| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The structure of the lung maximizes its surface area to increase gas diffusion. Because of the enormous number of alveoli (approximately 300 million in each human lung), the surface area of the lung is very large (75 m 2 ). Having such a large surface area increases the amount of gas that can diffuse into and out of the lungs.
Gas exchange during respiration occurs primarily through diffusion. Diffusion is a process in which transport is driven by a concentration gradient. Gas molecules move from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. Blood that is low in oxygen concentration and high in carbon dioxide concentration undergoes gas exchange with air in the lungs. The air in the lungs has a higher concentration of oxygen than that of oxygen-depleted blood and a lower concentration of carbon dioxide. This concentration gradient allows for gas exchange during respiration.
Partial pressure is a measure of the concentration of the individual components in a mixture of gases. The total pressure exerted by the mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the components in the mixture. The rate of diffusion of a gas is proportional to its partial pressure within the total gas mixture. This concept is discussed further in detail below.
Different animals have different lung capacities based on their activities. Cheetahs have evolved a much higher lung capacity than humans; it helps provide oxygen to all the muscles in the body and allows them to run very fast. Elephants also have a high lung capacity. In this case, it is not because they run fast but because they have a large body and must be able to take up oxygen in accordance with their body size.
Human lung size is determined by genetics, gender, and height. At maximal capacity, an average lung can hold almost six liters of air, but lungs do not usually operate at maximal capacity. Air in the lungs is measured in terms of lung volumes and lung capacities ( [link] and [link] ). Volume measures the amount of air for one function (such as inhalation or exhalation). Capacity is any two or more volumes (for example, how much can be inhaled from the end of a maximal exhalation).
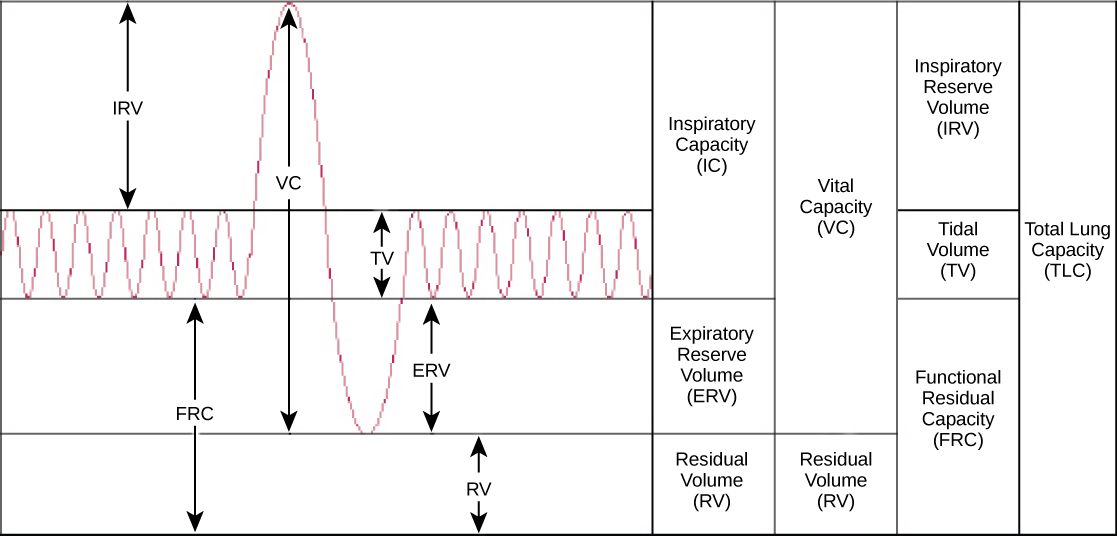
| Lung Volumes and Capacities (Avg Adult Male) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume/Capacity | Definition | Volume (liters) | Equations |
| Tidal volume (TV) | Amount of air inhaled during a normal breath | 0.5 | - |
| Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) | Amount of air that can be exhaled after a normal exhalation | 1.2 | - |
| Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) | Amount of air that can be further inhaled after a normal inhalation | 3.1 | - |
| Residual volume (RV) | Air left in the lungs after a forced exhalation | 1.2 | - |
| Vital capacity (VC) | Maximum amount of air that can be moved in or out of the lungs in a single respiratory cycle | 4.8 | ERV+TV+IRV |
| Inspiratory capacity (IC) | Volume of air that can be inhaled in addition to a normal exhalation | 3.6 | TV+IRV |
| Functional residual capacity (FRC) | Volume of air remaining after a normal exhalation | 2.4 | ERV+RV |
| Total lung capacity (TLC) | Total volume of air in the lungs after a maximal inspiration | 6.0 | RV+ERV+TV+IRV |
| Forced expiratory volume (FEV1) | How much air can be forced out of the lungs over a specific time period, usually one second | ~4.1 to 5.5 | - |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?