pressure can be controlled by drugs that inhibit ACE (called ACE inhibitors).
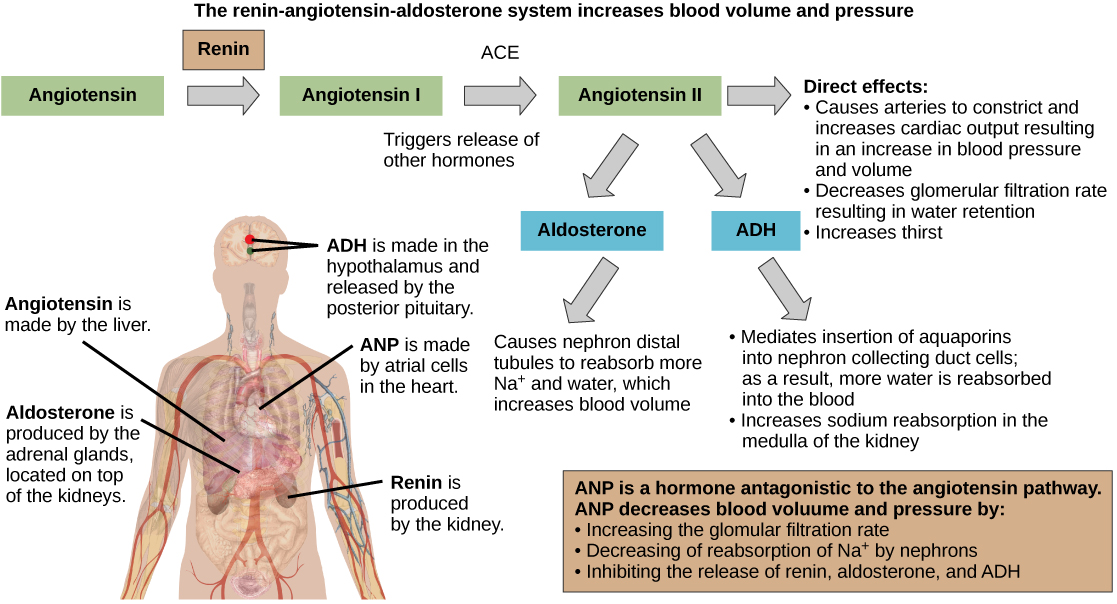
Mineralocorticoids are hormones synthesized by the adrenal cortex that affect osmotic balance. Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid that regulates sodium levels in the blood. Almost all of the sodium in the blood is reclaimed by the renal tubules under the influence of aldosterone. Because sodium is always reabsorbed by active transport and water follows sodium to maintain osmotic balance, aldosterone manages not only sodium levels but also the water levels in body fluids. In contrast, the aldosterone also stimulates potassium secretion concurrently with sodium reabsorption. In contrast, absence of aldosterone means that no sodium gets reabsorbed in the renal tubules and all of it gets excreted in the urine. In addition, the daily dietary potassium load is not secreted and the retention of K + can cause a dangerous increase in plasma K + concentration. Patients who have Addison's disease have a failing adrenal cortex and cannot produce aldosterone. They lose sodium in their urine constantly, and if the supply is not replenished, the consequences can be fatal.
As previously discussed, antidiuretic hormone or ADH (also called vasopressin ), as the name suggests, helps the body conserve water when body fluid volume, especially that of blood, is low. It is formed by the hypothalamus and is stored and released from the posterior pituitary. It acts by inserting aquaporins in the collecting ducts and promotes reabsorption of water. ADH also acts as a vasoconstrictor and increases blood pressure during hemorrhaging.
The atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) lowers blood pressure by acting as a vasodilator . It is released by cells in the atrium of the heart in response to high blood pressure and in patients with sleep apnea. ANP affects salt release, and because water passively follows salt to maintain osmotic balance, it also has a diuretic effect. ANP also prevents sodium reabsorption by the renal tubules, decreasing water reabsorption (thus acting as a diuretic) and lowering blood pressure. Its actions suppress the actions of aldosterone, ADH, and renin.
Hormonal cues help the kidneys synchronize the osmotic needs of the body. Hormones like epinephrine, norepinephrine, renin-angiotensin, aldosterone, anti-diuretic hormone, and atrial natriuretic peptide help regulate the needs of the body as well as the communication between the different organ systems.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?