| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All functions performed by the nervous system—from a simple motor reflex to more advanced functions like making a memory or a decision—require neurons to communicate with one another. While humans use words and body language to communicate, neurons use electrical and chemical signals. Just like a person in a committee, one neuron usually receives and synthesizes messages from multiple other neurons before “making the decision” to send the message on to other neurons.
For the nervous system to function, neurons must be able to send and receive signals. These signals are possible because each neuron has a charged cellular membrane (a voltage difference between the inside and the outside), and the charge of this membrane can change in response to neurotransmitter molecules released from other neurons and environmental stimuli. To understand how neurons communicate, one must first understand the basis of the baseline or ‘resting’ membrane charge.
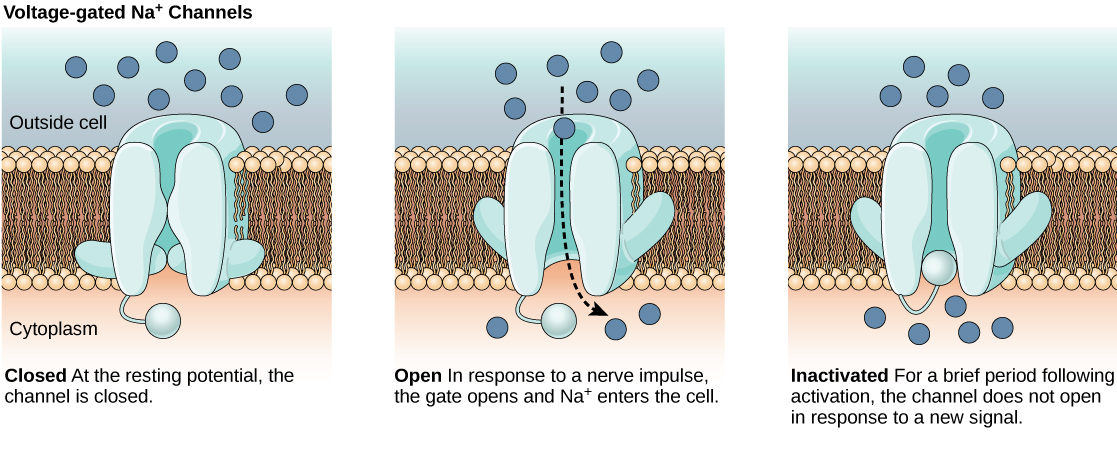
The lipid bilayer membrane that surrounds a neuron is impermeable to charged molecules or ions. To enter or exit the neuron, ions must pass through special proteins called ion channels that span the membrane. Ion channels have different configurations: open, closed, and inactive, as illustrated in [link] . Some ion channels need to be activated in order to open and allow ions to pass into or out of the cell. These ion channels are sensitive to the environment and can change their shape accordingly. Ion channels that change their structure in response to voltage changes are called voltage-gated ion channels. Voltage-gated ion channels regulate the relative concentrations of different ions inside and outside the cell. The difference in total charge between the inside and outside of the cell is called the membrane potential .
This video discusses the basis of the resting membrane potential.
A neuron at rest is negatively charged: the inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts more negative than the outside (−70 mV, note that this number varies by neuron type and by species). This voltage is called the resting membrane potential; it is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and outside the cell. If the membrane were equally permeable to all ions, each type of ion would flow across the membrane and the system would reach equilibrium. Because ions cannot simply cross the membrane at will, there are different concentrations of several ions inside and outside the cell, as shown in [link] . The difference in the number of positively charged potassium ions (K + ) inside and outside the cell dominates the resting membrane potential ( [link] ). When the membrane is at rest, K + ions accumulate inside the cell due to a net movement with the concentration gradient. The negative resting membrane potential is created and maintained by increasing the concentration of cations outside the cell (in the extracellular fluid) relative to inside the cell (in the cytoplasm). The negative charge within the cell is created by the cell membrane being more permeable to potassium ion movement than sodium ion movement. In neurons, potassium ions are maintained at high concentrations within the cell while sodium ions are maintained at high concentrations outside of the cell. The cell possesses potassium and sodium leakage channels that allow the two cations to diffuse down their concentration gradient. However, the neurons have far more potassium leakage channels than sodium leakage channels. Therefore, potassium diffuses out of the cell at a much faster rate than sodium leaks in. Because more cations are leaving the cell than are entering, this causes the interior of the cell to be negatively charged relative to the outside of the cell. The actions of the sodium potassium pump help to maintain the resting potential, once established. Recall that sodium potassium pumps brings two K + ions into the cell while removing three Na + ions per ATP consumed. As more cations are expelled from the cell than taken in, the inside of the cell remains negatively charged relative to the extracellular fluid. It should be noted that calcium ions (Cl – ) tend to accumulate outside of the cell because they are repelled by negatively-charged proteins within the cytoplasm.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?