| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
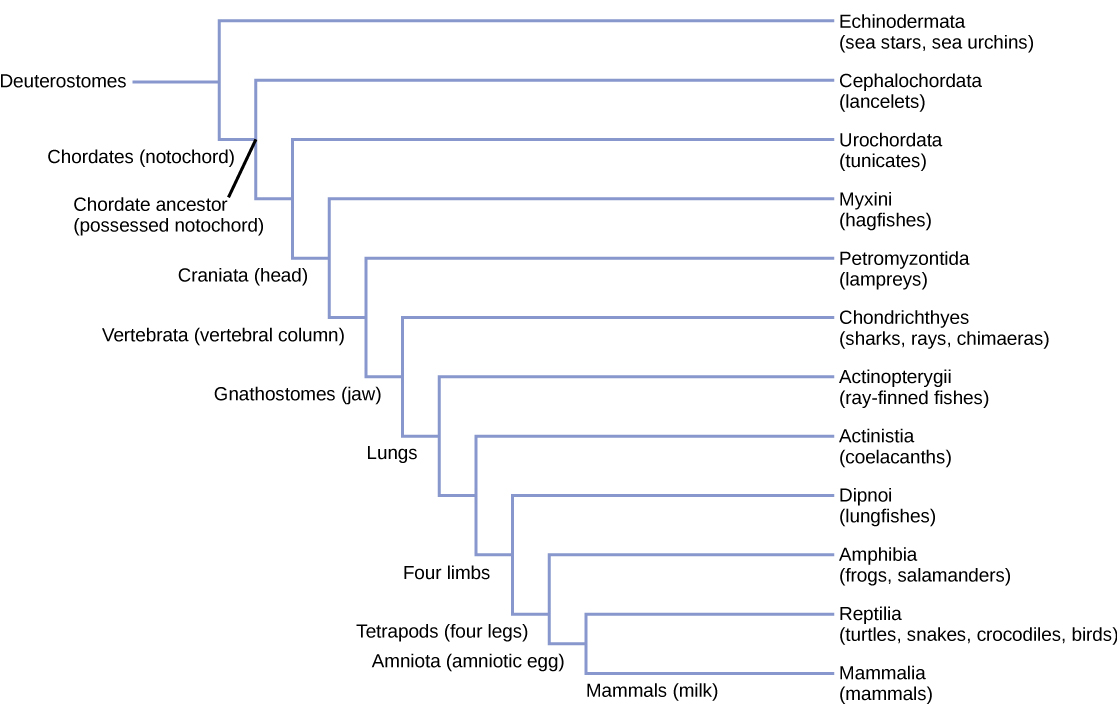
Vertebrates are members of the kingdom Animalia and the phylum Chordata ( [link] ). Recall that animals that possess bilateral symmetry can be divided into two groups—protostomes and deuterostomes—based on their patterns of embryonic development. The deuterostomes, whose name translates as “second mouth,” consist of two phyla: Chordata and Echinodermata. Echinoderms are invertebrate marine animals that have pentaradial symmetry and a spiny body covering, a group that includes sea stars, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers. The most conspicuous and familiar members of Chordata are vertebrates, but this phylum also includes two groups of invertebrate chordates.
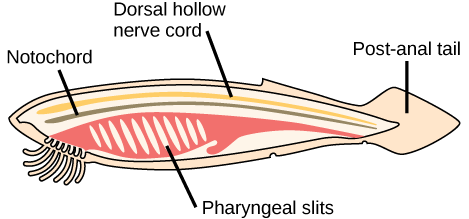
Animals in the phylum Chordata share four key features that appear at some stage during their development: a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail ( [link] ). In some groups, some of these are present only during embryonic development.
The chordates are named for the notochord , which is a flexible, rod-shaped structure that is found in the embryonic stage of all chordates and in the adult stage of some chordate species. It is located between the digestive tube and the nerve cord, and provides skeletal support through the length of the body. In some chordates, the notochord acts as the primary axial support of the body throughout the animal’s lifetime. In vertebrates, the notochord is present during embryonic development, at which time it induces the development of the neural tube and serves as a support for the developing embryonic body. The notochord, however, is not found in the postnatal stage of vertebrates; at this point, it has been replaced by the vertebral column (that is, the spine).
Which of the following statements about common features of chordates is true?
The dorsal hollow nerve cord derives from ectoderm that rolls into a hollow tube during development. In chordates, it is located dorsal to the notochord. In contrast, other animal phyla are characterized by solid nerve cords that are located either ventrally or laterally. The nerve cord found in most chordate embryos develops into the brain and spinal cord, which compose the central nervous system.
Pharyngeal slits are openings in the pharynx (the region just posterior to the mouth) that extend to the outside environment. In organisms that live in aquatic environments, pharyngeal slits allow for the exit of water that enters the mouth during feeding. Some invertebrate chordates use the pharyngeal slits to filter food out of the water that enters the mouth. In vertebrate fishes, the pharyngeal slits are modified into gill supports, and in jawed fishes, into jaw supports. In tetrapods, the slits are modified into components of the ear and tonsils. Tetrapod literally means “four-footed,” which refers to the phylogenetic history of various groups that evolved accordingly, even though some now possess fewer than two pairs of walking appendages. Tetrapods include amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?