| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Phylum Cnidaria includes animals that show radial or biradial symmetry and are diploblastic, that is, they develop from two embryonic layers. Nearly all (about 99 percent) cnidarians are marine species.
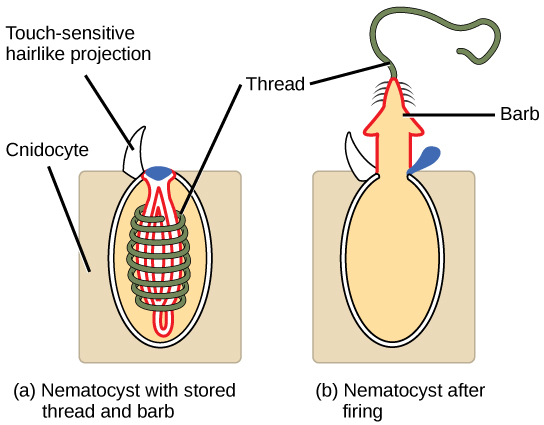
Cnidarians contain specialized cells known as cnidocytes (“stinging cells”) containing organelles called nematocysts (stingers). These cells are present around the mouth and tentacles, and serve to immobilize prey with toxins contained within the cells. Nematocysts contain coiled threads that may bear barbs. The outer wall of the cell has hairlike projections called cnidocils, which are sensitive to touch. When touched, the cells are known to fire coiled threads that can either penetrate the flesh of the prey or predators of cnidarians (see [link] ) or ensnare it. These coiled threads release toxins into the target and can often immobilize prey or scare away predators.
View this video animation showing two anemones engaged in a battle.
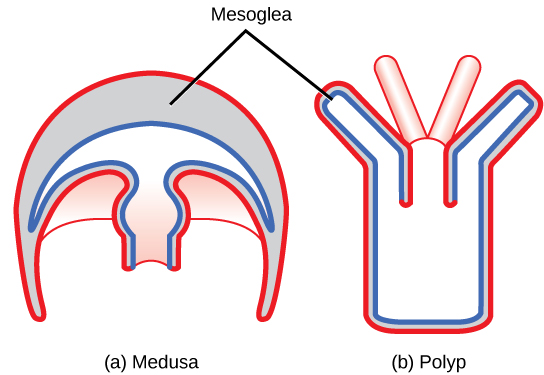
Animals in this phylum display two distinct morphological body plans: polyp or “stalk” and medusa or “bell” ( [link] ). An example of the polyp form is Hydra spp.; perhaps the most well-known medusoid animals are the jellies (jellyfish). Polyp forms are sessile as adults, with a single opening to the digestive system (the mouth) facing up with tentacles surrounding it. Medusa forms are motile, with the mouth and tentacles hanging down from an umbrella-shaped bell.
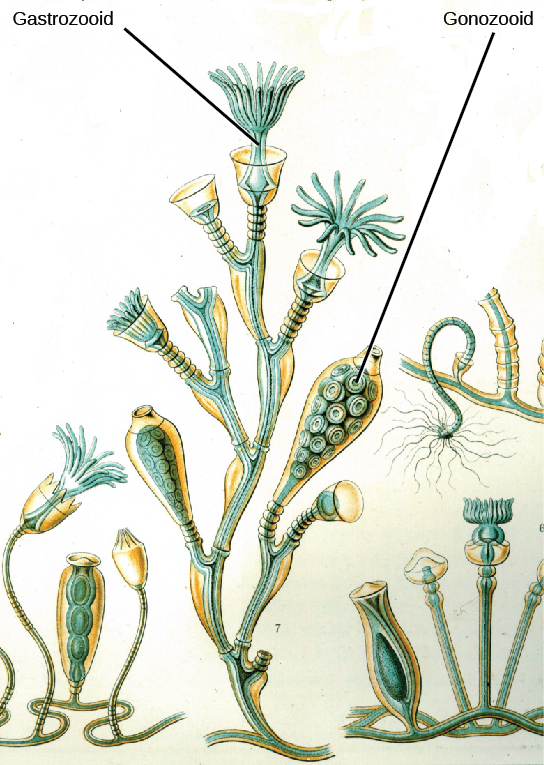
Some cnidarians are polymorphic, that is, they have two body plans during their life cycle. An example is the colonial hydroid called an Obelia. The sessile polyp form has, in fact, two types of polyps, shown in [link] . The first is the gastrozooid, which is adapted for capturing prey and feeding; the other type of polyp is the gonozooid, adapted for the asexual budding of medusa. When the reproductive buds mature, they break off and become free-swimming medusa, which are either male or female (dioecious). The male medusa makes sperm, whereas the female medusa makes eggs. After fertilization, the zygote develops into a blastula, which develops into a planula larva. The larva is free swimming for a while, but eventually attaches and a new colonial reproductive polyp is formed.


Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?